merge upstream
commit
c11ec3ce5b
PPOCRLabel/libs
applications
光功率计数码管字符识别
configs
det
ch_ppocr_v2.0
deploy
doc
ppocr/data/imaug
|
|
@ -48,6 +48,7 @@ class Shape(object):
|
|||
|
||||
def __init__(self, label=None, line_color=None, difficult=False, key_cls="None", paintLabel=False):
|
||||
self.label = label
|
||||
self.idx = 0
|
||||
self.points = []
|
||||
self.fill = False
|
||||
self.selected = False
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -72,6 +72,7 @@ PaddleOCR support a variety of cutting-edge algorithms related to OCR, and devel
|
|||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/dygraph/doc/joinus.PNG" width = "200" height = "200" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<a name="Supported-Chinese-model-list"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## PP-OCR Series Model List(Update on September 8th)
|
||||
|
||||
| Model introduction | Model name | Recommended scene | Detection model | Direction classifier | Recognition model |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -71,6 +71,8 @@ PaddleOCR旨在打造一套丰富、领先、且实用的OCR工具库,助力
|
|||
## 《动手学OCR》电子书
|
||||
- [《动手学OCR》电子书📚](./doc/doc_ch/ocr_book.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 场景应用
|
||||
- PaddleOCR场景应用覆盖通用,制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用,在PP-OCR、PP-Structure的通用能力基础之上,以notebook的形式展示利用场景数据微调、模型优化方法、数据增广等内容,为开发者快速落地OCR应用提供示范与启发。详情可查看[README](./applications)。
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="开源社区"></a>
|
||||
## 开源社区
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,652 @@
|
|||
# 基于PP-OCRv3的PCB字符识别
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目介绍](#1-项目介绍)
|
||||
- [2. 安装说明](#2-安装说明)
|
||||
- [3. 数据准备](#3-数据准备)
|
||||
- [4. 文本检测](#4-文本检测)
|
||||
- [4.1 预训练模型直接评估](#41-预训练模型直接评估)
|
||||
- [4.2 预训练模型+验证集padding直接评估](#42-预训练模型验证集padding直接评估)
|
||||
- [4.3 预训练模型+fine-tune](#43-预训练模型fine-tune)
|
||||
- [5. 文本识别](#5-文本识别)
|
||||
- [5.1 预训练模型直接评估](#51-预训练模型直接评估)
|
||||
- [5.2 三种fine-tune方案](#52-三种fine-tune方案)
|
||||
- [6. 模型导出](#6-模型导出)
|
||||
- [7. 端对端评测](#7-端对端评测)
|
||||
- [8. Jetson部署](#8-Jetson部署)
|
||||
- [9. 总结](#9-总结)
|
||||
- [更多资源](#更多资源)
|
||||
|
||||
# 1. 项目介绍
|
||||
|
||||
印刷电路板(PCB)是电子产品中的核心器件,对于板件质量的测试与监控是生产中必不可少的环节。在一些场景中,通过PCB中信号灯颜色和文字组合可以定位PCB局部模块质量问题,PCB文字识别中存在如下难点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 裁剪出的PCB图片宽高比例较小
|
||||
- 文字区域整体面积也较小
|
||||
- 包含垂直、水平多种方向文本
|
||||
|
||||
针对本场景,PaddleOCR基于全新的PP-OCRv3通过合成数据、微调以及其他场景适配方法完成小字符文本识别任务,满足企业上线要求。PCB检测、识别效果如 **图1** 所示:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/95d8e95bf1ab476987f2519c0f8f0c60a0cdc2c444804ed6ab08f2f7ab054880', width='500'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图1 PCB检测识别效果</div>
|
||||
|
||||
注:欢迎在AIStudio领取免费算力体验线上实训,项目链接: [基于PP-OCRv3实现PCB字符识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4008973)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. 安装说明
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下载PaddleOCR源码,安装依赖环境。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如仍需安装or安装更新,可以执行以下步骤
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
# git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 安装依赖包
|
||||
pip install -r /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
我们通过图片合成工具生成 **图2** 所示的PCB图片,整图只有高25、宽150左右、文字区域高9、宽45左右,包含垂直和水平2种方向的文本:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/bb7a345687814a3d83a29790f2a2b7d081495b3a920b43988c93da6039cad653" width="1000" ></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图2 数据集示例</div>
|
||||
|
||||
暂时不开源生成的PCB数据集,但是通过更换背景,通过如下代码生成数据即可:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd gen_data
|
||||
python3 gen.py --num_img=10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成图片参数解释:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
num_img:生成图片数量
|
||||
font_min_size、font_max_size:字体最大、最小尺寸
|
||||
bg_path:文字区域背景存放路径
|
||||
det_bg_path:整图背景存放路径
|
||||
fonts_path:字体路径
|
||||
corpus_path:语料路径
|
||||
output_dir:生成图片存储路径
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里生成 **100张** 相同尺寸和文本的图片,如 **图3** 所示,方便大家跑通实验。通过如下代码解压数据集:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/3277b750159f4b68b2b58506bfec9005d49aeb5fb1d9411e83f96f9ff7eb66a5" width="1000" ></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图3 案例提供数据集示例</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tar xf ./data/data148165/dataset.tar -C ./
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在生成数据集的时需要生成检测和识别训练需求的格式:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- **文本检测**
|
||||
|
||||
标注文件格式如下,中间用'\t'分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
" 图像文件名 json.dumps编码的图像标注信息"
|
||||
ch4_test_images/img_61.jpg [{"transcription": "MASA", "points": [[310, 104], [416, 141], [418, 216], [312, 179]]}, {...}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
json.dumps编码前的图像标注信息是包含多个字典的list,字典中的 `points` 表示文本框的四个点的坐标(x, y),从左上角的点开始顺时针排列。 `transcription` 表示当前文本框的文字,***当其内容为“###”时,表示该文本框无效,在训练时会跳过。***
|
||||
|
||||
- **文本识别**
|
||||
|
||||
标注文件的格式如下, txt文件中默认请将图片路径和图片标签用'\t'分割,如用其他方式分割将造成训练报错。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
" 图像文件名 图像标注信息 "
|
||||
|
||||
train_data/rec/train/word_001.jpg 简单可依赖
|
||||
train_data/rec/train/word_002.jpg 用科技让复杂的世界更简单
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 4. 文本检测
|
||||
|
||||
选用飞桨OCR开发套件[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)中的PP-OCRv3模型进行文本检测和识别。针对检测模型和识别模型,进行了共计9个方面的升级:
|
||||
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3检测模型对PP-OCRv2中的CML协同互学习文本检测蒸馏策略进行了升级,分别针对教师模型和学生模型进行进一步效果优化。其中,在对教师模型优化时,提出了大感受野的PAN结构LK-PAN和引入了DML蒸馏策略;在对学生模型优化时,提出了残差注意力机制的FPN结构RSE-FPN。
|
||||
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3的识别模块是基于文本识别算法SVTR优化。SVTR不再采用RNN结构,通过引入Transformers结构更加有效地挖掘文本行图像的上下文信息,从而提升文本识别能力。PP-OCRv3通过轻量级文本识别网络SVTR_LCNet、Attention损失指导CTC损失训练策略、挖掘文字上下文信息的数据增广策略TextConAug、TextRotNet自监督预训练模型、UDML联合互学习策略、UIM无标注数据挖掘方案,6个方面进行模型加速和效果提升。
|
||||
|
||||
更多细节请参考PP-OCRv3[技术报告](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用 **3种方案** 进行检测模型的训练、评估:
|
||||
- **PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + **验证集padding**直接评估
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + **fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
## **4.1 预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
|
||||
我们首先通过PaddleOCR提供的预训练模型在验证集上进行评估,如果评估指标能满足效果,可以直接使用预训练模型,不再需要训练。
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型直接评估步骤如下:
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR已经提供了PP-OCR系列模型,部分模型展示如下表所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 模型简介 | 模型名称 | 推荐场景 | 检测模型 | 方向分类器 | 识别模型 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(16.2M) | ch_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(13.4M) | en_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv2模型(13.0M) | ch_PP-OCRv2_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCR mobile模型(9.4M) | ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_pre.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文通用PP-OCR server模型(143.4M) | ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_xx | 服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_det_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_det_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_rec_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_rec_pre.tar) |
|
||||
|
||||
更多模型下载(包括多语言),可以参[考PP-OCR系列模型下载](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/models_list.md)
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们使用PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测模型,下载并解压预训练模型:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如果更换其他模型,更新下载链接和解压指令就可以
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
mkdir pretrain_models
|
||||
cd pretrain_models
|
||||
# 下载英文预训练模型
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
tar xf en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar && rm -rf en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
%cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_val.txt'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest: 尺寸
|
||||
limit_side_len: 48
|
||||
limit_type: 'min'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后在验证集上进行评估,具体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## **4.2 预训练模型+验证集padding直接评估**
|
||||
|
||||
考虑到PCB图片比较小,宽度只有25左右、高度只有140-170左右,我们在原图的基础上进行padding,再进行检测评估,padding前后效果对比如 **图4** 所示:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/e61e6ba685534eda992cea30a63a9c461646040ffd0c4d208a5eebb85897dcf7' width='600'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图4 padding前后对比图</div>
|
||||
|
||||
将图片都padding到300*300大小,因为坐标信息发生了变化,我们同时要修改标注文件,在`/home/aistudio/dataset`目录里也提供了padding之后的图片,大家也可以尝试训练和评估:
|
||||
|
||||
同上,我们需要修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_padding_val.txt
|
||||
Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest: 尺寸
|
||||
limit_side_len: 1100
|
||||
limit_type: 'min'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型评估。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## **4.3 预训练模型+fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
基于预训练模型,在生成的1500图片上进行fine-tune训练和评估,其中train数据1200张,val数据300张,修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.epoch_num: 这里设置为1,方便快速跑通,实际中根据数据量调整该值
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir:模型保存路径
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model:指向预训练模型路径,'./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student.pdparams'
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.learning_rate:调整学习率,本实验设置为0.0005
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_train.txt'
|
||||
Train.dataset.transforms.EastRandomCropData.size:训练尺寸改为[480,64]
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset/'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_val.txt'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest:评估尺寸,添加如下参数
|
||||
limit_side_len: 64
|
||||
limit_type:'min'
|
||||
```
|
||||
执行下面命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./output/ch_PP-OCR_V3_det/latest"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | hmean | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 | 64.64% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + 验证集padding | 72.13% |+7.5% | padding可以提升尺寸较小图片的检测效果|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune | 100% | +27.9% | fine-tune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
注:上述实验结果均是在1500张图片(1200张训练集,300张测试集)上训练、评估的得到,AIstudio只提供了100张数据,所以指标有所差异属于正常,只要策略有效、规律相同即可。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 5. 文本识别
|
||||
|
||||
我们分别使用如下4种方案进行训练、评估:
|
||||
|
||||
- **方案1**:**PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
- **方案2**:PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + **fine-tune**
|
||||
- **方案3**:PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune + **公开通用识别数据集**
|
||||
- **方案4**:PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune + **增加PCB图像数量**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## **5.1 预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
|
||||
同检测模型,我们首先使用PaddleOCR提供的识别预训练模型在PCB验证集上进行评估。
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型直接评估步骤如下:
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量文本识别模型,下载并解压预训练模型:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如果更换其他模型,更新下载链接和解压指令就可以
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain_models/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_distillation.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Metric.ignore_space: True:忽略空格
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/rec_gt_val.txt'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用下载的预训练模型进行评估:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## **5.2 三种fine-tune方案**
|
||||
|
||||
方案2、3、4训练和评估方式是相同的,因此在我们了解每个技术方案之后,再具体看修改哪些参数是相同,哪些是不同的。
|
||||
|
||||
**方案介绍:**
|
||||
|
||||
1) **方案2**:预训练模型 + **fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
- 在预训练模型的基础上进行fine-tune,使用1500张PCB进行训练和评估,其中训练集1200张,验证集300张。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2) **方案3**:预训练模型 + fine-tune + **公开通用识别数据集**
|
||||
|
||||
- 当识别数据比较少的情况,可以考虑添加公开通用识别数据集。在方案2的基础上,添加公开通用识别数据集,如lsvt、rctw等。
|
||||
|
||||
3)**方案4**:预训练模型 + fine-tune + **增加PCB图像数量**
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果能够获取足够多真实场景,我们可以通过增加数据量提升模型效果。在方案2的基础上,增加PCB的数量到2W张左右。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参数修改:**
|
||||
|
||||
接着我们看需要修改的参数,以上方案均需要修改配置文件`configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml`的参数,**修改一次即可**:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model:指向预训练模型路径,'pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy'
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.values:学习率,本实验设置为0.0005
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card: batch size,默认128,因为数据量小于128,因此我们设置为8,数据量大可以按默认的训练
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card: batch size,默认128,设置为4
|
||||
Metric.ignore_space: 忽略空格,本实验设置为True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**更换不同的方案**每次需要修改的参数:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.epoch_num: 这里设置为1,方便快速跑通,实际中根据数据量调整该值
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir:指向模型保存路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同时**方案3**修改以下参数
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:添加公开通用识别数据标注文件
|
||||
Eval.dataset.ratio_list:数据和公开通用识别数据每次采样比例,按实际修改即可
|
||||
```
|
||||
如 **图5** 所示:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/0fa18b25819042d9bbf3397c3af0e21433b23d52f7a84b0a8681b8e6a308d433' wdith=''></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图5 添加公开通用识别数据配置文件示例</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们提取Student模型的参数,在PCB数据集上进行fine-tune,可以参考如下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 学生模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("student_model."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "student_model." in key}
|
||||
# 查看学生模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改参数后,**每个方案**都执行如下命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./output/rec_ppocr_v3/latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
所有方案评估指标如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | acc | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接评估 | 46.67% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune | 42.02% |-4.6% | 在数据量不足的情况,反而比预训练模型效果低(也可以通过调整超参数再试试)|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 公开通用识别数据集 | 77% | +30% | 在数据量不足的情况下,可以考虑补充公开数据训练 |
|
||||
| 4 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 增加PCB图像数量 | 99.99% | +23% | 如果能获取更多数据量的情况,可以通过增加数据量提升效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
注:上述实验结果均是在1500张图片(1200张训练集,300张测试集)、2W张图片、添加公开通用识别数据集上训练、评估的得到,AIstudio只提供了100张数据,所以指标有所差异属于正常,只要策略有效、规律相同即可。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 6. 模型导出
|
||||
|
||||
inference 模型(paddle.jit.save保存的模型) 一般是模型训练,把模型结构和模型参数保存在文件中的固化模型,多用于预测部署场景。 训练过程中保存的模型是checkpoints模型,保存的只有模型的参数,多用于恢复训练等。 与checkpoints模型相比,inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 导出检测模型
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_V3_det/latest" \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir="./inference_model/ch_PP-OCR_V3_det/"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
因为上述模型只训练了1个epoch,因此我们使用训练最优的模型进行预测,存储在`/home/aistudio/best_models/`目录下,解压即可
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/best_models/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/PCB/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB.tar
|
||||
tar xf /home/aistudio/best_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB.tar -C /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain_models/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 检测模型inference模型预测
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_det.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="/home/aistudio/dataset/imgs/0000.jpg" \
|
||||
--det_algorithm="DB" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./pretrain_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB/" \
|
||||
--det_limit_side_len=48 \
|
||||
--det_limit_type='min' \
|
||||
--det_db_unclip_ratio=2.5 \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果存储在`inference_results`目录下,检测如下图所示:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/5939ae15a1f0445aaeec15c68107dbd897740a1ddd284bf8b583bb6242099157' width=''></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图6 检测结果</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
同理,导出识别模型并进行推理。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 导出识别模型
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model="./output/rec_ppocr_v3/latest" \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir="./inference_model/rec_ppocr_v3/"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同检测模型,识别模型也只训练了1个epoch,因此我们使用训练最优的模型进行预测,存储在`/home/aistudio/best_models/`目录下,解压即可
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/best_models/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/PCB/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB.tar
|
||||
tar xf /home/aistudio/best_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB.tar -C /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain_models/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 识别模型inference模型预测
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="../test_imgs/0000_rec.jpg" \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./pretrain_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3, 48, 320" \
|
||||
--use_space_char=False \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 检测+识别模型inference模型预测
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="../test_imgs/0000.jpg" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./pretrain_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--det_limit_side_len=48 \
|
||||
--det_limit_type='min' \
|
||||
--det_db_unclip_ratio=2.5 \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./pretrain_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3, 48, 320" \
|
||||
--draw_img_save_dir=./det_rec_infer/ \
|
||||
--use_space_char=False \
|
||||
--use_angle_cls=False \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
端到端预测结果存储在`det_res_infer`文件夹内,结果如下图所示:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/c570f343c29846c792da56ebaca16c50708477514dd048cea8bef37ffa85d03f'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图7 检测+识别结果</div>
|
||||
|
||||
# 7. 端对端评测
|
||||
|
||||
接下来介绍文本检测+文本识别的端对端指标评估方式。主要分为三步:
|
||||
|
||||
1)首先运行`tools/infer/predict_system.py`,将`image_dir`改为需要评估的数据文件家,得到保存的结果:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 检测+识别模型inference模型预测
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="../dataset/imgs/" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./pretrain_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--det_limit_side_len=48 \
|
||||
--det_limit_type='min' \
|
||||
--det_db_unclip_ratio=2.5 \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./pretrain_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3, 48, 320" \
|
||||
--draw_img_save_dir=./det_rec_infer/ \
|
||||
--use_space_char=False \
|
||||
--use_angle_cls=False \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
得到保存结果,文本检测识别可视化图保存在`det_rec_infer/`目录下,预测结果保存在`det_rec_infer/system_results.txt`中,格式如下:`0018.jpg [{"transcription": "E295", "points": [[88, 33], [137, 33], [137, 40], [88, 40]]}]`
|
||||
|
||||
2)然后将步骤一保存的数据转换为端对端评测需要的数据格式: 修改 `tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py`中的代码,convert_label函数中设置输入标签路径,Mode,保存标签路径等,对预测数据的GTlabel和预测结果的label格式进行转换。
|
||||
```
|
||||
ppocr_label_gt = "/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_val.txt"
|
||||
convert_label(ppocr_label_gt, "gt", "./save_gt_label/")
|
||||
|
||||
ppocr_label_gt = "/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/PCB_result/det_rec_infer/system_results.txt"
|
||||
convert_label(ppocr_label_gt, "pred", "./save_PPOCRV2_infer/")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行`convert_ppocr_label.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
得到如下结果:
|
||||
```
|
||||
├── ./save_gt_label/
|
||||
├── ./save_PPOCRV2_infer/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3) 最后,执行端对端评测,运行`tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py`计算端对端指标,运行方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pip install editdistance
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py ./save_gt_label/ ./save_PPOCRV2_infer/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用`预训练模型+fine-tune'检测模型`、`预训练模型 + 2W张PCB图片funetune`识别模型,在300张PCB图片上评估得到如下结果,fmeasure为主要关注的指标:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/37206ea48a244212ae7a821d50d1fd51faf3d7fe97ac47a29f04dfcbb377b019', width='700'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图8 端到端评估指标</div>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
注: 使用上述命令不能跑出该结果,因为数据集不相同,可以更换为自己训练好的模型,按上述流程运行
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 8. Jetson部署
|
||||
|
||||
我们只需要以下步骤就可以完成Jetson nano部署模型,简单易操作:
|
||||
|
||||
**1、在Jetson nano开发版上环境准备:**
|
||||
|
||||
* 安装PaddlePaddle
|
||||
|
||||
* 下载PaddleOCR并安装依赖
|
||||
|
||||
**2、执行预测**
|
||||
|
||||
* 将推理模型下载到jetson
|
||||
|
||||
* 执行检测、识别、串联预测即可
|
||||
|
||||
详细[参考流程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/deploy/Jetson/readme_ch.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
# 9. 总结
|
||||
|
||||
检测实验分别使用PP-OCRv3预训练模型在PCB数据集上进行了直接评估、验证集padding、 fine-tune 3种方案,识别实验分别使用PP-OCRv3预训练模型在PCB数据集上进行了直接评估、 fine-tune、添加公开通用识别数据集、增加PCB图片数量4种方案,指标对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* 检测
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | hmean | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| ---- | -------------------------------------------------------- | ------ | -------- | ------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接评估 | 64.64% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + 验证集padding直接评估 | 72.13% | +7.5% | padding可以提升尺寸较小图片的检测效果 |
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune | 100% | +27.9% | fine-tune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
* 识别
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | acc | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接评估 | 46.67% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune | 42.02% | -4.6% | 在数据量不足的情况,反而比预训练模型效果低(也可以通过调整超参数再试试) |
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 公开通用识别数据集 | 77% | +30% | 在数据量不足的情况下,可以考虑补充公开数据训练 |
|
||||
| 4 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 增加PCB图像数量 | 99.99% | +23% | 如果能获取更多数据量的情况,可以通过增加数据量提升效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
* 端到端
|
||||
|
||||
| det | rec | fmeasure |
|
||||
| --------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 增加PCB图像数量 | 93.3% |
|
||||
|
||||
*结论*
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的检测模型在未经过fine-tune的情况下,在PCB数据集上也有64.64%的精度,说明具有泛化能力。验证集padding之后,精度提升7.5%,在图片尺寸较小的情况,我们可以通过padding的方式提升检测效果。经过 fine-tune 后能够极大的提升检测效果,精度达到100%。
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的识别模型方案1和方案2对比可以发现,当数据量不足的情况,预训练模型精度可能比fine-tune效果还要高,所以我们可以先尝试预训练模型直接评估。如果在数据量不足的情况下想进一步提升模型效果,可以通过添加公开通用识别数据集,识别效果提升30%,非常有效。最后如果我们能够采集足够多的真实场景数据集,可以通过增加数据量提升模型效果,精度达到99.99%。
|
||||
|
||||
# 更多资源
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多深度学习知识、产业案例、面试宝典等,请参考:[awesome-DeepLearning](https://github.com/paddlepaddle/awesome-DeepLearning)
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多PaddleOCR使用教程,请参考:[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/dygraph)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 飞桨框架相关资料,请参考:[飞桨深度学习平台](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/?fr=paddleEdu_aistudio)
|
||||
|
||||
# 参考
|
||||
|
||||
* 数据生成代码库:https://github.com/zcswdt/Color_OCR_image_generator
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.0 KiB |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
|||
5ZQ
|
||||
I4UL
|
||||
PWL
|
||||
SNOG
|
||||
ZL02
|
||||
1C30
|
||||
O3H
|
||||
YHRS
|
||||
N03S
|
||||
1U5Y
|
||||
JTK
|
||||
EN4F
|
||||
YKJ
|
||||
DWNH
|
||||
R42W
|
||||
X0V
|
||||
4OF5
|
||||
08AM
|
||||
Y93S
|
||||
GWE2
|
||||
0KR
|
||||
9U2A
|
||||
DBQ
|
||||
Y6J
|
||||
ROZ
|
||||
K06
|
||||
KIEY
|
||||
NZQJ
|
||||
UN1B
|
||||
6X4
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 145 B |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 141 B |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,261 @@
|
|||
# copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This code is refer from:
|
||||
https://github.com/zcswdt/Color_OCR_image_generator
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_char_lines(txt_root_path):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc:get corpus line
|
||||
"""
|
||||
txt_files = os.listdir(txt_root_path)
|
||||
char_lines = []
|
||||
for txt in txt_files:
|
||||
f = open(os.path.join(txt_root_path, txt), mode='r', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
lines = f.readlines()
|
||||
f.close()
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
char_lines.append(line.strip())
|
||||
return char_lines
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_horizontal_text_picture(image_file, chars, fonts_list, cf):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc:gen horizontal text picture
|
||||
"""
|
||||
img = Image.open(image_file)
|
||||
if img.mode != 'RGB':
|
||||
img = img.convert('RGB')
|
||||
img_w, img_h = img.size
|
||||
|
||||
# random choice font
|
||||
font_path = random.choice(fonts_list)
|
||||
# random choice font size
|
||||
font_size = random.randint(cf.font_min_size, cf.font_max_size)
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
|
||||
|
||||
ch_w = []
|
||||
ch_h = []
|
||||
for ch in chars:
|
||||
wt, ht = font.getsize(ch)
|
||||
ch_w.append(wt)
|
||||
ch_h.append(ht)
|
||||
f_w = sum(ch_w)
|
||||
f_h = max(ch_h)
|
||||
|
||||
# add space
|
||||
char_space_width = max(ch_w)
|
||||
f_w += (char_space_width * (len(chars) - 1))
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = random.randint(0, img_w - f_w)
|
||||
y1 = random.randint(0, img_h - f_h)
|
||||
x2 = x1 + f_w
|
||||
y2 = y1 + f_h
|
||||
|
||||
crop_y1 = y1
|
||||
crop_x1 = x1
|
||||
crop_y2 = y2
|
||||
crop_x2 = x2
|
||||
|
||||
best_color = (0, 0, 0)
|
||||
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
|
||||
for i, ch in enumerate(chars):
|
||||
draw.text((x1, y1), ch, best_color, font=font)
|
||||
x1 += (ch_w[i] + char_space_width)
|
||||
crop_img = img.crop((crop_x1, crop_y1, crop_x2, crop_y2))
|
||||
return crop_img, chars
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_vertical_text_picture(image_file, chars, fonts_list, cf):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc:gen vertical text picture
|
||||
"""
|
||||
img = Image.open(image_file)
|
||||
if img.mode != 'RGB':
|
||||
img = img.convert('RGB')
|
||||
img_w, img_h = img.size
|
||||
# random choice font
|
||||
font_path = random.choice(fonts_list)
|
||||
# random choice font size
|
||||
font_size = random.randint(cf.font_min_size, cf.font_max_size)
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
|
||||
|
||||
ch_w = []
|
||||
ch_h = []
|
||||
for ch in chars:
|
||||
wt, ht = font.getsize(ch)
|
||||
ch_w.append(wt)
|
||||
ch_h.append(ht)
|
||||
f_w = max(ch_w)
|
||||
f_h = sum(ch_h)
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = random.randint(0, img_w - f_w)
|
||||
y1 = random.randint(0, img_h - f_h)
|
||||
x2 = x1 + f_w
|
||||
y2 = y1 + f_h
|
||||
|
||||
crop_y1 = y1
|
||||
crop_x1 = x1
|
||||
crop_y2 = y2
|
||||
crop_x2 = x2
|
||||
|
||||
best_color = (0, 0, 0)
|
||||
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
for ch in chars:
|
||||
draw.text((x1, y1), ch, best_color, font=font)
|
||||
y1 = y1 + ch_h[i]
|
||||
i = i + 1
|
||||
crop_img = img.crop((crop_x1, crop_y1, crop_x2, crop_y2))
|
||||
crop_img = crop_img.transpose(Image.ROTATE_90)
|
||||
return crop_img, chars
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_fonts(fonts_path):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc: get all fonts
|
||||
"""
|
||||
font_files = os.listdir(fonts_path)
|
||||
fonts_list=[]
|
||||
for font_file in font_files:
|
||||
font_path=os.path.join(fonts_path, font_file)
|
||||
fonts_list.append(font_path)
|
||||
return fonts_list
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--num_img', type=int, default=30, help="Number of images to generate")
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--font_min_size', type=int, default=11)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--font_max_size', type=int, default=12,
|
||||
help="Help adjust the size of the generated text and the size of the picture")
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--bg_path', type=str, default='./background',
|
||||
help='The generated text pictures will be pasted onto the pictures of this folder')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--det_bg_path', type=str, default='./det_background',
|
||||
help='The generated text pictures will use the pictures of this folder as the background')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--fonts_path', type=str, default='../../StyleText/fonts',
|
||||
help='The font used to generate the picture')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--corpus_path', type=str, default='./corpus',
|
||||
help='The corpus used to generate the text picture')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, default='./output/', help='Images save dir')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
cf = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
# save path
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# get corpus
|
||||
txt_root_path = cf.corpus_path
|
||||
char_lines = get_char_lines(txt_root_path=txt_root_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# get all fonts
|
||||
fonts_path = cf.fonts_path
|
||||
fonts_list = get_fonts(fonts_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# rec bg
|
||||
img_root_path = cf.bg_path
|
||||
imnames=os.listdir(img_root_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# det bg
|
||||
det_bg_path = cf.det_bg_path
|
||||
bg_pics = os.listdir(det_bg_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# OCR det files
|
||||
det_val_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'det_gt_val.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
det_train_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'det_gt_train.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
# det imgs
|
||||
det_save_dir = 'imgs/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + det_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + det_save_dir)
|
||||
det_val_save_dir = 'imgs_val/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + det_val_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + det_val_save_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# OCR rec files
|
||||
rec_val_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'rec_gt_val.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
rec_train_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'rec_gt_train.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
# rec imgs
|
||||
rec_save_dir = 'rec_imgs/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + rec_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + rec_save_dir)
|
||||
rec_val_save_dir = 'rec_imgs_val/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + rec_val_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + rec_val_save_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
val_ratio = cf.num_img * 0.2 # val dataset ratio
|
||||
|
||||
print('start generating...')
|
||||
for i in range(0, cf.num_img):
|
||||
imname = random.choice(imnames)
|
||||
img_path = os.path.join(img_root_path, imname)
|
||||
|
||||
rnd = random.random()
|
||||
# gen horizontal text picture
|
||||
if rnd < 0.5:
|
||||
gen_img, chars = get_horizontal_text_picture(img_path, char_lines[i], fonts_list, cf)
|
||||
ori_w, ori_h = gen_img.size
|
||||
gen_img = gen_img.crop((0, 3, ori_w, ori_h))
|
||||
# gen vertical text picture
|
||||
else:
|
||||
gen_img, chars = get_vertical_text_picture(img_path, char_lines[i], fonts_list, cf)
|
||||
ori_w, ori_h = gen_img.size
|
||||
gen_img = gen_img.crop((3, 0, ori_w, ori_h))
|
||||
|
||||
ori_w, ori_h = gen_img.size
|
||||
|
||||
# rec imgs
|
||||
save_img_name = str(i).zfill(4) + '.jpg'
|
||||
if i < val_ratio:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(rec_val_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
line = save_dir + '\t' + char_lines[i] + '\n'
|
||||
rec_val_file.write(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(rec_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
line = save_dir + '\t' + char_lines[i] + '\n'
|
||||
rec_train_file.write(line)
|
||||
gen_img.save(cf.output_dir + save_dir, quality = 95, subsampling=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# det img
|
||||
# random choice bg
|
||||
bg_pic = random.sample(bg_pics, 1)[0]
|
||||
det_img = Image.open(os.path.join(det_bg_path, bg_pic))
|
||||
# the PCB position is fixed, modify it according to your own scenario
|
||||
if bg_pic == '1.png':
|
||||
x1 = 38
|
||||
y1 = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x1 = 34
|
||||
y1 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
det_img.paste(gen_img, (x1, y1))
|
||||
# text pos
|
||||
chars_pos = [[x1, y1], [x1 + ori_w, y1], [x1 + ori_w, y1 + ori_h], [x1, y1 + ori_h]]
|
||||
label = [{"transcription":char_lines[i], "points":chars_pos}]
|
||||
if i < val_ratio:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(det_val_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
det_val_file.write(save_dir + '\t' + json.dumps(
|
||||
label, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(det_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
det_train_file.write(save_dir + '\t' + json.dumps(
|
||||
label, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
|
||||
det_img.save(cf.output_dir + save_dir, quality = 95, subsampling=0)
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
|||
# 场景应用
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR场景应用覆盖通用,制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用,在PP-OCR、PP-Structure的通用能力基础之上,以notebook的形式展示利用场景数据微调、模型优化方法、数据增广等内容,为开发者快速落地OCR应用提供示范与启发。
|
||||
|
||||
> 如需下载全部垂类模型,可以扫描下方二维码,关注公众号填写问卷后,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取20G OCR学习大礼包(内含《动手学OCR》电子书、课程回放视频、前沿论文等重磅资料)
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果您是企业开发者且未在下述场景中找到合适的方案,可以填写[OCR应用合作调研问卷](https://paddle.wjx.cn/vj/QwF7GKw.aspx),免费与官方团队展开不同层次的合作,包括但不限于问题抽象、确定技术方案、项目答疑、共同研发等。如果您已经使用PaddleOCR落地项目,也可以填写此问卷,与飞桨平台共同宣传推广,提升企业技术品宣。期待您的提交!
|
||||
|
||||
## 通用
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------- | -------- | ---------- | ------------ |
|
||||
| [高精度中文识别模型SVTR](./高精度中文识别模型.md) | 新增模型 | 手写体识别 | 新增字形支持 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 制造
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------- | -------------------- |
|
||||
| [数码管识别](./光功率计数码管字符识别/光功率计数码管字符识别.md) | 数码管数据合成、漏识别调优 | 电表识别 | 大分辨率图像检测调优 |
|
||||
| [液晶屏读数识别](./液晶屏读数识别.md) | 检测模型蒸馏、Serving部署 | [PCB文字识别](./PCB字符识别/PCB字符识别.md) | 小尺寸文本检测与识别 |
|
||||
| [包装生产日期](./包装生产日期识别.md) | 点阵字符合成、过曝过暗文字识别 | 液晶屏缺陷检测 | 非文字字符识别 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 金融
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------ | ------------------------ | ------------ | --------------------- |
|
||||
| [表单VQA](./多模态表单识别.md) | 多模态通用表单结构化提取 | 通用卡证识别 | 通用结构化提取 |
|
||||
| 增值税发票 | 尽请期待 | 身份证识别 | 结构化提取、图像阴影 |
|
||||
| 印章检测与识别 | 端到端弯曲文本识别 | 合同比对 | 密集文本检测、NLP串联 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 交通
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------- | ------------------------------ | ---------- | -------- |
|
||||
| [车牌识别](./轻量级车牌识别.md) | 多角度图像、轻量模型、端侧部署 | 快递单识别 | 尽请期待 |
|
||||
| 驾驶证/行驶证识别 | 尽请期待 | | |
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
|||
46.39
|
||||
40.08
|
||||
89.52
|
||||
-71.93
|
||||
23.19
|
||||
-81.02
|
||||
-34.09
|
||||
05.87
|
||||
-67.80
|
||||
-51.56
|
||||
-34.58
|
||||
37.91
|
||||
56.98
|
||||
29.01
|
||||
-90.13
|
||||
35.55
|
||||
66.07
|
||||
-90.35
|
||||
-50.93
|
||||
42.42
|
||||
21.40
|
||||
-30.99
|
||||
-71.78
|
||||
25.60
|
||||
-48.69
|
||||
-72.28
|
||||
-17.55
|
||||
-99.93
|
||||
-47.35
|
||||
-64.89
|
||||
-31.28
|
||||
-90.01
|
||||
05.17
|
||||
30.91
|
||||
30.56
|
||||
-06.90
|
||||
79.05
|
||||
67.74
|
||||
-32.31
|
||||
94.22
|
||||
28.75
|
||||
51.03
|
||||
-58.96
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,467 @@
|
|||
# 光功率计数码管字符识别
|
||||
|
||||
本案例将使用OCR技术自动识别光功率计显示屏文字,通过本章您可以掌握:
|
||||
|
||||
- PaddleOCR快速使用
|
||||
- 数据合成方法
|
||||
- 数据挖掘方法
|
||||
- 基于现有数据微调
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 背景介绍
|
||||
|
||||
光功率计(optical power meter )是指用于测量绝对光功率或通过一段光纤的光功率相对损耗的仪器。在光纤系统中,测量光功率是最基本的,非常像电子学中的万用表;在光纤测量中,光功率计是重负荷常用表。
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://bkimg.cdn.bcebos.com/pic/a08b87d6277f9e2f999f5e3e1c30e924b899f35a?x-bce-process=image/watermark,image_d2F0ZXIvYmFpa2U5Mg==,g_7,xp_5,yp_5/format,f_auto" width="400">
|
||||
|
||||
目前光功率计缺少将数据直接输出的功能,需要人工读数。这一项工作单调重复,如果可以使用机器替代人工,将节约大量成本。针对上述问题,希望通过摄像头拍照->智能读数的方式高效地完成此任务。
|
||||
|
||||
为实现智能读数,通常会采取文本检测+文本识别的方案:
|
||||
|
||||
第一步,使用文本检测模型定位出光功率计中的数字部分;
|
||||
|
||||
第二步,使用文本识别模型获得准确的数字和单位信息。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目主要介绍如何完成第二步文本识别部分,包括:真实评估集的建立、训练数据的合成、基于 PP-OCRv3 和 SVTR_Tiny 两个模型进行训练,以及评估和推理。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目难点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 光功率计数码管字符数据较少,难以获取。
|
||||
- 数码管中小数点占像素较少,容易漏识别。
|
||||
|
||||
针对以上问题, 本例选用 PP-OCRv3 和 SVTR_Tiny 两个高精度模型训练,同时提供了真实数据挖掘案例和数据合成案例。基于 PP-OCRv3 模型,在构建的真实评估集上精度从 52% 提升至 72%,SVTR_Tiny 模型精度可达到 78.9%。
|
||||
|
||||
aistudio项目链接: [光功率计数码管字符识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4049044?contributionType=1)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. PaddleOCR 快速使用
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR 旨在打造一套丰富、领先、且实用的OCR工具库,助力开发者训练出更好的模型,并应用落地。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
官方提供了适用于通用场景的高精轻量模型,首先使用官方提供的 PP-OCRv3 模型预测图片,验证下当前模型在光功率计场景上的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
- 准备环境
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -U pip
|
||||
python3 -m pip install paddleocr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 测试效果
|
||||
|
||||
测试图:
|
||||
|
||||
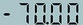
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
paddleocr --lang=ch --det=Fase --image_dir=data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
得到如下测试结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
('.7000', 0.6885431408882141)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发现数字识别较准,然而对负号和小数点识别不准确。 由于PP-OCRv3的训练数据大多为通用场景数据,在特定的场景上效果可能不够好。因此需要基于场景数据进行微调。
|
||||
|
||||
下面就主要介绍如何在光功率计(数码管)场景上微调训练。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 开始训练
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
特定的工业场景往往很难获取开源的真实数据集,光功率计也是如此。在实际工业场景中,可以通过摄像头采集的方法收集大量真实数据,本例中重点介绍数据合成方法和真实数据挖掘方法,如何利用有限的数据优化模型精度。
|
||||
|
||||
数据集分为两个部分:合成数据,真实数据, 其中合成数据由 text_renderer 工具批量生成得到, 真实数据通过爬虫等方式在百度图片中搜索并使用 PPOCRLabel 标注得到。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 合成数据
|
||||
|
||||
本例中数据合成工具使用的是 [text_renderer](https://github.com/Sanster/text_renderer), 该工具可以合成用于文本识别训练的文本行数据:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export https_proxy=http://172.19.57.45:3128
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/oh-my-ocr/text_renderer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import os
|
||||
python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -r docker/requirements.txt
|
||||
python3 main.py \
|
||||
--config example_data/example.py \
|
||||
--dataset img \
|
||||
--num_processes 2 \
|
||||
--log_period 10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
给定字体和语料,就可以合成较为丰富样式的文本行数据。 光功率计识别场景,目标是正确识别数码管文本,因此需要收集部分数码管字体,训练语料,用于合成文本识别数据。
|
||||
|
||||
将收集好的语料存放在 example_data 路径下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ln -s ./fonts/DS* text_renderer/example_data/font/
|
||||
ln -s ./corpus/digital.txt text_renderer/example_data/text/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改 text_renderer/example_data/font_list/font_list.txt ,选择需要的字体开始合成:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 main.py \
|
||||
--config example_data/digital_example.py \
|
||||
--dataset img \
|
||||
--num_processes 2 \
|
||||
--log_period 10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
合成图片会被存在目录 text_renderer/example_data/digital/chn_data 下
|
||||
|
||||
查看合成的数据样例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 真实数据挖掘
|
||||
|
||||
模型训练需要使用真实数据作为评价指标,否则很容易过拟合到简单的合成数据中。没有开源数据的情况下,可以利用部分无标注数据+标注工具获得真实数据。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. 数据搜集
|
||||
|
||||
使用[爬虫工具](https://github.com/Joeclinton1/google-images-download.git)获得无标注数据
|
||||
|
||||
2. [PPOCRLabel](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.5/PPOCRLabel) 完成半自动标注
|
||||
|
||||
PPOCRLabel是一款适用于OCR领域的半自动化图形标注工具,内置PP-OCR模型对数据自动标注和重新识别。使用Python3和PyQT5编写,支持矩形框标注、表格标注、不规则文本标注、关键信息标注模式,导出格式可直接用于PaddleOCR检测和识别模型的训练。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
收集完数据后就可以进行分配了,验证集中一般都是真实数据,训练集中包含合成数据+真实数据。本例中标注了155张图片,其中训练集和验证集的数目为100和55。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
最终 `data` 文件夹应包含以下几部分:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|-data
|
||||
|- synth_train.txt
|
||||
|- real_train.txt
|
||||
|- real_eval.txt
|
||||
|- synthetic_data
|
||||
|- word_001.png
|
||||
|- word_002.jpg
|
||||
|- word_003.jpg
|
||||
| ...
|
||||
|- real_data
|
||||
|- word_001.png
|
||||
|- word_002.jpg
|
||||
|- word_003.jpg
|
||||
| ...
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 模型选择
|
||||
|
||||
本案例提供了2种文本识别模型:PP-OCRv3 识别模型 和 SVTR_Tiny:
|
||||
|
||||
[PP-OCRv3 识别模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md):PP-OCRv3的识别模块是基于文本识别算法SVTR优化。SVTR不再采用RNN结构,通过引入Transformers结构更加有效地挖掘文本行图像的上下文信息,从而提升文本识别能力。并进行了一系列结构改进加速模型预测。
|
||||
|
||||
[SVTR_Tiny](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.00159):SVTR提出了一种用于场景文本识别的单视觉模型,该模型在patch-wise image tokenization框架内,完全摒弃了序列建模,在精度具有竞争力的前提下,模型参数量更少,速度更快。
|
||||
|
||||
以上两个策略在自建中文数据集上的精度和速度对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| ID | 策略 | 模型大小 | 精度 | 预测耗时(CPU + MKLDNN)|
|
||||
|-----|-----|--------|----| --- |
|
||||
| 01 | PP-OCRv2 | 8M | 74.8% | 8.54ms |
|
||||
| 02 | SVTR_Tiny | 21M | 80.1% | 97ms |
|
||||
| 03 | SVTR_LCNet(h32) | 12M | 71.9% | 6.6ms |
|
||||
| 04 | SVTR_LCNet(h48) | 12M | 73.98% | 7.6ms |
|
||||
| 05 | + GTC | 12M | 75.8% | 7.6ms |
|
||||
| 06 | + TextConAug | 12M | 76.3% | 7.6ms |
|
||||
| 07 | + TextRotNet | 12M | 76.9% | 7.6ms |
|
||||
| 08 | + UDML | 12M | 78.4% | 7.6ms |
|
||||
| 09 | + UIM | 12M | 79.4% | 7.6ms |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.3 开始训练
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载 PaddleOCR 代码库
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone -b release/2.5 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR提供了训练脚本、评估脚本和预测脚本,本节将以 PP-OCRv3 中文识别模型为例:
|
||||
|
||||
**Step1:下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载 pretrain model,您可以下载训练好的模型在自定义数据上进行finetune
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR/
|
||||
# 下载PP-OCRv3 中文预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrain_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压模型参数
|
||||
cd pretrain_models
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Step2:自定义字典文件**
|
||||
|
||||
接下来需要提供一个字典({word_dict_name}.txt),使模型在训练时,可以将所有出现的字符映射为字典的索引。
|
||||
|
||||
因此字典需要包含所有希望被正确识别的字符,{word_dict_name}.txt需要写成如下格式,并以 `utf-8` 编码格式保存:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
0
|
||||
1
|
||||
2
|
||||
3
|
||||
4
|
||||
5
|
||||
6
|
||||
7
|
||||
8
|
||||
9
|
||||
-
|
||||
.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
word_dict.txt 每行有一个单字,将字符与数字索引映射在一起,“3.14” 将被映射成 [3, 11, 1, 4]
|
||||
|
||||
* 内置字典
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR内置了一部分字典,可以按需使用。
|
||||
|
||||
`ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt` 是一个包含6623个字符的中文字典
|
||||
|
||||
`ppocr/utils/ic15_dict.txt` 是一个包含36个字符的英文字典
|
||||
|
||||
* 自定义字典
|
||||
|
||||
内置字典面向通用场景,具体的工业场景中,可能需要识别特殊字符,或者只需识别某几个字符,此时自定义字典会更提升模型精度。例如在光功率计场景中,需要识别数字和单位。
|
||||
|
||||
遍历真实数据标签中的字符,制作字典`digital_dict.txt`如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-
|
||||
.
|
||||
0
|
||||
1
|
||||
2
|
||||
3
|
||||
4
|
||||
5
|
||||
6
|
||||
7
|
||||
8
|
||||
9
|
||||
B
|
||||
E
|
||||
F
|
||||
H
|
||||
L
|
||||
N
|
||||
T
|
||||
W
|
||||
d
|
||||
k
|
||||
m
|
||||
n
|
||||
o
|
||||
z
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Step3:修改配置文件**
|
||||
|
||||
为了更好的使用预训练模型,训练推荐使用[ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml](../../configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml)配置文件,并参考下列说明修改配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
以 `ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml` 为例:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global:
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 添加自定义字典,如修改字典请将路径指向新字典
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/dict/digital_dict.txt
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 识别空格
|
||||
use_space_char: True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 添加学习率衰减策略
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Cosine
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.001
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
# 数据集格式,支持LMDBDataSet以及SimpleDataSet
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
# 数据集路径
|
||||
data_dir: ./data/
|
||||
# 训练集标签文件
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/digital_train.txt #11w
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/real_train.txt #100
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/dbm_img/dbm.txt #3w
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 0.3
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
...
|
||||
- RecResizeImg:
|
||||
# 修改 image_shape 以适应长文本
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 48, 320]
|
||||
...
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 单卡训练的batch_size
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
# 数据集格式,支持LMDBDataSet以及SimpleDataSet
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
# 数据集路径
|
||||
data_dir: ./data
|
||||
# 验证集标签文件
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/real_val.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
...
|
||||
- RecResizeImg:
|
||||
# 修改 image_shape 以适应长文本
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 48, 320]
|
||||
...
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
# 单卡验证的batch_size
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
**注意,训练/预测/评估时的配置文件请务必与训练一致。**
|
||||
|
||||
**Step4:启动训练**
|
||||
|
||||
*如果您安装的是cpu版本,请将配置文件中的 `use_gpu` 字段修改为false*
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# GPU训练 支持单卡,多卡训练
|
||||
# 训练数码管数据 训练日志会自动保存为 "{save_model_dir}" 下的train.log
|
||||
|
||||
#单卡训练(训练周期长,不建议)
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
|
||||
#多卡训练,通过--gpus参数指定卡号
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR支持训练和评估交替进行, 可以在 `configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml` 中修改 `eval_batch_step` 设置评估频率,默认每500个iter评估一次。评估过程中默认将最佳acc模型,保存为 `output/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distill/best_accuracy` 。
|
||||
|
||||
如果验证集很大,测试将会比较耗时,建议减少评估次数,或训练完再进行评估。
|
||||
|
||||
### SVTR_Tiny 训练
|
||||
|
||||
SVTR_Tiny 训练步骤与上面一致,SVTR支持的配置和模型训练权重可以参考[算法介绍文档](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_svtr.md)
|
||||
|
||||
**Step1:下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 下载 SVTR_Tiny 中文识别预训练模型和配置文件
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压模型参数
|
||||
tar -xf rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train.tar && rm -rf rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Step2:自定义字典文件**
|
||||
|
||||
字典依然使用自定义的 digital_dict.txt
|
||||
|
||||
**Step3:修改配置文件**
|
||||
|
||||
配置文件中对应修改字典路径和数据路径
|
||||
|
||||
**Step4:启动训练**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
## 单卡训练
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train/rec_svtr_tiny_6local_6global_stn_ch.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.4 验证效果
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理
|
||||
|
||||
* 指标评估
|
||||
|
||||
训练中模型参数默认保存在`Global.save_model_dir`目录下。在评估指标时,需要设置`Global.checkpoints`指向保存的参数文件。评估数据集可以通过 `configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml` 修改Eval中的 `label_file_path` 设置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# GPU 评估, Global.checkpoints 为待测权重
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0' tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.checkpoints={path/to/weights}/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 测试识别效果
|
||||
|
||||
使用 PaddleOCR 训练好的模型,可以通过以下脚本进行快速预测。
|
||||
|
||||
默认预测图片存储在 `infer_img` 里,通过 `-o Global.checkpoints` 加载训练好的参数文件:
|
||||
|
||||
根据配置文件中设置的 `save_model_dir` 和 `save_epoch_step` 字段,会有以下几种参数被保存下来:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
output/rec/
|
||||
├── best_accuracy.pdopt
|
||||
├── best_accuracy.pdparams
|
||||
├── best_accuracy.states
|
||||
├── config.yml
|
||||
├── iter_epoch_3.pdopt
|
||||
├── iter_epoch_3.pdparams
|
||||
├── iter_epoch_3.states
|
||||
├── latest.pdopt
|
||||
├── latest.pdparams
|
||||
├── latest.states
|
||||
└── train.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中 best_accuracy.* 是评估集上的最优模型;iter_epoch_x.* 是以 `save_epoch_step` 为间隔保存下来的模型;latest.* 是最后一个epoch的模型。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 预测英文结果
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model={path/to/weights}/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=test_digital.png
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预测图片:
|
||||
|
||||
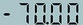
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
得到输入图像的预测结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
infer_img: test_digital.png
|
||||
result: ('-70.00', 0.9998967)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,685 @@
|
|||
# 一种基于PaddleOCR的产品包装生产日期识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目介绍](#1-项目介绍)
|
||||
- [2. 环境搭建](#2-环境搭建)
|
||||
- [3. 数据准备](#3-数据准备)
|
||||
- [4. 直接使用PP-OCRv3模型评估](#4-直接使用PPOCRv3模型评估)
|
||||
- [5. 基于合成数据finetune](#5-基于合成数据finetune)
|
||||
- [5.1 Text Renderer数据合成方法](#51-TextRenderer数据合成方法)
|
||||
- [5.1.1 下载Text Renderer代码](#511-下载TextRenderer代码)
|
||||
- [5.1.2 准备背景图片](#512-准备背景图片)
|
||||
- [5.1.3 准备语料](#513-准备语料)
|
||||
- [5.1.4 下载字体](#514-下载字体)
|
||||
- [5.1.5 运行数据合成命令](#515-运行数据合成命令)
|
||||
- [5.2 模型训练](#52-模型训练)
|
||||
- [6. 基于真实数据finetune](#6-基于真实数据finetune)
|
||||
- [6.1 python爬虫获取数据](#61-python爬虫获取数据)
|
||||
- [6.2 数据挖掘](#62-数据挖掘)
|
||||
- [6.3 模型训练](#63-模型训练)
|
||||
- [7. 基于合成+真实数据finetune](#7-基于合成+真实数据finetune)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目介绍
|
||||
|
||||
产品包装生产日期是计算机视觉图像识别技术在工业场景中的一种应用。产品包装生产日期识别技术要求能够将产品生产日期从复杂背景中提取并识别出来,在物流管理、物资管理中得到广泛应用。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 项目难点
|
||||
|
||||
1. 没有训练数据
|
||||
2. 图像质量层次不齐: 角度倾斜、图片模糊、光照不足、过曝等问题严重
|
||||
|
||||
针对以上问题, 本例选用PP-OCRv3这一开源超轻量OCR系统进行包装产品生产日期识别系统的开发。直接使用PP-OCRv3进行评估的精度为62.99%。为提升识别精度,我们首先使用数据合成工具合成了3k数据,基于这部分数据进行finetune,识别精度提升至73.66%。由于合成数据与真实数据之间的分布存在差异,为进一步提升精度,我们使用网络爬虫配合数据挖掘策略得到了1k带标签的真实数据,基于真实数据finetune的精度为71.33%。最后,我们综合使用合成数据和真实数据进行finetune,将识别精度提升至86.99%。各策略的精度提升效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 策略 | 精度|
|
||||
| :--------------- | :-------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv3评估 | 62.99|
|
||||
| 合成数据finetune | 73.66|
|
||||
| 真实数据finetune | 71.33|
|
||||
| 真实+合成数据finetune | 86.99|
|
||||
|
||||
AIStudio项目链接: [一种基于PaddleOCR的包装生产日期识别方法](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4287736)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 环境搭建
|
||||
|
||||
本任务基于Aistudio完成, 具体环境如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统: Linux
|
||||
- PaddlePaddle: 2.3
|
||||
- PaddleOCR: Release/2.5
|
||||
- text_renderer: master
|
||||
|
||||
下载PaddlleOCR代码并安装依赖库:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone -b dygraph https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
|
||||
# 安装依赖库
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
pip install -r PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
本项目使用人工预标注的300张图像作为测试集。
|
||||
|
||||
部分数据示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
标签文件格式如下:
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
数据路径 标签(中间以制表符分隔)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|数据集类型|数量|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|测试集| 300|
|
||||
|
||||
数据集[下载链接](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/149770),下载后可以通过下方命令解压:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
tar -xvf data.tar
|
||||
mv data ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
数据解压后的文件结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── mining_images # 挖掘的真实数据示例
|
||||
│ ├── mining_train.list # 挖掘的真实数据文件列表
|
||||
│ ├── render_images # 合成数据示例
|
||||
│ ├── render_train.list # 合成数据文件列表
|
||||
│ ├── val # 测试集数据
|
||||
│ └── val.list # 测试集数据文件列表
|
||||
| ├── bg # 合成数据所需背景图像
|
||||
│ └── corpus # 合成数据所需语料
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 直接使用PP-OCRv3模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
准备好测试数据后,可以使用PaddleOCR的PP-OCRv3模型进行识别。
|
||||
|
||||
- 下载预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
首先需要下载PP-OCR v3中英文识别模型文件,下载链接可以在https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md#6 获取,下载命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
mkdir ckpt
|
||||
wget -nc -P ckpt https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
pushd ckpt/
|
||||
tar -xvf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
popd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令进行PP-OCRv3评估:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"]
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中各参数含义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
-c: 指定使用的配置文件,ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml对应于OCRv3识别模型。
|
||||
-o: 覆盖配置文件中参数
|
||||
Global.checkpoints: 指定评估使用的模型文件路径
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir: 指定评估数据集路径
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list: 指定评估数据集文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5. 基于合成数据finetune
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.1 Text Renderer数据合成方法
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.1 下载Text Renderer代码
|
||||
|
||||
首先从github或gitee下载Text Renderer代码,并安装相关依赖。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://gitee.com/wowowoll/text_renderer.git
|
||||
|
||||
# 安装依赖库
|
||||
cd text_renderer
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用text renderer合成数据之前需要准备好背景图片、语料以及字体库,下面将逐一介绍各个步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.2 准备背景图片
|
||||
|
||||
观察日常生活中常见的包装生产日期图片,我们可以发现其背景相对简单。为此我们可以从网上找一下图片,截取部分图像块作为背景图像。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目已准备了部分图像作为背景图片,在第3部分完成数据准备后,可以得到我们准备好的背景图像,示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
背景图像存放于如下位置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
| ├── bg # 合成数据所需背景图像
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.3 准备语料
|
||||
|
||||
观察测试集生产日期图像,我们可以知道如下数据有如下特点:
|
||||
1. 由年月日组成,中间可能以“/”、“-”、“:”、“.”或者空格间隔,也可能以汉字年月日分隔
|
||||
2. 有些生产日期包含在产品批号中,此时可能包含具体时间、英文字母或数字标识
|
||||
|
||||
基于以上两点,我们编写语料生成脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from random import choice
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
cropus_num = 2000 #设置语料数量
|
||||
|
||||
def get_cropus(f):
|
||||
# 随机生成年份
|
||||
year = random.randint(0, 22)
|
||||
# 随机生成月份
|
||||
month = random.randint(1, 12)
|
||||
# 随机生成日期
|
||||
day_dict = {31: [1,3,5,7,8,10,12], 30: [4,6,9,11], 28: [2]}
|
||||
for item in day_dict:
|
||||
if month in day_dict[item]:
|
||||
day = random.randint(0, item)
|
||||
# 随机生成小时
|
||||
hours = random.randint(0, 24)
|
||||
# 随机生成分钟
|
||||
minute = random.randint(0, 60)
|
||||
# 随机生成秒数
|
||||
second = random.randint(0, 60)
|
||||
|
||||
# 随机生成产品标识字符
|
||||
length = random.randint(0, 6)
|
||||
file_id = []
|
||||
flag = 0
|
||||
my_dict = [i for i in range(48,58)] + [j for j in range(40, 42)] + [k for k in range(65,90)] # 大小写字母 + 括号
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, length):
|
||||
if flag:
|
||||
if i == flag+2: #括号匹配
|
||||
file_id.append(')')
|
||||
flag = 0
|
||||
continue
|
||||
sel = choice(my_dict)
|
||||
if sel == 41:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if sel == 40:
|
||||
if i == 1 or i > length-3:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
flag = i
|
||||
my_ascii = chr(sel)
|
||||
file_id.append(my_ascii)
|
||||
file_id_str = ''.join(file_id)
|
||||
|
||||
#随机生成产品标识字符
|
||||
file_id2 = random.randint(0, 9)
|
||||
|
||||
rad = random.random()
|
||||
if rad < 0.3:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}{:02d}{:02d} {}'.format(year, month, day, file_id_str))
|
||||
elif 0.3 < rad < 0.5:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}年{:02d}月{:02d}日'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
elif 0.5 < rad < 0.7:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}/{:02d}/{:02d}'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
elif 0.7 < rad < 0.8:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}-{:02d}-{:02d}'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
elif 0.8 < rad < 0.9:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}.{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
f.write('{:02d}:{:02d}:{:02d} {:02d}'.format(hours, minute, second, file_id2))
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
file_path = '/home/aistudio/text_renderer/my_data/cropus'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
|
||||
os.makedirs(file_path)
|
||||
file_name = os.path.join(file_path, 'books.txt')
|
||||
f = open(file_name, 'w')
|
||||
for i in range(cropus_num):
|
||||
get_cropus(f)
|
||||
if i < cropus_num-1:
|
||||
f.write('\n')
|
||||
|
||||
f.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
本项目已准备了部分语料,在第3部分完成数据准备后,可以得到我们准备好的语料库,默认位置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ └── corpus #合成数据所需语料
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.4 下载字体
|
||||
|
||||
观察包装生产日期,我们可以发现其使用的字体为点阵体。字体可以在如下网址下载:
|
||||
https://www.fonts.net.cn/fonts-en/tag-dianzhen-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
本项目已准备了部分字体,在第3部分完成数据准备后,可以得到我们准备好的字体,默认位置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ └── fonts #合成数据所需字体
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下载好字体后,还需要在list文件中指定字体文件存放路径,脚本如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd text_renderer/my_data/
|
||||
touch fonts.list
|
||||
ls /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/fonts/* > fonts.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.5 运行数据合成命令
|
||||
|
||||
完成数据准备后,my_data文件结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
my_data/
|
||||
├── cropus
|
||||
│ └── books.txt #语料库
|
||||
├── eng.txt #字符列表
|
||||
└── fonts.list #字体列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在运行合成数据命令之前,还有两处细节需要手动修改:
|
||||
1. 将默认配置文件`text_renderer/configs/default.yaml`中第9行enable的值设为`true`,即允许合成彩色图像。否则合成的都是灰度图。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# color boundary is in R,G,B format
|
||||
font_color:
|
||||
+ enable: true #false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 将`text_renderer/textrenderer/renderer.py`第184行作如下修改,取消padding。否则图片两端会有一些空白。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
padding = random.randint(s_bbox_width // 10, s_bbox_width // 8) #修改前
|
||||
padding = 0 #修改后
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行数据合成命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/text_renderer/
|
||||
python main.py --num_img=3000 \
|
||||
--fonts_list='./my_data/fonts.list' \
|
||||
--corpus_dir "./my_data/cropus" \
|
||||
--corpus_mode "list" \
|
||||
--bg_dir "/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/bg/" \
|
||||
--img_width 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
合成好的数据默认保存在`text_renderer/output`目录下,可进入该目录查看合成的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
合成数据示例如下
|
||||
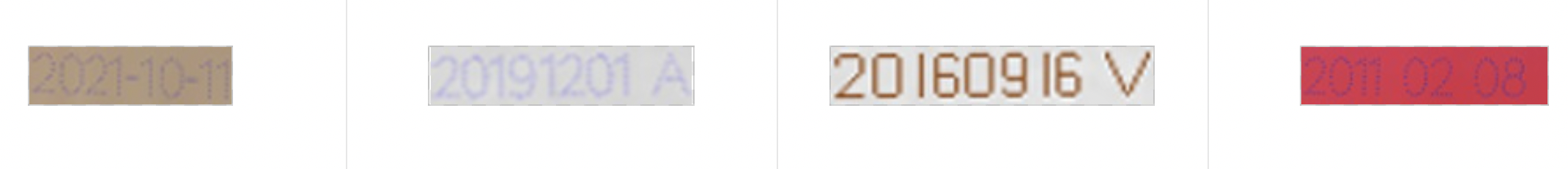
|
||||
|
||||
数据合成好后,还需要生成如下格式的训练所需的标注文件,
|
||||
```
|
||||
图像路径 标签
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下脚本即可生成标注文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
abspath = '/home/aistudio/text_renderer/output/default/'
|
||||
|
||||
#标注文件生成路径
|
||||
fout = open('./render_train.list', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
with open('./output/default/tmp_labels.txt','r') as f:
|
||||
lines = f.readlines()
|
||||
for item in lines:
|
||||
label = item[9:]
|
||||
filename = item[:8] + '.jpg'
|
||||
fout.write(abspath + filename + '\t' + label)
|
||||
|
||||
fout.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
经过以上步骤,我们便完成了包装生产日期数据合成。
|
||||
数据位于`text_renderer/output`,标注文件位于`text_renderer/render_train.list`。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目提供了生成好的数据供大家体验,完成步骤3的数据准备后,可得数据路径位于:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── render_images # 合成数据示例
|
||||
│ ├── render_train.list #合成数据文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.2 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
准备好合成数据后,我们可以使用以下命令,利用合成数据进行finetune:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.epoch_num=20 \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step='[0, 20]' \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=['./data/render_train.list'] \
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card=64 \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"] \
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card=64
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中各参数含义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
-c: 指定使用的配置文件,ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml对应于OCRv3识别模型。
|
||||
-o: 覆盖配置文件中参数
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model: 指定finetune使用的预训练模型
|
||||
Global.epoch_num: 指定训练的epoch数
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step: 间隔多少step做一次评估
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir: 训练数据集路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list: 训练集文件列表
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card: 训练单卡batch size
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir: 评估数据集路径
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list: 评估数据集文件列表
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card: 评估单卡batch size
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 6. 基于真实数据finetune
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用合成数据finetune能提升我们模型的识别精度,但由于合成数据和真实数据之间的分布可能有一定差异,因此作用有限。为进一步提高识别精度,本节介绍如何挖掘真实数据进行模型finetune。
|
||||
|
||||
数据挖掘的整体思路如下:
|
||||
1. 使用python爬虫从网上获取大量无标签数据
|
||||
2. 使用模型从大量无标签数据中构建出有效训练集
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.1 python爬虫获取数据
|
||||
|
||||
- 推荐使用[爬虫工具](https://github.com/Joeclinton1/google-images-download)获取无标签图片。
|
||||
|
||||
图片获取后,可按如下目录格式组织:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
sprider
|
||||
├── file.list
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── 00000.jpg
|
||||
│ ├── 00001.jpg
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.2 数据挖掘
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用PaddleOCR对获取到的图片进行挖掘,具体步骤如下:
|
||||
1. 使用 PP-OCRv3检测模型+svtr-tiny识别模型,对每张图片进行预测。
|
||||
2. 使用数据挖掘策略,得到有效图片。
|
||||
3. 将有效图片对应的图像区域和标签提取出来,构建训练集。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载预训练模型,PP-OCRv3检测模型下载链接:https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取svtr-tiny高精度中文识别预训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
完成下载后,可将模型存储于如下位置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── rec_vit_sub_64_363_all/ # svtr_tiny高精度识别模型
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 下载解压PP-OCRv3检测模型
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
wget -nc -P ckpt https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
pushd ckpt
|
||||
tar -xvf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
popd ckpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在使用PPOCRv3检测模型+svtr-tiny识别模型进行预测之前,有如下两处细节需要手动修改:
|
||||
1. 将`tools/infer/predict_rec.py`中第110行`imgW`修改为`320`
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#imgW = int((imgH * max_wh_ratio))
|
||||
imgW = 320
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 将`tools/infer/predict_system.py`第169行添加如下一行,将预测分数也写入结果文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
"scores": rec_res[idx][1],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
模型预测命令:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="/home/aistudio/sprider/data" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer/" \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/rec_vit_sub_64_363_all/" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3,32,320"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
获得预测结果后,我们使用数据挖掘策略得到有效图片。具体挖掘策略如下:
|
||||
1. 预测置信度高于95%
|
||||
2. 识别结果包含字符‘20’,即年份
|
||||
3. 没有中文,或者有中文并且‘日’和'月'同时在识别结果中
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 获取有效预测
|
||||
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
zh_pattern = re.compile(u'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+') #正则表达式,筛选字符是否包含中文
|
||||
|
||||
file_path = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/inference_results/system_results.txt'
|
||||
out_path = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/selected_results.txt'
|
||||
f_out = open(out_path, 'w')
|
||||
|
||||
with open(file_path, "r", encoding='utf-8') as fin:
|
||||
lines = fin.readlines()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
flag = False
|
||||
# 读取文件内容
|
||||
file_name, json_file = line.strip().split('\t')
|
||||
preds = json.loads(json_file)
|
||||
res = []
|
||||
for item in preds:
|
||||
transcription = item['transcription'] #获取识别结果
|
||||
scores = item['scores'] #获取识别得分
|
||||
# 挖掘策略
|
||||
if scores > 0.95:
|
||||
if '20' in transcription and len(transcription) > 4 and len(transcription) < 12:
|
||||
word = transcription
|
||||
if not(zh_pattern.search(word) and ('日' not in word or '月' not in word)):
|
||||
flag = True
|
||||
res.append(item)
|
||||
save_pred = file_name + "\t" + json.dumps(
|
||||
res, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n"
|
||||
if flag ==True:
|
||||
f_out.write(save_pred)
|
||||
|
||||
f_out.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后将有效预测对应的图像区域和标签提取出来,构建训练集。具体实现脚本如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
PATH = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/inference_results/' #数据原始路径
|
||||
SAVE_PATH = '/home/aistudio/mining_images/' #裁剪后数据保存路径
|
||||
file_list = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/selected_results.txt' #数据预测结果
|
||||
label_file = '/home/aistudio/mining_images/mining_train.list' #输出真实数据训练集标签list
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(SAVE_PATH):
|
||||
os.mkdir(SAVE_PATH)
|
||||
|
||||
f_label = open(label_file, 'w')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rotate_crop_image(img, points):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
根据检测结果points,从输入图像img中裁剪出相应的区域
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert len(points) == 4, "shape of points must be 4*2"
|
||||
img_crop_width = int(
|
||||
max(
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[1]),
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[2] - points[3])))
|
||||
img_crop_height = int(
|
||||
max(
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[3]),
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[1] - points[2])))
|
||||
pts_std = np.float32([[0, 0], [img_crop_width, 0],
|
||||
[img_crop_width, img_crop_height],
|
||||
[0, img_crop_height]])
|
||||
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std)
|
||||
# 形变或倾斜,会做透视变换,reshape成矩形
|
||||
dst_img = cv2.warpPerspective(
|
||||
img,
|
||||
M, (img_crop_width, img_crop_height),
|
||||
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE,
|
||||
flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
|
||||
dst_img_height, dst_img_width = dst_img.shape[0:2]
|
||||
if dst_img_height * 1.0 / dst_img_width >= 1.5:
|
||||
dst_img = np.rot90(dst_img)
|
||||
return dst_img
|
||||
|
||||
def crop_and_get_filelist(file_list):
|
||||
with open(file_list, "r", encoding='utf-8') as fin:
|
||||
lines = fin.readlines()
|
||||
|
||||
img_num = 0
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
img_name, json_file = line.strip().split('\t')
|
||||
preds = json.loads(json_file)
|
||||
for item in preds:
|
||||
transcription = item['transcription']
|
||||
points = item['points']
|
||||
points = np.array(points).astype('float32')
|
||||
#print('processing {}...'.format(img_name))
|
||||
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(PATH+img_name)
|
||||
dst_img = get_rotate_crop_image(img, points)
|
||||
h, w, c = dst_img.shape
|
||||
newWidth = int((32. / h) * w)
|
||||
newImg = cv2.resize(dst_img, (newWidth, 32))
|
||||
new_img_name = '{:05d}.jpg'.format(img_num)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(SAVE_PATH+new_img_name, dst_img)
|
||||
f_label.write(SAVE_PATH+new_img_name+'\t'+transcription+'\n')
|
||||
img_num += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
crop_and_get_filelist(file_list)
|
||||
f_label.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.3 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
通过数据挖掘,我们得到了真实场景数据和对应的标签。接下来使用真实数据finetune,观察精度提升效果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
利用真实数据进行finetune:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.epoch_num=20 \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step='[0, 20]' \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=['./data/mining_train.list'] \
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card=64 \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"] \
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card=64
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
各参数含义参考第6部分合成数据finetune,只需要对训练数据路径做相应的修改:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir: 训练数据集路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list: 训练集文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
示例使用我们提供的真实数据进行finetune,如想换成自己的数据,只需要相应的修改`Train.dataset.data_dir`和`Train.dataset.label_file_list`参数即可。
|
||||
|
||||
由于数据量不大,这里仅训练20个epoch即可。训练完成后,可以得到合成数据finetune后的精度为best acc=**71.33%**。
|
||||
|
||||
由于数量比较少,精度会比合成数据finetue的略低。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 7. 基于合成+真实数据finetune
|
||||
|
||||
为进一步提升模型精度,我们结合使用合成数据和挖掘到的真实数据进行finetune。
|
||||
|
||||
利用合成+真实数据进行finetune,各参数含义参考第6部分合成数据finetune,只需要对训练数据路径做相应的修改:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir: 训练数据集路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list: 训练集文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成训练list文件:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 生成训练集文件list
|
||||
cat /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/render_train.list /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/mining_train.list > /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/render_mining_train.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动训练:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.epoch_num=40 \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step='[0, 20]' \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=['./data/render_mining_train.list'] \
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card=64 \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"] \
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card=64
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
示例使用我们提供的真实+合成数据进行finetune,如想换成自己的数据,只需要相应的修改Train.dataset.data_dir和Train.dataset.label_file_list参数即可。
|
||||
|
||||
由于数据量不大,这里仅训练40个epoch即可。训练完成后,可以得到合成数据finetune后的精度为best acc=**86.99%**。
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,相较于原始PP-OCRv3的识别精度62.99%,使用合成数据+真实数据finetune后,识别精度能提升24%。
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,可以同样扫描上方二维码下载,将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理。
|
||||
|
||||
模型的推理部署方法可以参考repo文档: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/deploy/README_ch.md
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,33 @@
|
|||
# 1 项目说明
|
||||
# 多模态表单识别
|
||||
- [多模态表单识别](#多模态表单识别)
|
||||
- [1 项目说明](#1-项目说明)
|
||||
- [2 安装说明](#2-安装说明)
|
||||
- [3 数据准备](#3-数据准备)
|
||||
- [3.1 下载处理好的数据集](#31-下载处理好的数据集)
|
||||
- [3.2 转换为PaddleOCR检测和识别格式](#32-转换为paddleocr检测和识别格式)
|
||||
- [4 OCR](#4-ocr)
|
||||
- [4.1 文本检测](#41-文本检测)
|
||||
- [4.1.1 方案1:预训练模型](#411-方案1预训练模型)
|
||||
- [4.1.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+fine-tune](#412-方案2xfund数据集fine-tune)
|
||||
- [4.2 文本识别](#42-文本识别)
|
||||
- [4.2.1 方案1:预训练模型](#421-方案1预训练模型)
|
||||
- [4.2.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+finetune](#422-方案2xfund数据集finetune)
|
||||
- [4.2.3 方案3:XFUND数据集+finetune+真实通用识别数据](#423-方案3xfund数据集finetune真实通用识别数据)
|
||||
- [5 文档视觉问答(DOC-VQA)](#5-文档视觉问答doc-vqa)
|
||||
- [5.1 SER](#51-ser)
|
||||
- [5.1.1 模型训练](#511-模型训练)
|
||||
- [5.1.2 模型评估](#512-模型评估)
|
||||
- [5.1.3 模型预测](#513-模型预测)
|
||||
- [5.2 RE](#52-re)
|
||||
- [5.2.1 模型训练](#521-模型训练)
|
||||
- [5.2.2 模型评估](#522-模型评估)
|
||||
- [5.2.3 模型预测](#523-模型预测)
|
||||
- [6 导出Excel](#6-导出excel)
|
||||
- [获得模型](#获得模型)
|
||||
- [更多资源](#更多资源)
|
||||
- [参考链接](#参考链接)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1 项目说明
|
||||
|
||||
计算机视觉在金融领域的应用覆盖文字识别、图像识别、视频识别等,其中文字识别(OCR)是金融领域中的核心AI能力,其应用覆盖客户服务、风险防控、运营管理等各项业务,针对的对象包括通用卡证票据识别(银行卡、身份证、营业执照等)、通用文本表格识别(印刷体、多语言、手写体等)以及一些金融特色票据凭证。通过因此如果能够在结构化信息提取时同时利用文字、页面布局等信息,便可增强不同版式下的泛化性。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,39 +45,37 @@
|
|||
<center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/9bd844b970f94e5ba0bc0c5799bd819ea9b1861bb306471fabc2d628864d418e'></center>
|
||||
<center>图1 多模态表单识别流程图</center>
|
||||
|
||||
注:欢迎再AIStudio领取免费算力体验线上实训,项目链接: [多模态表单识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3884375)(配备Tesla V100、A100等高级算力资源)
|
||||
注:欢迎再AIStudio领取免费算力体验线上实训,项目链接: [多模态表单识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3884375?contributionType=1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 2 安装说明
|
||||
## 2 安装说明
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下载PaddleOCR源码,上述AIStudio项目中已经帮大家打包好的PaddleOCR(已经修改好配置文件),无需下载解压即可,只需安装依赖环境~
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! unzip -q PaddleOCR.zip
|
||||
unzip -q PaddleOCR.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如仍需安装or安装更新,可以执行以下步骤
|
||||
# ! git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git -b dygraph
|
||||
# ! git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
# git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git -b dygraph
|
||||
# git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 安装依赖包
|
||||
! pip install -U pip
|
||||
! pip install -r /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
! pip install paddleocr
|
||||
pip install -U pip
|
||||
pip install -r /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
pip install paddleocr
|
||||
|
||||
! pip install yacs gnureadline paddlenlp==2.2.1
|
||||
! pip install xlsxwriter
|
||||
pip install yacs gnureadline paddlenlp==2.2.1
|
||||
pip install xlsxwriter
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 3 数据准备
|
||||
## 3 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
这里使用[XFUN数据集](https://github.com/doc-analysis/XFUND)做为实验数据集。 XFUN数据集是微软提出的一个用于KIE任务的多语言数据集,共包含七个数据集,每个数据集包含149张训练集和50张验证集
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,7 +86,7 @@
|
|||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/0f84137778cd4ab6899c64109d452290e9c678ccf01744978bc9c0647adbba45" width="1000" ></center>
|
||||
<center>图2 数据集样例,左中文,右法语</center>
|
||||
|
||||
## 3.1 下载处理好的数据集
|
||||
### 3.1 下载处理好的数据集
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
处理好的XFUND中文数据集下载地址:[https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/XFUND.tar](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/XFUND.tar) ,可以运行如下指令完成中文数据集下载和解压。
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,13 +96,13 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/XFUND.tar
|
||||
! tar -xf XFUND.tar
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/XFUND.tar
|
||||
tar -xf XFUND.tar
|
||||
|
||||
# XFUN其他数据集使用下面的代码进行转换
|
||||
# 代码链接:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release%2F2.4/ppstructure/vqa/helper/trans_xfun_data.py
|
||||
# %cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
# !python3 ppstructure/vqa/tools/trans_xfun_data.py --ori_gt_path=path/to/json_path --output_path=path/to/save_path
|
||||
# python3 ppstructure/vqa/tools/trans_xfun_data.py --ori_gt_path=path/to/json_path --output_path=path/to/save_path
|
||||
# %cd ../
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -119,7 +146,7 @@
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 3.2 转换为PaddleOCR检测和识别格式
|
||||
### 3.2 转换为PaddleOCR检测和识别格式
|
||||
|
||||
使用XFUND训练PaddleOCR检测和识别模型,需要将数据集格式改为训练需求的格式。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -147,7 +174,7 @@ train_data/rec/train/word_002.jpg 用科技让复杂的世界更简单
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! unzip -q /home/aistudio/data/data140302/XFUND_ori.zip -d /home/aistudio/data/data140302/
|
||||
unzip -q /home/aistudio/data/data140302/XFUND_ori.zip -d /home/aistudio/data/data140302/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
已经提供转换脚本,执行如下代码即可转换成功:
|
||||
|
|
@ -155,21 +182,20 @@ train_data/rec/train/word_002.jpg 用科技让复杂的世界更简单
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/
|
||||
! python trans_xfund_data.py
|
||||
python trans_xfund_data.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 4 OCR
|
||||
## 4 OCR
|
||||
|
||||
选用飞桨OCR开发套件[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/README_ch.md)中的PP-OCRv2模型进行文本检测和识别。PP-OCRv2在PP-OCR的基础上,进一步在5个方面重点优化,检测模型采用CML协同互学习知识蒸馏策略和CopyPaste数据增广策略;识别模型采用LCNet轻量级骨干网络、UDML 改进知识蒸馏策略和[Enhanced CTC loss](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/doc/doc_ch/enhanced_ctc_loss.md)损失函数改进,进一步在推理速度和预测效果上取得明显提升。更多细节请参考PP-OCRv2[技术报告](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03144)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 4.1 文本检测
|
||||
### 4.1 文本检测
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用2种方案进行训练、评估:
|
||||
- **PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型**
|
||||
- **XFUND数据集+fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
### **4.1.1 方案1:预训练模型**
|
||||
#### 4.1.1 方案1:预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -195,8 +221,8 @@ PaddleOCR已经提供了PP-OCR系列模型,部分模型展示如下表所示
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain/
|
||||
! wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
! tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
% cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -226,7 +252,7 @@ Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
! python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -237,9 +263,9 @@ Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
|||
| -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 | 77.26% |
|
||||
|
||||
使用文本检测预训练模型在XFUND验证集上评估,达到77%左右,充分说明ppocr提供的预训练模型有一定的泛化能力。
|
||||
使用文本检测预训练模型在XFUND验证集上评估,达到77%左右,充分说明ppocr提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力。
|
||||
|
||||
### **4.1.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+fine-tune**
|
||||
#### 4.1.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+fine-tune
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR提供的蒸馏预训练模型包含了多个模型的参数,我们提取Student模型的参数,在XFUND数据集上进行finetune,可以参考如下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -281,7 +307,7 @@ Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest:评估尺寸,添加如下参数
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -290,12 +316,18 @@ Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest:评估尺寸,添加如下参数
|
|||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/5a75137c5f924dfeb6956b5818812298cc3dc7992ac84954b4175be9adf83c77"></center>
|
||||
<center>图8 文本检测方案2-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`,这里为大家提供训练好的模型`./pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune/best_accuracy`,[模型下载地址](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/sheet_recognition/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune.zip)
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`。如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
! python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -305,7 +337,7 @@ Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest:评估尺寸,添加如下参数
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
! python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -331,7 +363,7 @@ Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest:评估尺寸,添加如下参数
|
|||
# 加载配置文件`ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml`,从`pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune`目录下加载`best_accuracy`模型
|
||||
# inference模型保存在`./output/det_db_inference`目录下
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
! python tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model="pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune/best_accuracy" \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir="./output/det_db_inference/"
|
||||
|
|
@ -374,12 +406,11 @@ use_gpu:是否使用GPU
|
|||
|
||||
| 方案 | hmeans | 结果分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 | 77.26% | ppocr提供的预训练模型有一定的泛化能力 |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 | 77.26% | ppocr提供的预训练模型有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集 | 79.27% | |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+finetune | 85.24% | finetune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 4.2 文本识别
|
||||
### 4.2 文本识别
|
||||
|
||||
我们分别使用如下3种方案进行训练、评估:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -387,8 +418,7 @@ use_gpu:是否使用GPU
|
|||
- XFUND数据集+fine-tune
|
||||
- XFUND数据集+fine-tune+真实通用识别数据
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### **4.2.1 方案1:预训练模型**
|
||||
#### 4.2.1 方案1:预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -401,8 +431,8 @@ use_gpu:是否使用GPU
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain/
|
||||
! wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar
|
||||
! tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar
|
||||
% cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -424,7 +454,7 @@ Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./pretrain/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -435,9 +465,9 @@ Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
|||
| -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 | 67.48% |
|
||||
|
||||
使用文本预训练模型在XFUND验证集上评估,acc达到67%左右,充分说明ppocr提供的预训练模型有一定的泛化能力。
|
||||
使用文本预训练模型在XFUND验证集上评估,acc达到67%左右,充分说明ppocr提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力。
|
||||
|
||||
### **4.2.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+finetune**
|
||||
#### 4.2.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+finetune
|
||||
|
||||
同检测模型,我们提取Student模型的参数,在XFUND数据集上进行finetune,可以参考如下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -474,11 +504,9 @@ Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
|||
```
|
||||
执行如下命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -493,7 +521,7 @@ Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./pretrain/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-finetune/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -506,7 +534,7 @@ Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
|||
|
||||
使用XFUND数据集+finetune训练,在验证集上评估达到72%左右,说明 finetune会提升垂类场景效果。
|
||||
|
||||
### **4.2.3 方案3:XFUND数据集+finetune+真实通用识别数据**
|
||||
#### 4.2.3 方案3:XFUND数据集+finetune+真实通用识别数据
|
||||
|
||||
接着我们在上述`XFUND数据集+finetune`实验的基础上,添加真实通用识别数据,进一步提升识别效果。首先准备真实通用识别数据,并上传到AIStudio:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -528,7 +556,7 @@ Train.dataset.ratio_list:动态采样
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -538,11 +566,11 @@ Train.dataset.ratio_list:动态采样
|
|||
|
||||
<center>图16 文本识别方案3-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`,这里为大家提供训练好的模型`./pretrain/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-readldata/best_accuracy`,[模型下载地址](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/sheet_recognition/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-realdata.zip)
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./pretrain/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-realdata/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -580,7 +608,7 @@ Train.dataset.ratio_list:动态采样
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! python tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="./doc/vqa/input/zh_val_21.jpg" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./output/det_db_inference/" \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./output/rec_crnn_inference/" \
|
||||
|
|
@ -592,11 +620,11 @@ Train.dataset.ratio_list:动态采样
|
|||
|
||||
| 方案 | acc | 结果分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 | 67.48% | ppocr提供的预训练模型有一定的泛化能力 |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 | 67.48% | ppocr提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+fine-tune |72.33% | finetune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+fine-tune+真实通用识别数据 | 85.29% | 真实通用识别数据对于性能提升很有帮助 |
|
||||
|
||||
# 5 文档视觉问答(DOC-VQA)
|
||||
## 5 文档视觉问答(DOC-VQA)
|
||||
|
||||
VQA指视觉问答,主要针对图像内容进行提问和回答,DOC-VQA是VQA任务中的一种,DOC-VQA主要针对文本图像的文字内容提出问题。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -608,14 +636,13 @@ PaddleOCR中DOC-VQA系列算法基于PaddleNLP自然语言处理算法库实现L
|
|||
```python
|
||||
%cd pretrain
|
||||
#下载SER模型
|
||||
! wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pplayout/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar && tar -xvf ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pplayout/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar && tar -xvf ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar
|
||||
#下载RE模型
|
||||
! wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pplayout/re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar && tar -xvf re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pplayout/re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar && tar -xvf re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar
|
||||
%cd ../
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 5.1 SER
|
||||
### 5.1 SER
|
||||
|
||||
SER: 语义实体识别 (Semantic Entity Recognition), 可以完成对图像中的文本识别与分类。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -647,7 +674,7 @@ SER: 语义实体识别 (Semantic Entity Recognition), 可以完成对图像
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py -c configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py -c configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会打印出`precision`, `recall`, `hmean`等指标。 在`./output/ser_layoutxlm/`文件夹中会保存训练日志,最优的模型和最新epoch的模型。
|
||||
|
|
@ -664,7 +691,7 @@ SER: 语义实体识别 (Semantic Entity Recognition), 可以完成对图像
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -684,7 +711,7 @@ SER: 语义实体识别 (Semantic Entity Recognition), 可以完成对图像
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/infer_vqa_token_ser.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/infer_vqa_token_ser.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/ \
|
||||
Global.infer_img=doc/vqa/input/zh_val_42.jpg
|
||||
|
|
@ -704,7 +731,7 @@ plt.figure(figsize=(48,24))
|
|||
plt.imshow(img)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5.2 RE
|
||||
### 5.2 RE
|
||||
|
||||
基于 RE 任务,可以完成对图象中的文本内容的关系提取,如判断问题对(pair)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -729,7 +756,7 @@ plt.imshow(img)
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/train.py -c configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/train.py -c configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会打印出`precision`, `recall`, `hmean`等指标。 在`./output/re_layoutxlm/`文件夹中会保存训练日志,最优的模型和最新epoch的模型
|
||||
|
|
@ -744,7 +771,7 @@ plt.imshow(img)
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -760,20 +787,14 @@ plt.imshow(img)
|
|||
|
||||
<center>图26 RE-模型预测</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用OCR引擎 + SER + RE串联预测
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令即可完成OCR引擎 + SER + RE的串联预测, 以预训练SER和RE模型为例:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令即可完成OCR引擎 + SER + RE的串联预测, 以预训练SER和RE模型为例,
|
||||
|
||||
最终会在config.Global.save_res_path字段所配置的目录下保存预测结果可视化图像以及预测结果文本文件,预测结果文本文件名为infer_results.txt。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
! CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/infer_vqa_token_ser_re.py \
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/infer_vqa_token_ser_re.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/ \
|
||||
Global.infer_img=test_imgs/ \
|
||||
|
|
@ -787,10 +808,9 @@ plt.imshow(img)
|
|||
test_imgs/t131.jpg {"政治面税": "群众", "性别": "男", "籍贯": "河北省邯郸市", "婚姻状况": "亏末婚口已婚口已娇", "通讯地址": "邯郸市阳光苑7号楼003", "民族": "汉族", "毕业院校": "河南工业大学", "户口性质": "口农村城镇", "户口地址": "河北省邯郸市", "联系电话": "13288888888", "健康状况": "健康", "姓名": "小六", "好高cm": "180", "出生年月": "1996年8月9日", "文化程度": "本科", "身份证号码": "458933777777777777"}
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
展示预测结果
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 展示预测结果
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
%matplotlib inline
|
||||
|
|
@ -800,7 +820,7 @@ plt.figure(figsize=(48,24))
|
|||
plt.imshow(img)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 6 导出Excel
|
||||
## 6 导出Excel
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/ab93d3d90d77437a81c9534b2dd1d3e39ef81e8473054fd3aeff6e837ebfb827"></center>
|
||||
<center>图27 导出Excel</center>
|
||||
|
|
@ -859,7 +879,7 @@ with open('output/re/infer_results.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fin:
|
|||
workbook.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 更多资源
|
||||
## 更多资源
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多深度学习知识、产业案例、面试宝典等,请参考:[awesome-DeepLearning](https://github.com/paddlepaddle/awesome-DeepLearning)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -869,7 +889,7 @@ workbook.close()
|
|||
|
||||
- 飞桨框架相关资料,请参考:[飞桨深度学习平台](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/?fr=paddleEdu_aistudio)
|
||||
|
||||
# 参考链接
|
||||
## 参考链接
|
||||
|
||||
- LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.08836.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,616 @@
|
|||
# 基于PP-OCRv3的液晶屏读数识别
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目背景及意义](#1-项目背景及意义)
|
||||
- [2. 项目内容](#2-项目内容)
|
||||
- [3. 安装环境](#3-安装环境)
|
||||
- [4. 文字检测](#4-文字检测)
|
||||
- [4.1 PP-OCRv3检测算法介绍](#41-PP-OCRv3检测算法介绍)
|
||||
- [4.2 数据准备](#42-数据准备)
|
||||
- [4.3 模型训练](#43-模型训练)
|
||||
- [4.3.1 预训练模型直接评估](#431-预训练模型直接评估)
|
||||
- [4.3.2 预训练模型直接finetune](#432-预训练模型直接finetune)
|
||||
- [4.3.3 基于预训练模型Finetune_student模型](#433-基于预训练模型Finetune_student模型)
|
||||
- [4.3.4 基于预训练模型Finetune_teacher模型](#434-基于预训练模型Finetune_teacher模型)
|
||||
- [4.3.5 采用CML蒸馏进一步提升student模型精度](#435-采用CML蒸馏进一步提升student模型精度)
|
||||
- [4.3.6 模型导出推理](#436-4.3.6-模型导出推理)
|
||||
- [5. 文字识别](#5-文字识别)
|
||||
- [5.1 PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍](#51-PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍)
|
||||
- [5.2 数据准备](#52-数据准备)
|
||||
- [5.3 模型训练](#53-模型训练)
|
||||
- [5.4 模型导出推理](#54-模型导出推理)
|
||||
- [6. 系统串联](#6-系统串联)
|
||||
- [6.1 后处理](#61-后处理)
|
||||
- [7. PaddleServing部署](#7-PaddleServing部署)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目背景及意义
|
||||
目前光学字符识别(OCR)技术在我们的生活当中被广泛使用,但是大多数模型在通用场景下的准确性还有待提高,针对于此我们借助飞桨提供的PaddleOCR套件较容易的实现了在垂类场景下的应用。
|
||||
|
||||
该项目以国家质量基础(NQI)为准绳,充分利用大数据、云计算、物联网等高新技术,构建覆盖计量端、实验室端、数据端和硬件端的完整计量解决方案,解决传统计量校准中存在的难题,拓宽计量检测服务体系和服务领域;解决无数传接口或数传接口不统一、不公开的计量设备,以及计量设备所处的环境比较恶劣,不适合人工读取数据。通过OCR技术实现远程计量,引领计量行业向智慧计量转型和发展。
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 项目内容
|
||||
本项目基于PaddleOCR开源套件,以PP-OCRv3检测和识别模型为基础,针对液晶屏读数识别场景进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
Aistudio项目链接:[OCR液晶屏读数识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4080130)
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 安装环境
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 首先git官方的PaddleOCR项目,安装需要的依赖
|
||||
# 第一次运行打开该注释
|
||||
# git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 文字检测
|
||||
文本检测的任务是定位出输入图像中的文字区域。近年来学术界关于文本检测的研究非常丰富,一类方法将文本检测视为目标检测中的一个特定场景,基于通用目标检测算法进行改进适配,如TextBoxes[1]基于一阶段目标检测器SSD[2]算法,调整目标框使之适合极端长宽比的文本行,CTPN[3]则是基于Faster RCNN[4]架构改进而来。但是文本检测与目标检测在目标信息以及任务本身上仍存在一些区别,如文本一般长宽比较大,往往呈“条状”,文本行之间可能比较密集,弯曲文本等,因此又衍生了很多专用于文本检测的算法。本项目基于PP-OCRv3算法进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1 PP-OCRv3检测算法介绍
|
||||
PP-OCRv3检测模型是对PP-OCRv2中的CML(Collaborative Mutual Learning) 协同互学习文本检测蒸馏策略进行了升级。如下图所示,CML的核心思想结合了①传统的Teacher指导Student的标准蒸馏与 ②Students网络之间的DML互学习,可以让Students网络互学习的同时,Teacher网络予以指导。PP-OCRv3分别针对教师模型和学生模型进行进一步效果优化。其中,在对教师模型优化时,提出了大感受野的PAN结构LK-PAN和引入了DML(Deep Mutual Learning)蒸馏策略;在对学生模型优化时,提出了残差注意力机制的FPN结构RSE-FPN。
|
||||
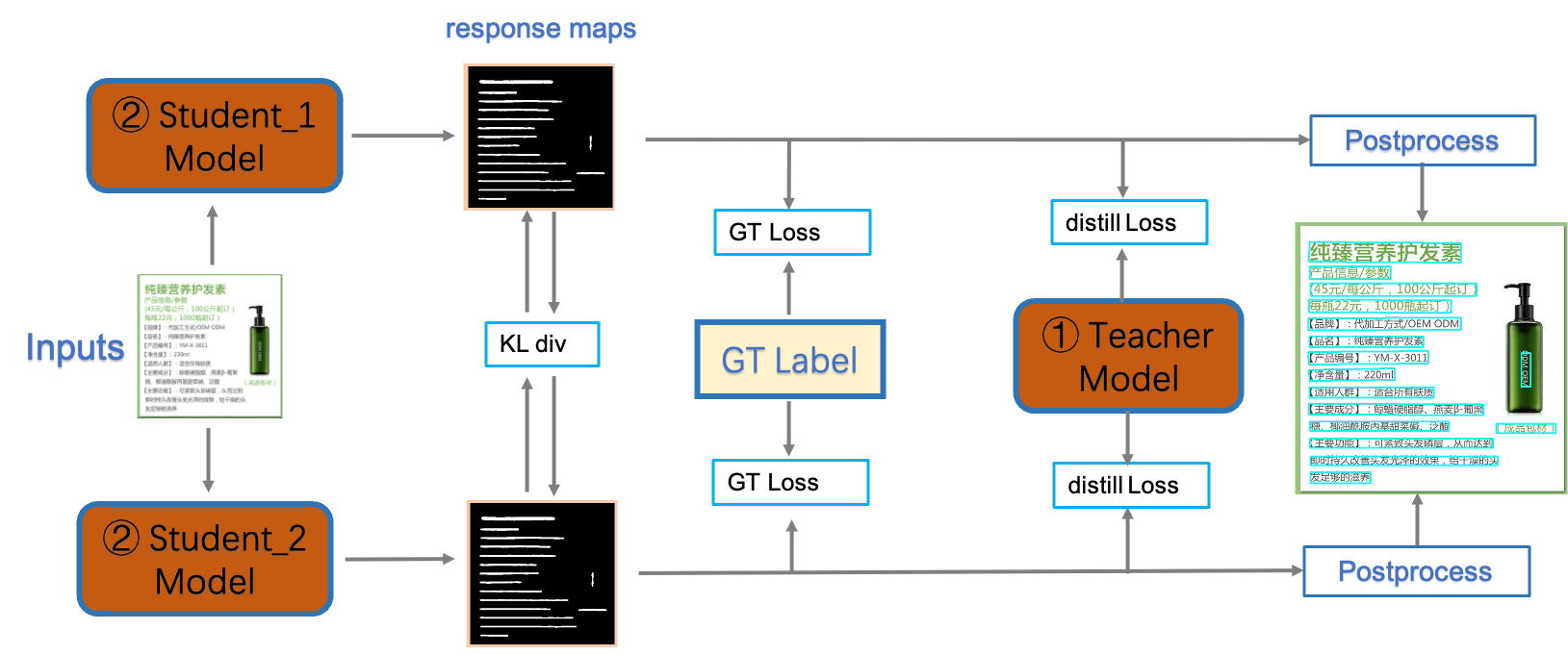
|
||||
|
||||
详细优化策略描述请参考[PP-OCRv3优化策略](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md#2)
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2 数据准备
|
||||
[计量设备屏幕字符检测数据集](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/127845)数据来源于实际项目中各种计量设备的数显屏,以及在网上搜集的一些其他数显屏,包含训练集755张,测试集355张。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 在PaddleOCR下创建新的文件夹train_data
|
||||
mkdir train_data
|
||||
# 下载数据集并解压到指定路径下
|
||||
unzip icdar2015.zip -d train_data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 随机查看文字检测数据集图片
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
train = './train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test'
|
||||
# 从指定目录中选取一张图片
|
||||
def get_one_image(train):
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
files = os.listdir(train)
|
||||
n = len(files)
|
||||
ind = np.random.randint(0,n)
|
||||
img_dir = os.path.join(train,files[ind])
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_dir)
|
||||
plt.imshow(image)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
image = image.resize([208, 208])
|
||||
|
||||
get_one_image(train)
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4.3 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.1 预训练模型直接评估
|
||||
下载我们需要的PP-OCRv3检测预训练模型,更多选择请自行选择其他的[文字检测模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/models_list.md#1-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E6%A3%80%E6%B5%8B%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#使用该指令下载需要的预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrained_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压预训练模型文件
|
||||
tar -xf ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar -C pretrained_models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在训练之前,我们可以直接使用下面命令来评估预训练模型的效果:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估预训练模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.5%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.2 预训练模型直接finetune
|
||||
##### 修改配置文件
|
||||
我们使用configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch:100
|
||||
save_epoch_step:10
|
||||
eval_batch_step:[0, 50]
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det/
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00025
|
||||
num_workers: 0 # 如果单卡训练,建议将Train和Eval的loader部分的num_workers设置为0,否则会出现`/dev/shm insufficient`的报错
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 开始训练
|
||||
使用我们上面修改的配置文件configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml,训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 开始训练模型
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.5%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.2%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.3 基于预训练模型Finetune_student模型
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch:100
|
||||
save_epoch_step:10
|
||||
eval_batch_step:[0, 50]
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_student/
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00025
|
||||
num_workers: 0 # 如果单卡训练,建议将Train和Eval的loader部分的num_workers设置为0,否则会出现`/dev/shm insufficient`的报错
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_student/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.5%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.2%|
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune学生模型 |80.0%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.4 基于预训练模型Finetune_teacher模型
|
||||
|
||||
首先需要从提供的预训练模型best_accuracy.pdparams中提取teacher参数,组合成适合dml训练的初始化模型,提取代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd ./pretrained_models/
|
||||
# transform teacher params in best_accuracy.pdparams into teacher_dml.paramers
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
# load pretrained model
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
# keep teacher params
|
||||
t_params = {key[len("Teacher."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Teacher." in key}
|
||||
|
||||
# print(t_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
s_params = {"Student." + key: t_params[key] for key in t_params}
|
||||
s2_params = {"Student2." + key: t_params[key] for key in t_params}
|
||||
s_params = {**s_params, **s2_params}
|
||||
# print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_dml.pdparams")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch:100
|
||||
save_epoch_step:10
|
||||
eval_batch_step:[0, 50]
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_teacher/
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_dml
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00025
|
||||
num_workers: 0 # 如果单卡训练,建议将Train和Eval的loader部分的num_workers设置为0,否则会出现`/dev/shm insufficient`的报错
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_dml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_teacher/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.5%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.2%|
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune学生模型 |80.0%|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune教师模型 |84.8%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.5 采用CML蒸馏进一步提升student模型精度
|
||||
|
||||
需要从4.3.3和4.3.4训练得到的best_accuracy.pdparams中提取各自代表student和teacher的参数,组合成适合cml训练的初始化模型,提取代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# transform teacher params and student parameters into cml model
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
t_params = paddle.load("./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_teacher/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(t_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
s_params = paddle.load("./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_student/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
for key in all_params:
|
||||
# teacher is OK
|
||||
if "Teacher." in key:
|
||||
new_key = key.replace("Teacher", "Student")
|
||||
#print("{} >> {}\n".format(key, new_key))
|
||||
assert all_params[key].shape == t_params[new_key].shape
|
||||
all_params[key] = t_params[new_key]
|
||||
|
||||
if "Student." in key:
|
||||
new_key = key.replace("Student.", "")
|
||||
#print("{} >> {}\n".format(key, new_key))
|
||||
assert all_params[key].shape == s_params[new_key].shape
|
||||
all_params[key] = s_params[new_key]
|
||||
|
||||
if "Student2." in key:
|
||||
new_key = key.replace("Student2.", "")
|
||||
print("{} >> {}\n".format(key, new_key))
|
||||
assert all_params[key].shape == s_params[new_key].shape
|
||||
all_params[key] = s_params[new_key]
|
||||
|
||||
paddle.save(all_params, "./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_cml_student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_cml_student Global.save_model_dir=./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_finetune/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_finetune/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.5%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.2%|
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune学生模型 |80.0%|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune教师模型 |84.8%|
|
||||
| 4 | 基于2和3训练好的模型fintune |82.7%|
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.6 模型导出推理
|
||||
训练完成后,可以将训练模型转换成inference模型。inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
##### 4.3.6.1 模型导出
|
||||
导出命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 转化为推理模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_finetune/best_accuracy \
|
||||
-o Global.save_inference_dir="./inference/det_ppocrv3"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 4.3.6.2 模型推理
|
||||
导出模型后,可以使用如下命令进行推理预测:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 推理预测
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_det.py --image_dir="train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test/1.jpg" --det_model_dir="./inference/det_ppocrv3/Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5. 文字识别
|
||||
文本识别的任务是识别出图像中的文字内容,一般输入来自于文本检测得到的文本框截取出的图像文字区域。文本识别一般可以根据待识别文本形状分为规则文本识别和不规则文本识别两大类。规则文本主要指印刷字体、扫描文本等,文本大致处在水平线位置;不规则文本往往不在水平位置,存在弯曲、遮挡、模糊等问题。不规则文本场景具有很大的挑战性,也是目前文本识别领域的主要研究方向。本项目基于PP-OCRv3算法进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.1 PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的识别模块是基于文本识别算法[SVTR](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.00159)优化。SVTR不再采用RNN结构,通过引入Transformers结构更加有效地挖掘文本行图像的上下文信息,从而提升文本识别能力。如下图所示,PP-OCRv3采用了6个优化策略。
|
||||
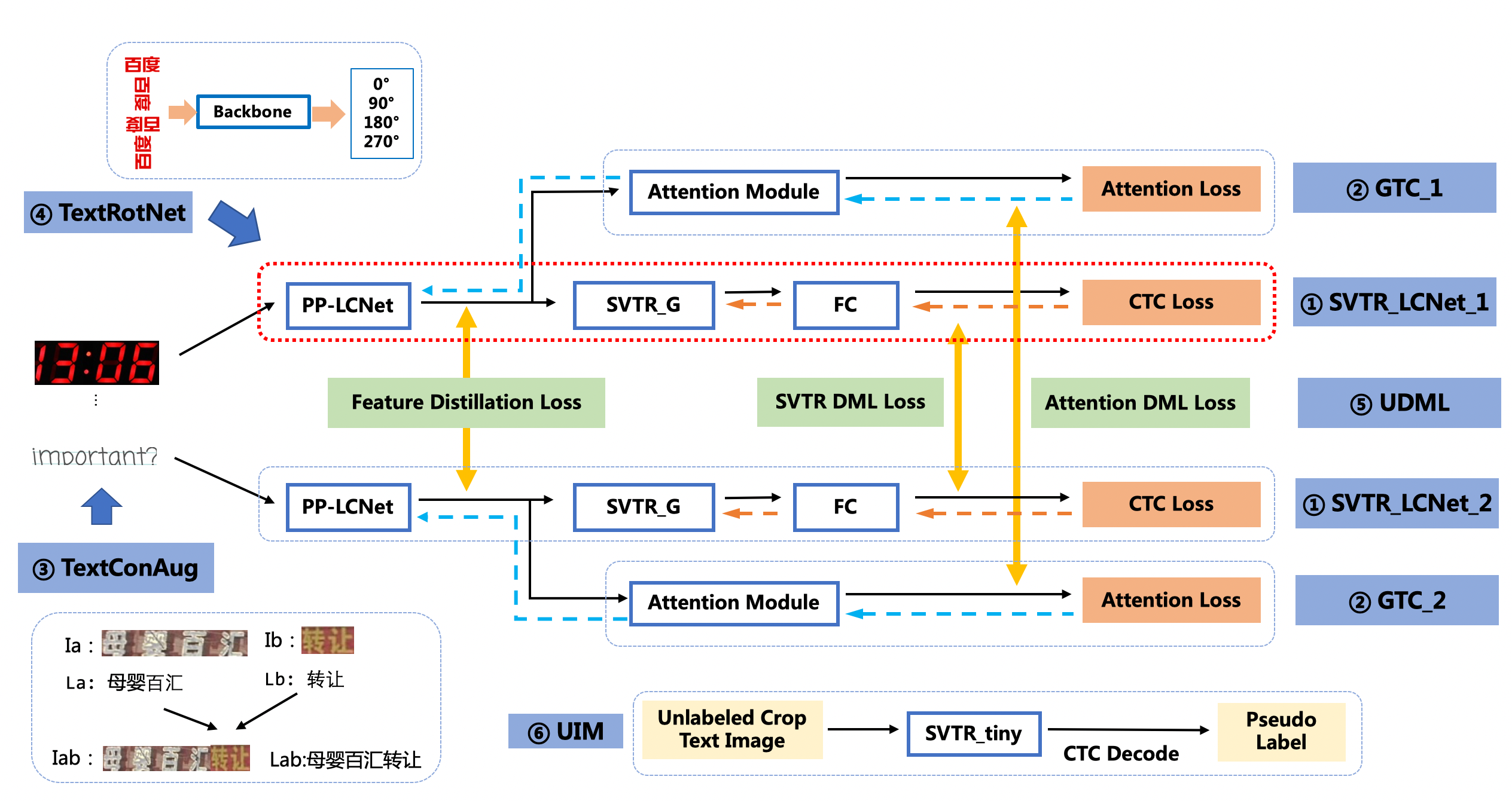
|
||||
|
||||
优化策略汇总如下:
|
||||
* SVTR_LCNet:轻量级文本识别网络
|
||||
* GTC:Attention指导CTC训练策略
|
||||
* TextConAug:挖掘文字上下文信息的数据增广策略
|
||||
* TextRotNet:自监督的预训练模型
|
||||
* UDML:联合互学习策略
|
||||
* UIM:无标注数据挖掘方案
|
||||
|
||||
详细优化策略描述请参考[PP-OCRv3优化策略](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md#3-%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E4%BC%98%E5%8C%96)
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.2 数据准备
|
||||
[计量设备屏幕字符识别数据集](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/128714)数据来源于实际项目中各种计量设备的数显屏,以及在网上搜集的一些其他数显屏,包含训练集19912张,测试集4099张。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 解压下载的数据集到指定路径下
|
||||
unzip ic15_data.zip -d train_data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 随机查看文字检测数据集图片
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
train = './train_data/ic15_data/train'
|
||||
# 从指定目录中选取一张图片
|
||||
def get_one_image(train):
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
files = os.listdir(train)
|
||||
n = len(files)
|
||||
ind = np.random.randint(0,n)
|
||||
img_dir = os.path.join(train,files[ind])
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_dir)
|
||||
plt.imshow(image)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
image = image.resize([208, 208])
|
||||
|
||||
get_one_image(train)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.3 模型训练
|
||||
#### 下载预训练模型
|
||||
下载我们需要的PP-OCRv3识别预训练模型,更多选择请自行选择其他的[文字识别模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/models_list.md#2-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 使用该指令下载需要的预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrained_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压预训练模型文件
|
||||
tar -xf ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar -C pretrained_models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 修改配置文件
|
||||
我们使用configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch_num: 100 # 训练epoch数
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 10
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [0, 100] # 评估间隔,每隔100step评估一次
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: true
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy # 预训练模型路径
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt
|
||||
use_space_char: true # 使用空格
|
||||
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Cosine # 修改学习率衰减策略为Cosine
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.0002 # 修改fine-tune的学习率
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2 # 修改warmup轮数
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/ic15_data/ # 训练集图片路径
|
||||
ext_op_transform_idx: 1
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/ic15_data/rec_gt_train.txt # 训练集标签
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 64
|
||||
drop_last: true
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/ic15_data/ # 测试集图片路径
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/ic15_data/rec_gt_test.txt # 测试集标签
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: false
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 64
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在训练之前,我们可以直接使用下面命令来评估预训练模型的效果:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估预训练模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |accuracy|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测 |70.4%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 开始训练
|
||||
我们使用上面修改好的配置文件configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml,预训练模型,数据集路径,学习率,训练轮数等都已经设置完毕后,可以使用下面命令开始训练。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 开始训练识别模型
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练完成后,可以对训练模型中最好的进行测试,评估命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估finetune效果
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.checkpoints="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |accuracy|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测 |70.4%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型finetune |82.2%|
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.4 模型导出推理
|
||||
训练完成后,可以将训练模型转换成inference模型。inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
#### 模型导出
|
||||
导出命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 转化为推理模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec/best_accuracy" Global.save_inference_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 模型推理
|
||||
导出模型后,可以使用如下命令进行推理预测
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 推理预测
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="train_data/ic15_data/test/1_crop_0.jpg" --rec_model_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 6. 系统串联
|
||||
我们将上面训练好的检测和识别模型进行系统串联测试,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#串联测试
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py --image_dir="./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test/142.jpg" --det_model_dir="./inference/det_ppocrv3/Student" --rec_model_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试结果保存在`./inference_results/`目录下,可以用下面代码进行可视化
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
# 显示结果
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
img_path= "./inference_results/142.jpg"
|
||||
img = Image.open(img_path)
|
||||
plt.figure("test_img", figsize=(30,30))
|
||||
plt.imshow(img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
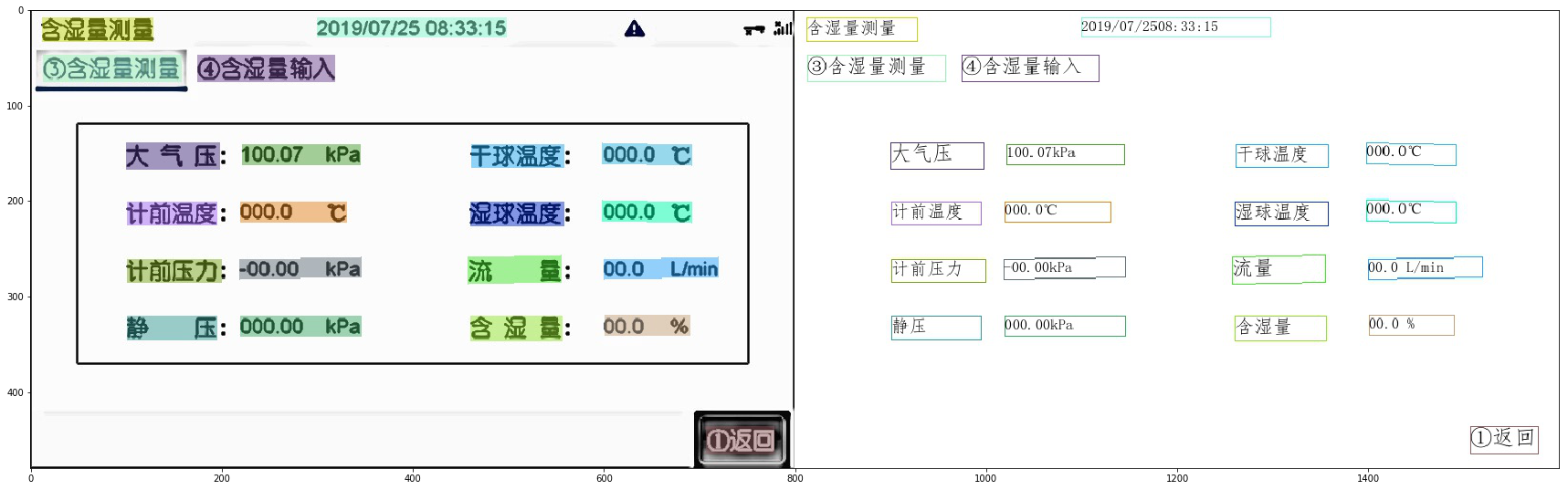
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.1 后处理
|
||||
如果需要获取key-value信息,可以基于启发式的规则,将识别结果与关键字库进行匹配;如果匹配上了,则取该字段为key, 后面一个字段为value。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def postprocess(rec_res):
|
||||
keys = ["型号", "厂家", "版本号", "检定校准分类", "计量器具编号", "烟尘流量",
|
||||
"累积体积", "烟气温度", "动压", "静压", "时间", "试验台编号", "预测流速",
|
||||
"全压", "烟温", "流速", "工况流量", "标杆流量", "烟尘直读嘴", "烟尘采样嘴",
|
||||
"大气压", "计前温度", "计前压力", "干球温度", "湿球温度", "流量", "含湿量"]
|
||||
key_value = []
|
||||
if len(rec_res) > 1:
|
||||
for i in range(len(rec_res) - 1):
|
||||
rec_str, _ = rec_res[i]
|
||||
for key in keys:
|
||||
if rec_str in key:
|
||||
key_value.append([rec_str, rec_res[i + 1][0]])
|
||||
break
|
||||
return key_value
|
||||
key_value = postprocess(filter_rec_res)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 7. PaddleServing部署
|
||||
首先需要安装PaddleServing部署相关的环境
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python -m pip install paddle-serving-server-gpu
|
||||
python -m pip install paddle_serving_client
|
||||
python -m pip install paddle-serving-app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.1 转化检测模型
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd deploy/pdserving/
|
||||
python -m paddle_serving_client.convert --dirname ../../inference/det_ppocrv3/Student/ \
|
||||
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
|
||||
--params_filename inference.pdiparams \
|
||||
--serving_server ./ppocr_det_v3_serving/ \
|
||||
--serving_client ./ppocr_det_v3_client/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.2 转化识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python -m paddle_serving_client.convert --dirname ../../inference/rec_ppocrv3/Student \
|
||||
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
|
||||
--params_filename inference.pdiparams \
|
||||
--serving_server ./ppocr_rec_v3_serving/ \
|
||||
--serving_client ./ppocr_rec_v3_client/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.3 启动服务
|
||||
首先可以将后处理代码加入到web_service.py中,具体修改如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 代码153行后面增加下面代码
|
||||
def _postprocess(rec_res):
|
||||
keys = ["型号", "厂家", "版本号", "检定校准分类", "计量器具编号", "烟尘流量",
|
||||
"累积体积", "烟气温度", "动压", "静压", "时间", "试验台编号", "预测流速",
|
||||
"全压", "烟温", "流速", "工况流量", "标杆流量", "烟尘直读嘴", "烟尘采样嘴",
|
||||
"大气压", "计前温度", "计前压力", "干球温度", "湿球温度", "流量", "含湿量"]
|
||||
key_value = []
|
||||
if len(rec_res) > 1:
|
||||
for i in range(len(rec_res) - 1):
|
||||
rec_str, _ = rec_res[i]
|
||||
for key in keys:
|
||||
if rec_str in key:
|
||||
key_value.append([rec_str, rec_res[i + 1][0]])
|
||||
break
|
||||
return key_value
|
||||
key_value = _postprocess(rec_list)
|
||||
res = {"result": str(key_value)}
|
||||
# res = {"result": str(result_list)}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动服务端
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python web_service.py 2>&1 >log.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.4 发送请求
|
||||
然后再开启一个新的终端,运行下面的客户端代码
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python pipeline_http_client.py --image_dir ../../train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test/142.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以获取到最终的key-value结果:
|
||||
```
|
||||
大气压, 100.07kPa
|
||||
干球温度, 0000℃
|
||||
计前温度, 0000℃
|
||||
湿球温度, 0000℃
|
||||
计前压力, -0000kPa
|
||||
流量, 00.0L/min
|
||||
静压, 00000kPa
|
||||
含湿量, 00.0 %
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -249,7 +249,7 @@ tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
|||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预训练模型下载完成后,我们使用[ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml](../configs/chepai/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml) 配置文件进行后续实验,在开始评估之前需要对配置文件中部分字段进行设置,具体如下:
|
||||
预训练模型下载完成后,我们使用[ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml](../configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml) 配置文件进行后续实验,在开始评估之前需要对配置文件中部分字段进行设置,具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 模型存储和训练相关:
|
||||
1. Global.pretrained_model: 指向PP-OCRv3文本检测预训练模型地址
|
||||
|
|
@ -311,7 +311,6 @@ python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o
|
|||
|
||||
在上述命令中,通过`-o`的方式修改了配置文件中的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
训练好的模型地址为: [det_ppocr_v3_finetune.tar](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/license_plate_recognition/det_ppocr_v3_finetune.tar)
|
||||
|
||||
**评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -354,8 +353,6 @@ python3.7 deploy/slim/quantization/quant.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCR
|
|||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练好的模型地址为: [det_ppocr_v3_quant.tar](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/license_plate_recognition/det_ppocr_v3_quant.tar)
|
||||
|
||||
量化后指标对比如下
|
||||
|
||||
|方案|hmeans| 模型大小 | 预测速度(lite) |
|
||||
|
|
@ -436,6 +433,12 @@ python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
|||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
评估部分日志如下:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:02] ppocr INFO: load pretrain successful from models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
|
|
@ -528,7 +531,6 @@ python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
|||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
训练好的模型地址为: [rec_ppocr_v3_finetune.tar](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/license_plate_recognition/rec_ppocr_v3_finetune.tar)
|
||||
|
||||
**评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -570,7 +572,6 @@ python3.7 deploy/slim/quantization/quant.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_
|
|||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
训练好的模型地址为: [rec_ppocr_v3_quant.tar](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/license_plate_recognition/rec_ppocr_v3_quant.tar)
|
||||
|
||||
量化后指标对比如下
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -787,12 +788,12 @@ python tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
|||
|
||||
- 端侧部署
|
||||
|
||||
端侧部署我们采用基于 PaddleLite 的 cpp 推理。Paddle Lite是飞桨轻量化推理引擎,为手机、IOT端提供高效推理能力,并广泛整合跨平台硬件,为端侧部署及应用落地问题提供轻量化的部署方案。具体可参考 [PaddleOCR lite教程](../dygraph/deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)
|
||||
端侧部署我们采用基于 PaddleLite 的 cpp 推理。Paddle Lite是飞桨轻量化推理引擎,为手机、IOT端提供高效推理能力,并广泛整合跨平台硬件,为端侧部署及应用落地问题提供轻量化的部署方案。具体可参考 [PaddleOCR lite教程](../deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.5 实验总结
|
||||
|
||||
我们分别使用PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量预训练模型在车牌数据集上进行了直接评估和 fine-tune 和 fine-tune +量化3种方案的实验,并基于[PaddleOCR lite教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)进行了速度测试,指标对比如下:
|
||||
我们分别使用PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量预训练模型在车牌数据集上进行了直接评估和 fine-tune 和 fine-tune +量化3种方案的实验,并基于[PaddleOCR lite教程](../deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)进行了速度测试,指标对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 检测
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
|||
# 高精度中文场景文本识别模型SVTR
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 简介
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3是百度开源的超轻量级场景文本检测识别模型库,其中超轻量的场景中文识别模型SVTR_LCNet使用了SVTR算法结构。为了保证速度,SVTR_LCNet将SVTR模型的Local Blocks替换为LCNet,使用两层Global Blocks。在中文场景中,PP-OCRv3识别主要使用如下优化策略:
|
||||
- GTC:Attention指导CTC训练策略;
|
||||
- TextConAug:挖掘文字上下文信息的数据增广策略;
|
||||
- TextRotNet:自监督的预训练模型;
|
||||
- UDML:联合互学习策略;
|
||||
- UIM:无标注数据挖掘方案。
|
||||
|
||||
其中 *UIM:无标注数据挖掘方案* 使用了高精度的SVTR中文模型进行无标注文件的刷库,该模型在PP-OCRv3识别的数据集上训练,精度对比如下表。
|
||||
|
||||
|中文识别算法|模型|UIM|精度|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |--- |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3|SVTR_LCNet| w/o |78.4%|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3|SVTR_LCNet| w |79.4%|
|
||||
|SVTR|SVTR-Tiny|-|82.5%|
|
||||
|
||||
aistudio项目链接: [高精度中文场景文本识别模型SVTR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4263032)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. SVTR中文模型使用
|
||||
|
||||
### 环境准备
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本任务基于Aistudio完成, 具体环境如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统: Linux
|
||||
- PaddlePaddle: 2.3
|
||||
- PaddleOCR: dygraph
|
||||
|
||||
下载 PaddleOCR代码
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone -b dygraph https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装依赖库
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r PaddleOCR/requirements.txt -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 快速使用
|
||||
|
||||
获取SVTR中文模型文件,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 解压模型文件
|
||||
tar xf svtr_ch_high_accuracy.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预测中文文本,以下图为例:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
预测命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# CPU预测
|
||||
python tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_svtrnet_ch.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./svtr_ch_high_accuracy/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg Global.use_gpu=False
|
||||
|
||||
# GPU预测
|
||||
#python tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_svtrnet_ch.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./svtr_ch_high_accuracy/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg Global.use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到最后打印结果为
|
||||
- result: 韩国小馆 0.9853458404541016
|
||||
|
||||
0.9853458404541016为预测置信度。
|
||||
|
||||
### 推理模型导出与预测
|
||||
|
||||
inference 模型(paddle.jit.save保存的模型) 一般是模型训练,把模型结构和模型参数保存在文件中的固化模型,多用于预测部署场景。 训练过程中保存的模型是checkpoints模型,保存的只有模型的参数,多用于恢复训练等。 与checkpoints模型相比,inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
|
||||
运行识别模型转inference模型命令,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/rec_svtrnet_ch.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./svtr_ch_high_accuracy/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/svtr_ch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
转换成功后,在目录下有三个文件:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
inference/svtr_ch/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams # 识别inference模型的参数文件
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info # 识别inference模型的参数信息,可忽略
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel # 识别inference模型的program文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
inference模型预测,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# CPU预测
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg" --rec_algorithm='SVTR' --rec_model_dir=./inference/svtr_ch/ --rec_image_shape='3, 32, 320' --rec_char_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt --use_gpu=False
|
||||
|
||||
# GPU预测
|
||||
#python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg" --rec_algorithm='SVTR' --rec_model_dir=./inference/svtr_ch/ --rec_image_shape='3, 32, 320' --rec_char_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt --use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用SVTR算法时,需要指定--rec_algorithm='SVTR'
|
||||
- 如果使用自定义字典训练的模型,需要将--rec_char_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt修改为自定义的字典
|
||||
- --rec_image_shape='3, 32, 320' 该参数不能去掉
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 18
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: DBFPN
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 18
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: DBFPN
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ Loss:
|
|||
- ["Student", "Teacher"]
|
||||
maps_name: "thrink_maps"
|
||||
weight: 1.0
|
||||
act: "softmax"
|
||||
# act: None
|
||||
model_name_pairs: ["Student", "Teacher"]
|
||||
key: maps
|
||||
- DistillationDBLoss:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
model_type: det
|
||||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
in_channels: 3
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
model_type: det
|
||||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
in_channels: 3
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
|
|
@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
model_type: det
|
||||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
in_channels: 3
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
|
|
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ Loss:
|
|||
- ["Student", "Student2"]
|
||||
maps_name: "thrink_maps"
|
||||
weight: 1.0
|
||||
act: "softmax"
|
||||
# act: None
|
||||
model_name_pairs: ["Student", "Student2"]
|
||||
key: maps
|
||||
- DistillationDBLoss:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 18
|
||||
disable_se: True
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
debug: false
|
||||
use_gpu: true
|
||||
epoch_num: 1000
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 20
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/det_r50_icdar15/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 200
|
||||
eval_batch_step:
|
||||
- 0
|
||||
- 2000
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: false
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrain_models/ResNet50_dcn_asf_synthtext_pretrained
|
||||
checkpoints: null
|
||||
save_inference_dir: null
|
||||
use_visualdl: false
|
||||
infer_img: doc/imgs_en/img_10.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./checkpoints/det_db/predicts_db.txt
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: det
|
||||
algorithm: DB++
|
||||
Transform: null
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
dcn_stage: [False, True, True, True]
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: DBFPN
|
||||
out_channels: 256
|
||||
use_asf: True
|
||||
Head:
|
||||
name: DBHead
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: DBLoss
|
||||
balance_loss: true
|
||||
main_loss_type: BCELoss
|
||||
alpha: 5
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: Momentum
|
||||
momentum: 0.9
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: DecayLearningRate
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.007
|
||||
epochs: 1000
|
||||
factor: 0.9
|
||||
end_lr: 0
|
||||
weight_decay: 0.0001
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: DBPostProcess
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.6
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: DetMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/train_icdar2015_label.txt
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: false
|
||||
- DetLabelEncode: null
|
||||
- IaaAugment:
|
||||
augmenter_args:
|
||||
- type: Fliplr
|
||||
args:
|
||||
p: 0.5
|
||||
- type: Affine
|
||||
args:
|
||||
rotate:
|
||||
- -10
|
||||
- 10
|
||||
- type: Resize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
size:
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 3
|
||||
- EastRandomCropData:
|
||||
size:
|
||||
- 640
|
||||
- 640
|
||||
max_tries: 10
|
||||
keep_ratio: true
|
||||
- MakeShrinkMap:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
min_text_size: 8
|
||||
- MakeBorderMap:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
thresh_min: 0.3
|
||||
thresh_max: 0.7
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean:
|
||||
- 0.48109378172549
|
||||
- 0.45752457890196
|
||||
- 0.40787054090196
|
||||
std:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
order: hwc
|
||||
- ToCHWImage: null
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys:
|
||||
- image
|
||||
- threshold_map
|
||||
- threshold_mask
|
||||
- shrink_map
|
||||
- shrink_mask
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 4
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test_icdar2015_label.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: false
|
||||
- DetLabelEncode: null
|
||||
- DetResizeForTest:
|
||||
image_shape:
|
||||
- 1152
|
||||
- 2048
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean:
|
||||
- 0.48109378172549
|
||||
- 0.45752457890196
|
||||
- 0.40787054090196
|
||||
std:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
order: hwc
|
||||
- ToCHWImage: null
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys:
|
||||
- image
|
||||
- shape
|
||||
- polys
|
||||
- ignore_tags
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: false
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 1
|
||||
num_workers: 2
|
||||
profiler_options: null
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
debug: false
|
||||
use_gpu: true
|
||||
epoch_num: 1000
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 20
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/det_r50_td_tr/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 200
|
||||
eval_batch_step:
|
||||
- 0
|
||||
- 2000
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: false
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrain_models/ResNet50_dcn_asf_synthtext_pretrained
|
||||
checkpoints: null
|
||||
save_inference_dir: null
|
||||
use_visualdl: false
|
||||
infer_img: doc/imgs_en/img_10.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./checkpoints/det_db/predicts_db.txt
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: det
|
||||
algorithm: DB++
|
||||
Transform: null
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
dcn_stage: [False, True, True, True]
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: DBFPN
|
||||
out_channels: 256
|
||||
use_asf: True
|
||||
Head:
|
||||
name: DBHead
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: DBLoss
|
||||
balance_loss: true
|
||||
main_loss_type: BCELoss
|
||||
alpha: 5
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: Momentum
|
||||
momentum: 0.9
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: DecayLearningRate
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.007
|
||||
epochs: 1000
|
||||
factor: 0.9
|
||||
end_lr: 0
|
||||
weight_decay: 0.0001
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: DBPostProcess
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.5
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: DetMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/TD_TR/TD500/train_gt_labels.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/TD_TR/TR400/gt_labels.txt
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: false
|
||||
- DetLabelEncode: null
|
||||
- IaaAugment:
|
||||
augmenter_args:
|
||||
- type: Fliplr
|
||||
args:
|
||||
p: 0.5
|
||||
- type: Affine
|
||||
args:
|
||||
rotate:
|
||||
- -10
|
||||
- 10
|
||||
- type: Resize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
size:
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 3
|
||||
- EastRandomCropData:
|
||||
size:
|
||||
- 640
|
||||
- 640
|
||||
max_tries: 10
|
||||
keep_ratio: true
|
||||
- MakeShrinkMap:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
min_text_size: 8
|
||||
- MakeBorderMap:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
thresh_min: 0.3
|
||||
thresh_max: 0.7
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean:
|
||||
- 0.48109378172549
|
||||
- 0.45752457890196
|
||||
- 0.40787054090196
|
||||
std:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
order: hwc
|
||||
- ToCHWImage: null
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys:
|
||||
- image
|
||||
- threshold_map
|
||||
- threshold_mask
|
||||
- shrink_map
|
||||
- shrink_mask
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 4
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/TD_TR/TD500/test_gt_labels.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: false
|
||||
- DetLabelEncode: null
|
||||
- DetResizeForTest:
|
||||
image_shape:
|
||||
- 736
|
||||
- 736
|
||||
keep_ratio: True
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean:
|
||||
- 0.48109378172549
|
||||
- 0.45752457890196
|
||||
- 0.40787054090196
|
||||
std:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
order: hwc
|
||||
- ToCHWImage: null
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys:
|
||||
- image
|
||||
- shape
|
||||
- polys
|
||||
- ignore_tags
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: false
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 1
|
||||
num_workers: 2
|
||||
profiler_options: null
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: DBFPN
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: FCE
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
dcn_stage: [False, True, True, True]
|
||||
out_indices: [1,2,3]
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: EAST
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: EASTFPN
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: PSE
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 50
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: FPN
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
algorithm: DB
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet
|
||||
name: ResNet_vd
|
||||
layers: 18
|
||||
disable_se: True
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Global:
|
|||
checkpoints:
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
class_path: ./train_data/wildreceipt/class_list.txt
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/wildreceipt/class_list.txt
|
||||
infer_img: ./train_data/wildreceipt/1.txt
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/sdmgr_kie/predicts_kie.txt
|
||||
img_scale: [ 1024, 512 ]
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,6 +72,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- KieLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
character_dict_path: ./train_data/wildreceipt/dict.txt
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- KieResize:
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,7 +89,6 @@ Eval:
|
|||
data_dir: ./train_data/wildreceipt
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/wildreceipt/wildreceipt_test.txt
|
||||
# - /paddle/data/PaddleOCR/train_data/wildreceipt/1.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ Global:
|
|||
eval_batch_step: [0, 2000]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: True
|
||||
pretrained_model:
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
infer_img: doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: NRTRLoss
|
||||
name: CELoss
|
||||
smoothing: True
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,8 +68,8 @@ Train:
|
|||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- NRTRLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
- NRTRRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [100, 32]
|
||||
- GrayRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [100, 32] # W H
|
||||
resize_type: PIL # PIL or OpenCV
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,14 +82,14 @@ Train:
|
|||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: LMDBDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/evaluation/
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/validation/
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- NRTRLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
- NRTRRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [100, 32]
|
||||
- GrayRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [100, 32] # W H
|
||||
resize_type: PIL # PIL or OpenCV
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
|
|
@ -97,5 +97,5 @@ Eval:
|
|||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
num_workers: 1
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
use_shared_memory: False
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: 10
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 20
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/rec/r45_abinet/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 1
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 2000 iterations
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [0, 2000]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: True
|
||||
pretrained_model:
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
infer_img: doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png
|
||||
# for data or label process
|
||||
character_dict_path:
|
||||
character_type: en
|
||||
max_text_length: 25
|
||||
infer_mode: False
|
||||
use_space_char: False
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/rec/predicts_abinet.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: Adam
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.99
|
||||
clip_norm: 20.0
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Piecewise
|
||||
decay_epochs: [6]
|
||||
values: [0.0001, 0.00001]
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: 'L2'
|
||||
factor: 0.
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: rec
|
||||
algorithm: ABINet
|
||||
in_channels: 3
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ResNet45
|
||||
Head:
|
||||
name: ABINetHead
|
||||
use_lang: True
|
||||
iter_size: 3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: CELoss
|
||||
ignore_index: &ignore_index 100 # Must be greater than the number of character classes
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: ABINetLabelDecode
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: RecMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: acc
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: LMDBDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/training/
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- ABINetRecAug:
|
||||
- ABINetLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
ignore_index: *ignore_index
|
||||
- ABINetRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 32, 128]
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 96
|
||||
drop_last: True
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: LMDBDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/validation/
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- ABINetLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
ignore_index: *ignore_index
|
||||
- ABINetRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 32, 128]
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
use_shared_memory: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Optimizer:
|
|||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.99
|
||||
epsilon: 0.00000008
|
||||
epsilon: 8.e-8
|
||||
weight_decay: 0.05
|
||||
no_weight_decay_name: norm pos_embed
|
||||
one_dim_param_no_weight_decay: true
|
||||
|
|
@ -77,14 +77,13 @@ Metric:
|
|||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: LMDBDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/training/
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/training
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- CTCLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
- RecResizeImg:
|
||||
character_dict_path:
|
||||
- SVTRRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 64, 256]
|
||||
padding: False
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,14 +97,13 @@ Train:
|
|||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: LMDBDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/validation/
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/validation
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- CTCLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
- RecResizeImg:
|
||||
character_dict_path:
|
||||
- SVTRRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 64, 256]
|
||||
padding: False
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: true
|
||||
epoch_num: 100
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 20
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/rec/svtr_ch_all/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 10
|
||||
eval_batch_step:
|
||||
- 0
|
||||
- 2000
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: true
|
||||
pretrained_model: null
|
||||
checkpoints: null
|
||||
save_inference_dir: null
|
||||
use_visualdl: false
|
||||
infer_img: doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt
|
||||
max_text_length: 25
|
||||
infer_mode: false
|
||||
use_space_char: true
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/rec/predicts_svtr_tiny_ch_all.txt
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.99
|
||||
epsilon: 8.0e-08
|
||||
weight_decay: 0.05
|
||||
no_weight_decay_name: norm pos_embed
|
||||
one_dim_param_no_weight_decay: true
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Cosine
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.0005
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: rec
|
||||
algorithm: SVTR
|
||||
Transform: null
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: SVTRNet
|
||||
img_size:
|
||||
- 32
|
||||
- 320
|
||||
out_char_num: 40
|
||||
out_channels: 96
|
||||
patch_merging: Conv
|
||||
embed_dim:
|
||||
- 64
|
||||
- 128
|
||||
- 256
|
||||
depth:
|
||||
- 3
|
||||
- 6
|
||||
- 3
|
||||
num_heads:
|
||||
- 2
|
||||
- 4
|
||||
- 8
|
||||
mixer:
|
||||
- Local
|
||||
- Local
|
||||
- Local
|
||||
- Local
|
||||
- Local
|
||||
- Local
|
||||
- Global
|
||||
- Global
|
||||
- Global
|
||||
- Global
|
||||
- Global
|
||||
- Global
|
||||
local_mixer:
|
||||
- - 7
|
||||
- 11
|
||||
- - 7
|
||||
- 11
|
||||
- - 7
|
||||
- 11
|
||||
last_stage: true
|
||||
prenorm: false
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: SequenceEncoder
|
||||
encoder_type: reshape
|
||||
Head:
|
||||
name: CTCHead
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: CTCLoss
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: CTCLabelDecode
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: RecMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: acc
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/train_list.txt
|
||||
ext_op_transform_idx: 1
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: false
|
||||
- RecConAug:
|
||||
prob: 0.5
|
||||
ext_data_num: 2
|
||||
image_shape:
|
||||
- 32
|
||||
- 320
|
||||
- 3
|
||||
- RecAug: null
|
||||
- CTCLabelEncode: null
|
||||
- SVTRRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape:
|
||||
- 3
|
||||
- 32
|
||||
- 320
|
||||
padding: true
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys:
|
||||
- image
|
||||
- label
|
||||
- length
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
drop_last: true
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/val_list.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: false
|
||||
- CTCLabelEncode: null
|
||||
- SVTRRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape:
|
||||
- 3
|
||||
- 32
|
||||
- 320
|
||||
padding: true
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys:
|
||||
- image
|
||||
- label
|
||||
- length
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: false
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
num_workers: 2
|
||||
profiler_options: null
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: 20
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 20
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/rec/vitstr_none_ce/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 1
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 2000 iterations after the 0th iteration#
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [0, 2000]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: True
|
||||
pretrained_model:
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
infer_img: doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png
|
||||
# for data or label process
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/EN_symbol_dict.txt
|
||||
max_text_length: 25
|
||||
infer_mode: False
|
||||
use_space_char: False
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/rec/predicts_vitstr.txt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: Adadelta
|
||||
epsilon: 1.e-8
|
||||
rho: 0.95
|
||||
clip_norm: 5.0
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
learning_rate: 1.0
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: rec
|
||||
algorithm: ViTSTR
|
||||
in_channels: 1
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: ViTSTR
|
||||
scale: tiny
|
||||
Neck:
|
||||
name: SequenceEncoder
|
||||
encoder_type: reshape
|
||||
Head:
|
||||
name: CTCHead
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: CELoss
|
||||
with_all: True
|
||||
ignore_index: &ignore_index 0 # Must be zero or greater than the number of character classes
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: ViTSTRLabelDecode
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: RecMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: acc
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: LMDBDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/training/
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- ViTSTRLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
ignore_index: *ignore_index
|
||||
- GrayRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [224, 224] # W H
|
||||
resize_type: PIL # PIL or OpenCV
|
||||
inter_type: 'Image.BICUBIC'
|
||||
scale: false
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 48
|
||||
drop_last: True
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: LMDBDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/data_lmdb_release/validation/
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- ViTSTRLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
ignore_index: *ignore_index
|
||||
- GrayRecResizeImg:
|
||||
image_shape: [224, 224] # W H
|
||||
resize_type: PIL # PIL or OpenCV
|
||||
inter_type: 'Image.BICUBIC'
|
||||
scale: false
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
num_workers: 2
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: true
|
||||
epoch_num: 17
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 20
|
||||
print_batch_step: 100
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/table_master/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 17
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [0, 6259]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: true
|
||||
pretrained_model: null
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
save_inference_dir: output/table_master/infer
|
||||
use_visualdl: false
|
||||
infer_img: ppstructure/docs/table/table.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/table_master
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/dict/table_master_structure_dict.txt
|
||||
infer_mode: false
|
||||
max_text_length: 500
|
||||
process_total_num: 0
|
||||
process_cut_num: 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: Adam
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: MultiStepDecay
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.001
|
||||
milestones: [12, 15]
|
||||
gamma: 0.1
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 0.02
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: table
|
||||
algorithm: TableMaster
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: TableResNetExtra
|
||||
gcb_config:
|
||||
ratio: 0.0625
|
||||
headers: 1
|
||||
att_scale: False
|
||||
fusion_type: channel_add
|
||||
layers: [False, True, True, True]
|
||||
layers: [1,2,5,3]
|
||||
Head:
|
||||
name: TableMasterHead
|
||||
hidden_size: 512
|
||||
headers: 8
|
||||
dropout: 0
|
||||
d_ff: 2024
|
||||
max_text_length: 500
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: TableMasterLoss
|
||||
ignore_index: 42 # set to len of dict + 3
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: TableMasterLabelDecode
|
||||
box_shape: pad
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: TableMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: acc
|
||||
compute_bbox_metric: False
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: PubTabDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/table/pubtabnet/train/
|
||||
label_file_list: [train_data/table/pubtabnet/PubTabNet_2.0.0_train.jsonl]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- TableMasterLabelEncode:
|
||||
learn_empty_box: False
|
||||
merge_no_span_structure: True
|
||||
replace_empty_cell_token: True
|
||||
- ResizeTableImage:
|
||||
max_len: 480
|
||||
resize_bboxes: True
|
||||
- PaddingTableImage:
|
||||
size: [480, 480]
|
||||
- TableBoxEncode:
|
||||
use_xywh: True
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
|
||||
std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
|
||||
order: hwc
|
||||
- ToCHWImage: null
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [image, structure, bboxes, bbox_masks, shape]
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 10
|
||||
drop_last: True
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: PubTabDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/table/pubtabnet/train/
|
||||
label_file_list: [train_data/table/pubtabnet/PubTabNet_2.0.0_val.jsonl]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage:
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- TableMasterLabelEncode:
|
||||
learn_empty_box: False
|
||||
merge_no_span_structure: True
|
||||
replace_empty_cell_token: True
|
||||
- ResizeTableImage:
|
||||
max_len: 480
|
||||
resize_bboxes: True
|
||||
- PaddingTableImage:
|
||||
size: [480, 480]
|
||||
- TableBoxEncode:
|
||||
use_xywh: True
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
|
||||
std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
|
||||
order: hwc
|
||||
- ToCHWImage: null
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [image, structure, bboxes, bbox_masks, shape]
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 10
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
|
|
@ -4,21 +4,20 @@ Global:
|
|||
log_smooth_window: 20
|
||||
print_batch_step: 5
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/table_mv3/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 3
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 400
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 400 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [0, 400]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: True
|
||||
pretrained_model:
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
infer_img: doc/table/table.jpg
|
||||
infer_img: ppstructure/docs/table/table.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: output/table_mv3
|
||||
# for data or label process
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt
|
||||
character_type: en
|
||||
max_text_length: 100
|
||||
max_elem_length: 800
|
||||
max_cell_num: 500
|
||||
max_text_length: 800
|
||||
infer_mode: False
|
||||
process_total_num: 0
|
||||
process_cut_num: 0
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,11 +43,8 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
Head:
|
||||
name: TableAttentionHead
|
||||
hidden_size: 256
|
||||
l2_decay: 0.00001
|
||||
loc_type: 2
|
||||
max_text_length: 100
|
||||
max_elem_length: 800
|
||||
max_cell_num: 500
|
||||
max_text_length: 800
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: TableAttentionLoss
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,28 +57,34 @@ PostProcess:
|
|||
Metric:
|
||||
name: TableMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: acc
|
||||
compute_bbox_metric: false # cost many time, set False for training
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: PubTabDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/table/pubtabnet/train/
|
||||
label_file_path: train_data/table/pubtabnet/PubTabNet_2.0.0_train.jsonl
|
||||
label_file_list: [train_data/table/pubtabnet/PubTabNet_2.0.0_train.jsonl]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- TableLabelEncode:
|
||||
learn_empty_box: False
|
||||
merge_no_span_structure: False
|
||||
replace_empty_cell_token: False
|
||||
- TableBoxEncode:
|
||||
- ResizeTableImage:
|
||||
max_len: 488
|
||||
- TableLabelEncode:
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- PaddingTableImage:
|
||||
size: [488, 488]
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'structure', 'bbox_list', 'sp_tokens', 'bbox_list_mask']
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'image', 'structure', 'bboxes', 'bbox_masks', 'shape' ]
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 32
|
||||
|
|
@ -92,24 +94,29 @@ Train:
|
|||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: PubTabDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/table/pubtabnet/val/
|
||||
label_file_path: train_data/table/pubtabnet/PubTabNet_2.0.0_val.jsonl
|
||||
data_dir: /home/zhoujun20/table/PubTabNe/pubtabnet/val/
|
||||
label_file_list: [/home/zhoujun20/table/PubTabNe/pubtabnet/val_500.jsonl]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: BGR
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- TableLabelEncode:
|
||||
learn_empty_box: False
|
||||
merge_no_span_structure: False
|
||||
replace_empty_cell_token: False
|
||||
- TableBoxEncode:
|
||||
- ResizeTableImage:
|
||||
max_len: 488
|
||||
- TableLabelEncode:
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- PaddingTableImage:
|
||||
size: [488, 488]
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: ['image', 'structure', 'bbox_list', 'sp_tokens', 'bbox_list_mask']
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'image', 'structure', 'bboxes', 'bbox_masks', 'shape' ]
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/re_layoutlmv2_funsd
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 57 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/83624198.png
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/re_layoutlmv2_funsd/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutLMv2"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutLMv2ForRe
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: LossFromOutput
|
||||
key: loss
|
||||
reduction: mean
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
clip_norm: 10
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 10
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQAReTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQAReTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/training_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/train.json
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: True
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/FUNSD/class_list.txt
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQAReTokenRelation:
|
||||
- VQAReTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'entities', 'relations']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
collate_fn: ListCollator
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/test.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: True
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQAReTokenRelation:
|
||||
- VQAReTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1./255.
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'entities', 'relations']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
collate_fn: ListCollator
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,16 +3,16 @@ Global:
|
|||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/re_layoutlmv2/
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/re_layoutlmv2_xfund_zh
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 19 ]
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 57 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2048
|
||||
infer_img: doc/vqa/input/zh_val_21.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/re/
|
||||
infer_img: ppstructure/docs/vqa/input/zh_val_21.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/re_layoutlmv2_xfund_zh/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ Architecture:
|
|||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutLMv2ForRe
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: LossFromOutput
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_train/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/xfun_normalize_train.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/train.json
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: True
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ppstructure/vqa/labels/labels_ser.txt
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/XFUND/class_list_xfun.txt
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
|
|
@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids','entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids','image', 'entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_val/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/xfun_normalize_val.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/val.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids','entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image','entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/re_layoutxlm_funsd
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 57 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/83624198.png
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/re_layoutxlm_funsd/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutXLM"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutXLMForRe
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: LossFromOutput
|
||||
key: loss
|
||||
reduction: mean
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
clip_norm: 10
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 10
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQAReTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQAReTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/training_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/train_v4.json
|
||||
# - ./train_data/FUNSD/train.json
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: True
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/FUNSD/class_list.txt
|
||||
use_textline_bbox_info: &use_textline_bbox_info True
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQAReTokenRelation:
|
||||
- VQAReTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'entities', 'relations']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 16
|
||||
collate_fn: ListCollator
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/test_v4.json
|
||||
# - ./train_data/FUNSD/test.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: True
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
use_textline_bbox_info: *use_textline_bbox_info
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQAReTokenRelation:
|
||||
- VQAReTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'entities', 'relations']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 8
|
||||
collate_fn: ListCollator
|
||||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ Global:
|
|||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: doc/vqa/input/zh_val_21.jpg
|
||||
infer_img: ppstructure/docs/vqa/input/zh_val_21.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/re/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_train/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/xfun_normalize_train.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/train.json
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: True
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ppstructure/vqa/labels/labels_ser.txt
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/XFUND/class_list_xfun.txt
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
|
|
@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids','entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox','attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_val/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/xfun_normalize_val.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/val.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids','entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'entities', 'relations'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlm_funsd
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 57 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/83624198.png
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutlm_funsd/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutLM"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutLMForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 7
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMLoss
|
||||
num_classes: *num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Linear
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
epochs: *epoch_num
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/FUNSD/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/training_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/train.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
use_textline_bbox_info: &use_textline_bbox_info True
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/test.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
use_textline_bbox_info: *use_textline_bbox_info
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlm_sroie
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 200 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/SROIE/test/X00016469670.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutlm_sroie/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutLM"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutLMForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 9
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMLoss
|
||||
num_classes: *num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Linear
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
epochs: *epoch_num
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/SROIE/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/SROIE/train
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/SROIE/train.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
use_textline_bbox_info: &use_textline_bbox_info True
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/SROIE/test
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/SROIE/test.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
use_textline_bbox_info: *use_textline_bbox_info
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,16 +3,16 @@ Global:
|
|||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlm/
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlm_xfund_zh
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 19 ]
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 57 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: doc/vqa/input/zh_val_0.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser/
|
||||
infer_img: ppstructure/docs/vqa/input/zh_val_42.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutlm_xfund_zh/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
|
|
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ Optimizer:
|
|||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ppstructure/vqa/labels/labels_ser.txt
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/XFUND/class_list_xfun.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_train/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/xfun_normalize_train.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/train.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids','labels', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_val/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/xfun_normalize_val.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/val.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'labels', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlmv2_funsd
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 100 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/83624198.png
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutlmv2_funsd/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutLMv2"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutLMv2ForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 7
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMLoss
|
||||
num_classes: *num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Linear
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
epochs: *epoch_num
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/FUNSD/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/training_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/train.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/test.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlmv2_sroie
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 200 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/SROIE/test/X00016469670.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutlmv2_sroie/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutLMv2"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutLMv2ForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 9
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMLoss
|
||||
num_classes: *num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Linear
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
epochs: *epoch_num
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/SROIE/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/SROIE/train
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/SROIE/train.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/SROIE/test
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/SROIE/test.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ Global:
|
|||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlmv2/
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutlmv2_xfund_zh/
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 19 ]
|
||||
|
|
@ -11,8 +11,8 @@ Global:
|
|||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: doc/vqa/input/zh_val_0.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser/
|
||||
infer_img: ppstructure/docs/vqa/input/zh_val_42.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutlmv2_xfund_zh/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Optimizer:
|
|||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ppstructure/vqa/labels/labels_ser.txt
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/XFUND/class_list_xfun.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_train/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/xfun_normalize_train.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/train.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids','labels', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_val/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/xfun_normalize_val.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/val.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'labels', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutxlm_funsd
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 57 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/83624198.png
|
||||
save_res_path: output/ser_layoutxlm_funsd/res/
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutXLM"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutXLMForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 7
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMLoss
|
||||
num_classes: *num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Linear
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
epochs: *epoch_num
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/FUNSD/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/FUNSD/training_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/train.json
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/FUNSD/testing_data/images/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/FUNSD/test.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutxlm_sroie
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 200 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data/SROIE/test/X00016469670.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: res_img_aug_with_gt
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutXLM"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutXLMForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 9
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMLoss
|
||||
num_classes: *num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Linear
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
epochs: *epoch_num
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/SROIE/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/SROIE/train
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/SROIE/train.txt
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/SROIE/test
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/SROIE/test.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
use_gpu: True
|
||||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 100
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutxlm_wildreceipt
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 200 ]
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: False
|
||||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: train_data//wildreceipt/image_files/Image_12/10/845be0dd6f5b04866a2042abd28d558032ef2576.jpeg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutxlm_wildreceipt/res
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutXLM"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutXLMForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 51
|
||||
|
||||
Loss:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMLoss
|
||||
num_classes: *num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
name: AdamW
|
||||
beta1: 0.9
|
||||
beta2: 0.999
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Linear
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00005
|
||||
epochs: *epoch_num
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2
|
||||
regularizer:
|
||||
name: L2
|
||||
factor: 0.00000
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ./train_data/wildreceipt/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/wildreceipt/
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/wildreceipt/wildreceipt_train.txt
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: &max_seq_len 512
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/wildreceipt
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/wildreceipt/wildreceipt_test.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: False
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: *class_path
|
||||
- VQATokenPad:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
return_attention_mask: True
|
||||
- VQASerTokenChunk:
|
||||
max_seq_len: *max_seq_len
|
||||
- Resize:
|
||||
size: [224,224]
|
||||
- NormalizeImage:
|
||||
scale: 1
|
||||
mean: [ 123.675, 116.28, 103.53 ]
|
||||
std: [ 58.395, 57.12, 57.375 ]
|
||||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
# dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 8
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ Global:
|
|||
epoch_num: &epoch_num 200
|
||||
log_smooth_window: 10
|
||||
print_batch_step: 10
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutxlm/
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ser_layoutxlm_xfund_zh
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 2000
|
||||
# evaluation is run every 10 iterations after the 0th iteration
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [ 0, 19 ]
|
||||
|
|
@ -11,8 +11,8 @@ Global:
|
|||
save_inference_dir:
|
||||
use_visualdl: False
|
||||
seed: 2022
|
||||
infer_img: doc/vqa/input/zh_val_42.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser
|
||||
infer_img: ppstructure/docs/vqa/input/zh_val_42.jpg
|
||||
save_res_path: ./output/ser_layoutxlm_xfund_zh/res
|
||||
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: vqa
|
||||
|
|
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ Optimizer:
|
|||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenLayoutLMPostProcess
|
||||
class_path: &class_path ppstructure/vqa/labels/labels_ser.txt
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/XFUND/class_list_xfun.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: VQASerTokenMetric
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_train/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/xfun_normalize_train.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_train/train.json
|
||||
ratio_list: [ 1.0 ]
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ Train:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids','labels', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: True
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/XFUND/zh_val/image
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/xfun_normalize_val.json
|
||||
- train_data/XFUND/zh_val/val.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
|
|
@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ Eval:
|
|||
order: 'hwc'
|
||||
- ToCHWImage:
|
||||
- KeepKeys:
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'labels', 'bbox', 'image', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
keep_keys: [ 'input_ids', 'bbox', 'attention_mask', 'token_type_ids', 'image', 'labels'] # dataloader will return list in this order
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: False
|
||||
drop_last: False
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
|||
include/inputs.h
|
||||
include/outputs.h
|
||||
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
build/
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
|||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
# distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
# under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Makefile to build demo
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup build environment
|
||||
BUILD_DIR := build
|
||||
|
||||
ARM_CPU = ARMCM55
|
||||
ETHOSU_PATH = /opt/arm/ethosu
|
||||
CMSIS_PATH ?= ${ETHOSU_PATH}/cmsis
|
||||
ETHOSU_PLATFORM_PATH ?= ${ETHOSU_PATH}/core_platform
|
||||
STANDALONE_CRT_PATH := $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR))/runtime
|
||||
CORSTONE_300_PATH = ${ETHOSU_PLATFORM_PATH}/targets/corstone-300
|
||||
PKG_COMPILE_OPTS = -g -Wall -O2 -Wno-incompatible-pointer-types -Wno-format -mcpu=cortex-m55 -mthumb -mfloat-abi=hard -std=gnu99
|
||||
CMAKE ?= cmake
|
||||
CC = arm-none-eabi-gcc
|
||||
AR = arm-none-eabi-ar
|
||||
RANLIB = arm-none-eabi-ranlib
|
||||
PKG_CFLAGS = ${PKG_COMPILE_OPTS} \
|
||||
-I${STANDALONE_CRT_PATH}/include \
|
||||
-I${STANDALONE_CRT_PATH}/src/runtime/crt/include \
|
||||
-I${PWD}/include \
|
||||
-I${CORSTONE_300_PATH} \
|
||||
-I${CMSIS_PATH}/Device/ARM/${ARM_CPU}/Include/ \
|
||||
-I${CMSIS_PATH}/CMSIS/Core/Include \
|
||||
-I${CMSIS_PATH}/CMSIS/NN/Include \
|
||||
-I${CMSIS_PATH}/CMSIS/DSP/Include \
|
||||
-I$(abspath $(BUILD_DIR))/codegen/host/include
|
||||
CMSIS_NN_CMAKE_FLAGS = -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=$(abspath $(BUILD_DIR))/../arm-none-eabi-gcc.cmake \
|
||||
-DTARGET_CPU=cortex-m55 \
|
||||
-DBUILD_CMSIS_NN_FUNCTIONS=YES
|
||||
PKG_LDFLAGS = -lm -specs=nosys.specs -static -T corstone300.ld
|
||||
|
||||
$(ifeq VERBOSE,1)
|
||||
QUIET ?=
|
||||
$(else)
|
||||
QUIET ?= @
|
||||
$(endif)
|
||||
|
||||
DEMO_MAIN = src/demo_bare_metal.c
|
||||
CODEGEN_SRCS = $(wildcard $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR))/codegen/host/src/*.c)
|
||||
CODEGEN_OBJS = $(subst .c,.o,$(CODEGEN_SRCS))
|
||||
CMSIS_STARTUP_SRCS = $(wildcard ${CMSIS_PATH}/Device/ARM/${ARM_CPU}/Source/*.c)
|
||||
UART_SRCS = $(wildcard ${CORSTONE_300_PATH}/*.c)
|
||||
|
||||
demo: $(BUILD_DIR)/demo
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR)/stack_allocator.o: $(STANDALONE_CRT_PATH)/src/runtime/crt/memory/stack_allocator.c
|
||||
$(QUIET)mkdir -p $(@D)
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(CC) -c $(PKG_CFLAGS) -o $@ $^
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR)/crt_backend_api.o: $(STANDALONE_CRT_PATH)/src/runtime/crt/common/crt_backend_api.c
|
||||
$(QUIET)mkdir -p $(@D)
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(CC) -c $(PKG_CFLAGS) -o $@ $^
|
||||
|
||||
# Build generated code
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR)/libcodegen.a: $(CODEGEN_SRCS)
|
||||
$(QUIET)cd $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/codegen/host/src) && $(CC) -c $(PKG_CFLAGS) $(CODEGEN_SRCS)
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(AR) -cr $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/libcodegen.a) $(CODEGEN_OBJS)
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(RANLIB) $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/libcodegen.a)
|
||||
|
||||
# Build CMSIS startup code
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/libcmsis_startup.a: $(CMSIS_STARTUP_SRCS)
|
||||
$(QUIET)mkdir -p $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/libcmsis_startup)
|
||||
$(QUIET)cd $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/libcmsis_startup) && $(CC) -c $(PKG_CFLAGS) -D${ARM_CPU} $^
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(AR) -cr $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/libcmsis_startup.a) $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR))/libcmsis_startup/*.o
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(RANLIB) $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/libcmsis_startup.a)
|
||||
|
||||
CMSIS_SHA_FILE=${CMSIS_PATH}/977abe9849781a2e788b02282986480ff4e25ea6.sha
|
||||
ifneq ("$(wildcard $(CMSIS_SHA_FILE))","")
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/libcmsis-nn.a:
|
||||
$(QUIET)mkdir -p $(@D)
|
||||
$(QUIET)cd $(CMSIS_PATH)/CMSIS/NN && $(CMAKE) -B $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/cmsis_nn) $(CMSIS_NN_CMAKE_FLAGS)
|
||||
$(QUIET)cd $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/cmsis_nn) && $(MAKE) all
|
||||
else
|
||||
# Build CMSIS-NN
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/SoftmaxFunctions/libCMSISNNSoftmax.a:
|
||||
$(QUIET)mkdir -p $(@D)
|
||||
$(QUIET)cd $(CMSIS_PATH)/CMSIS/NN && $(CMAKE) -B $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/cmsis_nn) $(CMSIS_NN_CMAKE_FLAGS)
|
||||
$(QUIET)cd $(abspath $(BUILD_DIR)/cmsis_nn) && $(MAKE) all
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
# Build demo application
|
||||
ifneq ("$(wildcard $(CMSIS_SHA_FILE))","")
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR)/demo: $(DEMO_MAIN) $(UART_SRCS) $(BUILD_DIR)/stack_allocator.o $(BUILD_DIR)/crt_backend_api.o \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/libcodegen.a ${BUILD_DIR}/libcmsis_startup.a ${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/libcmsis-nn.a
|
||||
$(QUIET)mkdir -p $(@D)
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(CC) $(PKG_CFLAGS) $(FREERTOS_FLAGS) -o $@ -Wl,--whole-archive $^ -Wl,--no-whole-archive $(PKG_LDFLAGS)
|
||||
else
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR)/demo: $(DEMO_MAIN) $(UART_SRCS) $(BUILD_DIR)/stack_allocator.o $(BUILD_DIR)/crt_backend_api.o \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/libcodegen.a ${BUILD_DIR}/libcmsis_startup.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/SoftmaxFunctions/libCMSISNNSoftmax.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/FullyConnectedFunctions/libCMSISNNFullyConnected.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/SVDFunctions/libCMSISNNSVDF.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/ReshapeFunctions/libCMSISNNReshape.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/ActivationFunctions/libCMSISNNActivation.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/NNSupportFunctions/libCMSISNNSupport.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/ConcatenationFunctions/libCMSISNNConcatenation.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/BasicMathFunctions/libCMSISNNBasicMaths.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/ConvolutionFunctions/libCMSISNNConvolutions.a \
|
||||
${BUILD_DIR}/cmsis_nn/Source/PoolingFunctions/libCMSISNNPooling.a
|
||||
$(QUIET)mkdir -p $(@D)
|
||||
$(QUIET)$(CC) $(PKG_CFLAGS) $(FREERTOS_FLAGS) -o $@ -Wl,--whole-archive $^ -Wl,--no-whole-archive $(PKG_LDFLAGS)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
$(QUIET)rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)/codegen
|
||||
|
||||
cleanall:
|
||||
$(QUIET)rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
.SUFFIXES:
|
||||
|
||||
.DEFAULT: demo
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
|
|||
<!--- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one -->
|
||||
<!--- or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file -->
|
||||
<!--- distributed with this work for additional information -->
|
||||
<!--- regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file -->
|
||||
<!--- to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the -->
|
||||
<!--- "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance -->
|
||||
<!--- with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at -->
|
||||
|
||||
<!--- http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 -->
|
||||
|
||||
<!--- Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, -->
|
||||
<!--- software distributed under the License is distributed on an -->
|
||||
<!--- "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY -->
|
||||
<!--- KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the -->
|
||||
<!--- specific language governing permissions and limitations -->
|
||||
<!--- under the License. -->
|
||||
|
||||
English | [简体中文](README_ch.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Running PaddleOCR text recognition model on bare metal Arm(R) Cortex(R)-M55 CPU using Arm Virtual Hardware
|
||||
======================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
This folder contains an example of how to run a PaddleOCR model on bare metal [Cortex(R)-M55 CPU](https://www.arm.com/products/silicon-ip-cpu/cortex-m/cortex-m55) using [Arm Virtual Hardware](https://www.arm.com/products/development-tools/simulation/virtual-hardware).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Running environment and prerequisites
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
Case 1: If the demo is run in Arm Virtual Hardware Amazon Machine Image(AMI) instance hosted by [AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/pp/prodview-urbpq7yo5va7g?sr=0-1&ref_=beagle&applicationId=AWSMPContessa)/[AWS China](https://awsmarketplace.amazonaws.cn/marketplace/pp/prodview-2y7nefntbmybu), the following software will be installed through [configure_avh.sh](./configure_avh.sh) script. It will install automatically when you run the application through [run_demo.sh](./run_demo.sh) script.
|
||||
You can refer to this [guide](https://arm-software.github.io/AVH/main/examples/html/MicroSpeech.html#amilaunch) to launch an Arm Virtual Hardware AMI instance.
|
||||
|
||||
Case 2: If the demo is run in the [ci_cpu Docker container](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/docker/Dockerfile.ci_cpu) provided with [TVM](https://github.com/apache/tvm), then the following software will already be installed.
|
||||
|
||||
Case 3: If the demo is not run in the ci_cpu Docker container, then you will need the following:
|
||||
- Software required to build and run the demo (These can all be installed by running
|
||||
tvm/docker/install/ubuntu_install_ethosu_driver_stack.sh.)
|
||||
- [Fixed Virtual Platform (FVP) based on Arm(R) Corstone(TM)-300 software](https://developer.arm.com/tools-and-software/open-source-software/arm-platforms-software/arm-ecosystem-fvps)
|
||||
- [cmake 3.19.5](https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/)
|
||||
- [GCC toolchain from Arm(R)](https://developer.arm.com/-/media/Files/downloads/gnu-rm/10-2020q4/gcc-arm-none-eabi-10-2020-q4-major-x86_64-linux.tar.bz2)
|
||||
- [Arm(R) Ethos(TM)-U NPU driver stack](https://review.mlplatform.org)
|
||||
- [CMSIS](https://github.com/ARM-software/CMSIS_5)
|
||||
- The python libraries listed in the requirements.txt of this directory
|
||||
- These can be installed by running the following from the current directory:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r ./requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In case2 and case3:
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to update your PATH environment variable to include the path to cmake 3.19.5 and the FVP.
|
||||
For example if you've installed these in ```/opt/arm``` , then you would do the following:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export PATH=/opt/arm/FVP_Corstone_SSE-300/models/Linux64_GCC-6.4:/opt/arm/cmake/bin:$PATH
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will also need TVM which can either be:
|
||||
- Installed from TLCPack(see [TLCPack](https://tlcpack.ai/))
|
||||
- Built from source (see [Install from Source](https://tvm.apache.org/docs/install/from_source.html))
|
||||
- When building from source, the following need to be set in config.cmake:
|
||||
- set(USE_CMSISNN ON)
|
||||
- set(USE_MICRO ON)
|
||||
- set(USE_LLVM ON)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Running the demo application
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
Type the following command to run the bare metal text recognition application ([src/demo_bare_metal.c](./src/demo_bare_metal.c)):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./run_demo.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not able to use Arm Virtual Hardware Amazon Machine Image(AMI) instance hosted by AWS/AWS China, specify argument --enable_FVP to 1 to make the application run on local Fixed Virtual Platforms (FVPs) executables.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./run_demo.sh --enable_FVP 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the Ethos(TM)-U platform and/or CMSIS have not been installed in /opt/arm/ethosu then
|
||||
the locations for these can be specified as arguments to run_demo.sh, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./run_demo.sh --cmsis_path /home/tvm-user/cmsis \
|
||||
--ethosu_platform_path /home/tvm-user/ethosu/core_platform
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With [run_demo.sh](./run_demo.sh) to run the demo application, it will:
|
||||
- Set up running environment by installing the required prerequisites automatically if running in Arm Virtual Hardware Amazon AMI instance(not specify --enable_FVP to 1)
|
||||
- Download a PaddleOCR text recognition model
|
||||
- Use tvmc to compile the text recognition model for Cortex(R)-M55 CPU and CMSIS-NN
|
||||
- Create a C header file inputs.c containing the image data as a C array
|
||||
- Create a C header file outputs.c containing a C array where the output of inference will be stored
|
||||
- Build the demo application
|
||||
- Run the demo application on a Arm Virtual Hardware based on Arm(R) Corstone(TM)-300 software
|
||||
- The application will report the text on the image and the corresponding score.
|
||||
|
||||
Using your own image
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
The create_image.py script takes a single argument on the command line which is the path of the
|
||||
image to be converted into an array of bytes for consumption by the model.
|
||||
|
||||
The demo can be modified to use an image of your choice by changing the following line in run_demo.sh
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 ./convert_image.py path/to/image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Model description
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
The example is built on [PP-OCRv3](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md) English recognition model released by [PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR). Since Arm(R) Cortex(R)-M55 CPU does not support rnn operator, we delete the unsupported operator based on the PP-OCRv3 text recognition model to obtain the current 2.7M English recognition model.
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3 is the third version of the PP-OCR series model. This series of models has the following features:
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3: ultra-lightweight OCR system: detection (3.6M) + direction classifier (1.4M) + recognition (12M) = 17.0M
|
||||
- Support more than 80 kinds of multi-language recognition models, including English, Chinese, French, German, Arabic, Korean, Japanese and so on. For details
|
||||
- Support vertical text recognition, and long text recognition
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
|||
<!--- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one -->
|
||||
<!--- or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file -->
|
||||
<!--- distributed with this work for additional information -->
|
||||
<!--- regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file -->
|
||||
<!--- to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the -->
|
||||
<!--- "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance -->
|
||||
<!--- with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at -->
|
||||
|
||||
<!--- http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 -->
|
||||
|
||||
<!--- Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, -->
|
||||
<!--- software distributed under the License is distributed on an -->
|
||||
<!--- "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY -->
|
||||
<!--- KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the -->
|
||||
<!--- specific language governing permissions and limitations -->
|
||||
<!--- under the License. -->
|
||||
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||
|
||||
通过TVM在 Arm(R) Cortex(R)-M55 CPU 上运行 PaddleOCR文 本能识别模型
|
||||
===============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
此文件夹包含如何使用 TVM 在 Cortex(R)-M55 CPU 上运行 PaddleOCR 模型的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
依赖
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
本demo运行在TVM提供的docker环境上,在该环境中已经安装好的必须的软件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在非docker环境中,需要手动安装如下依赖项:
|
||||
|
||||
- 软件可通过[安装脚本](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/docker/install/ubuntu_install_ethosu_driver_stack.sh)一键安装
|
||||
- [Fixed Virtual Platform (FVP) based on Arm(R) Corstone(TM)-300 software](https://developer.arm.com/tools-and-software/open-source-software/arm-platforms-software/arm-ecosystem-fvps)
|
||||
- [cmake 3.19.5](https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/)
|
||||
- [GCC toolchain from Arm(R)](https://developer.arm.com/-/media/Files/downloads/gnu-rm/10-2020q4/gcc-arm-none-eabi-10-2020-q4-major-x86_64-linux.tar.bz2)
|
||||
- [Arm(R) Ethos(TM)-U NPU driver stack](https://review.mlplatform.org)
|
||||
- [CMSIS](https://github.com/ARM-software/CMSIS_5)
|
||||
- python 依赖
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r ./requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
- TVM
|
||||
- 从源码安装([Install from Source](https://tvm.apache.org/docs/install/from_source.html))
|
||||
从源码安装时,需要设置如下字段
|
||||
- set(USE_CMSISNN ON)
|
||||
- set(USE_MICRO ON)
|
||||
- set(USE_LLVM ON)
|
||||
- 从TLCPack 安装([TLCPack](https://tlcpack.ai/))
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后需要更新环境变量,以软件安装地址为`/opt/arm`为例:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export PATH=/opt/arm/FVP_Corstone_SSE-300/models/Linux64_GCC-6.4:/opt/arm/cmake/bin:$PATH
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行demo
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
使用如下命令可以一键运行demo
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./run_demo.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果 Ethos(TM)-U 平台或 CMSIS 没有安装在 `/opt/arm/ethosu` 中,可通过参数进行设置,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./run_demo.sh --cmsis_path /home/tvm-user/cmsis \
|
||||
--ethosu_platform_path /home/tvm-user/ethosu/core_platform
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`./run_demo.sh`脚本会执行如下步骤:
|
||||
- 下载 PaddleOCR 文字识别模型
|
||||
- 使用tvm将PaddleOCR 文字识别模型编译为 Cortex(R)-M55 CPU 和 CMSIS-NN 后端的可执行文件
|
||||
- 创建一个包含输入图像数据的头文件`inputs.c`
|
||||
- 创建一个包含输出tensor大小的头文件`outputs.c`
|
||||
- 编译可执行程序
|
||||
- 运行程序
|
||||
- 输出图片上的文字和置信度
|
||||
|
||||
使用自己的图片
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
替换 `run_demo.sh ` 中140行处的图片地址即可
|
||||
|
||||
使用自己的模型
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
替换 `run_demo.sh ` 中130行处的模型地址即可
|
||||
|
||||
模型描述
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
在这个demo中,我们使用的模型是基于[PP-OCRv3](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)的英文识别模型。由于Arm(R) Cortex(R)-M55 CPU不支持rnn算子,我们在PP-OCRv3原始文本识别模型的基础上进行适配,最终模型大小为2.7M。
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3是[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)发布的PP-OCR系列模型的第三个版本,该系列模型具有以下特点:
|
||||
- 超轻量级OCR系统:检测(3.6M)+方向分类器(1.4M)+识别(12M)=17.0M。
|
||||
- 支持80多种多语言识别模型,包括英文、中文、法文、德文、阿拉伯文、韩文、日文等。
|
||||
- 支持竖排文本识别,长文本识别。
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
|||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
# distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
# under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
if (__TOOLCHAIN_LOADED)
|
||||
return()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
set(__TOOLCHAIN_LOADED TRUE)
|
||||
|
||||
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME Generic)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_COMPILER "arm-none-eabi-gcc")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "arm-none-eabi-g++")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR "cortex-m55" CACHE STRING "Select Arm(R) Cortex(R)-M architecture. (cortex-m0, cortex-m3, cortex-m33, cortex-m4, cortex-m55, cortex-m7, etc)")
|
||||
|
||||
set(CMAKE_TRY_COMPILE_TARGET_TYPE STATIC_LIBRARY)
|
||||
|
||||
SET(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_PROGRAM NEVER)
|
||||
SET(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_LIBRARY ONLY)
|
||||
SET(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_INCLUDE ONLY)
|
||||
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 99)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
|
||||
|
||||
# The system processor could for example be set to cortex-m33+nodsp+nofp.
|
||||
set(__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET ${CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR})
|
||||
string(REPLACE "+" ";" __CPU_FEATURES ${__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET})
|
||||
list(POP_FRONT __CPU_FEATURES CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR)
|
||||
|
||||
string(FIND ${__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET} "+" __OFFSET)
|
||||
if(__OFFSET GREATER_EQUAL 0)
|
||||
string(SUBSTRING ${__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET} ${__OFFSET} -1 CPU_FEATURES)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add -mcpu to the compile options to override the -mcpu the CMake toolchain adds
|
||||
add_compile_options(-mcpu=${__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET})
|
||||
|
||||
# Set floating point unit
|
||||
if("${__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET}" MATCHES "\\+fp")
|
||||
set(FLOAT hard)
|
||||
elseif("${__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET}" MATCHES "\\+nofp")
|
||||
set(FLOAT soft)
|
||||
elseif("${CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR}" STREQUAL "cortex-m33" OR
|
||||
"${CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR}" STREQUAL "cortex-m55")
|
||||
set(FLOAT hard)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
set(FLOAT soft)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
add_compile_options(-mfloat-abi=${FLOAT})
|
||||
add_link_options(-mfloat-abi=${FLOAT})
|
||||
|
||||
# Link target
|
||||
add_link_options(-mcpu=${__CPU_COMPILE_TARGET})
|
||||
add_link_options(-Xlinker -Map=output.map)
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Compile options
|
||||
#
|
||||
set(cxx_flags "-fno-unwind-tables;-fno-rtti;-fno-exceptions")
|
||||
|
||||
add_compile_options("-Wall;-Wextra;-Wsign-compare;-Wunused;-Wswitch-default;\
|
||||
-Wdouble-promotion;-Wredundant-decls;-Wshadow;-Wnull-dereference;\
|
||||
-Wno-format-extra-args;-Wno-unused-function;-Wno-unused-label;\
|
||||
-Wno-missing-field-initializers;-Wno-return-type;-Wno-format;-Wno-int-conversion"
|
||||
"$<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>:${cxx_flags}>"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
|||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2022 Arm Limited and Contributors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
# distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
# under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
set -e
|
||||
set -u
|
||||
set -o pipefail
|
||||
|
||||
# Show usage
|
||||
function show_usage() {
|
||||
cat <<EOF
|
||||
Usage: Set up running environment by installing the required prerequisites.
|
||||
-h, --help
|
||||
Display this help message.
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$#" -eq 1 ] && [ "$1" == "--help" -o "$1" == "-h" ]; then
|
||||
show_usage
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
elif [ "$#" -ge 1 ]; then
|
||||
show_usage
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mStart setting up running environment\e[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
# Install CMSIS
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mStart installing CMSIS\e[0m"
|
||||
CMSIS_PATH="/opt/arm/ethosu/cmsis"
|
||||
mkdir -p "${CMSIS_PATH}"
|
||||
|
||||
CMSIS_SHA="977abe9849781a2e788b02282986480ff4e25ea6"
|
||||
CMSIS_SHASUM="86c88d9341439fbb78664f11f3f25bc9fda3cd7de89359324019a4d87d169939eea85b7fdbfa6ad03aa428c6b515ef2f8cd52299ce1959a5444d4ac305f934cc"
|
||||
CMSIS_URL="http://github.com/ARM-software/CMSIS_5/archive/${CMSIS_SHA}.tar.gz"
|
||||
DOWNLOAD_PATH="/tmp/${CMSIS_SHA}.tar.gz"
|
||||
|
||||
wget ${CMSIS_URL} -O "${DOWNLOAD_PATH}"
|
||||
echo "$CMSIS_SHASUM" ${DOWNLOAD_PATH} | sha512sum -c
|
||||
tar -xf "${DOWNLOAD_PATH}" -C "${CMSIS_PATH}" --strip-components=1
|
||||
touch "${CMSIS_PATH}"/"${CMSIS_SHA}".sha
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mCMSIS Installation SUCCESS\e[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
# Install Arm(R) Ethos(TM)-U NPU driver stack
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mStart installing Arm(R) Ethos(TM)-U NPU driver stack\e[0m"
|
||||
git clone "https://review.mlplatform.org/ml/ethos-u/ethos-u-core-platform" /opt/arm/ethosu/core_platform
|
||||
cd /opt/arm/ethosu/core_platform
|
||||
git checkout tags/"21.11"
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mArm(R) Ethos(TM)-U Core Platform Installation SUCCESS\e[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
# Install Arm(R) GNU Toolchain
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mStart installing Arm(R) GNU Toolchain\e[0m"
|
||||
mkdir -p /opt/arm/gcc-arm-none-eabi
|
||||
export gcc_arm_url='https://developer.arm.com/-/media/Files/downloads/gnu-rm/10-2020q4/gcc-arm-none-eabi-10-2020-q4-major-x86_64-linux.tar.bz2?revision=ca0cbf9c-9de2-491c-ac48-898b5bbc0443&la=en&hash=68760A8AE66026BCF99F05AC017A6A50C6FD832A'
|
||||
curl --retry 64 -sSL ${gcc_arm_url} | tar -C /opt/arm/gcc-arm-none-eabi --strip-components=1 -jx
|
||||
export PATH=/opt/arm/gcc-arm-none-eabi/bin:$PATH
|
||||
arm-none-eabi-gcc --version
|
||||
arm-none-eabi-g++ --version
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mArm(R) Arm(R) GNU Toolchain Installation SUCCESS\e[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
# Install TVM from TLCPack
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mStart installing TVM\e[0m"
|
||||
pip install tlcpack-nightly -f https://tlcpack.ai/wheels
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mTVM Installation SUCCESS\e[0m"
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
|||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
# distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
# under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import pathlib
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
def resize_norm_img(img, image_shape, padding=True):
|
||||
imgC, imgH, imgW = image_shape
|
||||
h = img.shape[0]
|
||||
w = img.shape[1]
|
||||
if not padding:
|
||||
resized_image = cv2.resize(
|
||||
img, (imgW, imgH), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
|
||||
resized_w = imgW
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ratio = w / float(h)
|
||||
if math.ceil(imgH * ratio) > imgW:
|
||||
resized_w = imgW
|
||||
else:
|
||||
resized_w = int(math.ceil(imgH * ratio))
|
||||
resized_image = cv2.resize(img, (resized_w, imgH))
|
||||
resized_image = resized_image.astype('float32')
|
||||
if image_shape[0] == 1:
|
||||
resized_image = resized_image / 255
|
||||
resized_image = resized_image[np.newaxis, :]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
resized_image = resized_image.transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255
|
||||
resized_image -= 0.5
|
||||
resized_image /= 0.5
|
||||
padding_im = np.zeros((imgC, imgH, imgW), dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
padding_im[:, :, 0:resized_w] = resized_image
|
||||
return padding_im
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_header_file(name, tensor_name, tensor_data, output_path):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This function generates a header file containing the data from the numpy array provided.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
file_path = pathlib.Path(f"{output_path}/" + name).resolve()
|
||||
# Create header file with npy_data as a C array
|
||||
raw_path = file_path.with_suffix(".h").resolve()
|
||||
with open(raw_path, "w") as header_file:
|
||||
header_file.write(
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
+ f"const size_t {tensor_name}_len = {tensor_data.size};\n"
|
||||
+ f'__attribute__((section(".data.tvm"), aligned(16))) float {tensor_name}[] = '
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
header_file.write("{")
|
||||
for i in np.ndindex(tensor_data.shape):
|
||||
header_file.write(f"{tensor_data[i]}, ")
|
||||
header_file.write("};\n\n")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_headers(image_name):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This function generates C header files for the input and output arrays required to run inferences
|
||||
"""
|
||||
img_path = os.path.join("./", f"{image_name}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Resize image to 32x320
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
|
||||
img = resize_norm_img(img, [3,32,320])
|
||||
img_data = img.astype("float32")
|
||||
|
||||
# # Add the batch dimension, as we are expecting 4-dimensional input: NCHW.
|
||||
img_data = np.expand_dims(img_data, axis=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create input header file
|
||||
create_header_file("inputs", "input", img_data, "./include")
|
||||
# Create output header file
|
||||
output_data = np.zeros([7760], np.float)
|
||||
create_header_file(
|
||||
"outputs",
|
||||
"output",
|
||||
output_data,
|
||||
"./include",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
create_headers(sys.argv[1])
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,295 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
* distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
*
|
||||
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
* under the License.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*------------------ Reference System Memories -------------
|
||||
+===================+============+=======+============+============+
|
||||
| Memory | Address | Size | CPU Access | NPU Access |
|
||||
+===================+============+=======+============+============+
|
||||
| ITCM | 0x00000000 | 512KB | Yes (RO) | No |
|
||||
+-------------------+------------+-------+------------+------------+
|
||||
| DTCM | 0x20000000 | 512KB | Yes (R/W) | No |
|
||||
+-------------------+------------+-------+------------+------------+
|
||||
| SSE-300 SRAM | 0x21000000 | 2MB | Yes (R/W) | Yes (R/W) |
|
||||
+-------------------+------------+-------+------------+------------+
|
||||
| Data SRAM | 0x01000000 | 2MB | Yes (R/W) | Yes (R/W) |
|
||||
+-------------------+------------+-------+------------+------------+
|
||||
| DDR | 0x60000000 | 32MB | Yes (R/W) | Yes (R/W) |
|
||||
+-------------------+------------+-------+------------+------------+ */
|
||||
|
||||
/*---------------------- ITCM Configuration ----------------------------------
|
||||
<h> Flash Configuration
|
||||
<o0> Flash Base Address <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
<o1> Flash Size (in Bytes) <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
</h>
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
__ROM_BASE = 0x00000000;
|
||||
__ROM_SIZE = 0x00080000;
|
||||
|
||||
/*--------------------- DTCM RAM Configuration ----------------------------
|
||||
<h> RAM Configuration
|
||||
<o0> RAM Base Address <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
<o1> RAM Size (in Bytes) <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
</h>
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
__RAM_BASE = 0x20000000;
|
||||
__RAM_SIZE = 0x00080000;
|
||||
|
||||
/*----------------------- Data SRAM Configuration ------------------------------
|
||||
<h> Data SRAM Configuration
|
||||
<o0> DATA_SRAM Base Address <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
<o1> DATA_SRAM Size (in Bytes) <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
</h>
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
__DATA_SRAM_BASE = 0x01000000;
|
||||
__DATA_SRAM_SIZE = 0x00200000;
|
||||
|
||||
/*--------------------- Embedded SRAM Configuration ----------------------------
|
||||
<h> SRAM Configuration
|
||||
<o0> SRAM Base Address <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
<o1> SRAM Size (in Bytes) <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
</h>
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
__SRAM_BASE = 0x21000000;
|
||||
__SRAM_SIZE = 0x00200000;
|
||||
|
||||
/*--------------------- Stack / Heap Configuration ----------------------------
|
||||
<h> Stack / Heap Configuration
|
||||
<o0> Stack Size (in Bytes) <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
<o1> Heap Size (in Bytes) <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
</h>
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
__STACK_SIZE = 0x00008000;
|
||||
__HEAP_SIZE = 0x00008000;
|
||||
|
||||
/*--------------------- Embedded RAM Configuration ----------------------------
|
||||
<h> DDR Configuration
|
||||
<o0> DDR Base Address <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
<o1> DDR Size (in Bytes) <0x0-0xFFFFFFFF:8>
|
||||
</h>
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
__DDR_BASE = 0x60000000;
|
||||
__DDR_SIZE = 0x02000000;
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
*-------------------- <<< end of configuration section >>> -------------------
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
MEMORY
|
||||
{
|
||||
ITCM (rx) : ORIGIN = __ROM_BASE, LENGTH = __ROM_SIZE
|
||||
DTCM (rwx) : ORIGIN = __RAM_BASE, LENGTH = __RAM_SIZE
|
||||
DATA_SRAM (rwx) : ORIGIN = __DATA_SRAM_BASE, LENGTH = __DATA_SRAM_SIZE
|
||||
SRAM (rwx) : ORIGIN = __SRAM_BASE, LENGTH = __SRAM_SIZE
|
||||
DDR (rwx) : ORIGIN = __DDR_BASE, LENGTH = __DDR_SIZE
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Linker script to place sections and symbol values. Should be used together
|
||||
* with other linker script that defines memory regions ITCM and RAM.
|
||||
* It references following symbols, which must be defined in code:
|
||||
* Reset_Handler : Entry of reset handler
|
||||
*
|
||||
* It defines following symbols, which code can use without definition:
|
||||
* __exidx_start
|
||||
* __exidx_end
|
||||
* __copy_table_start__
|
||||
* __copy_table_end__
|
||||
* __zero_table_start__
|
||||
* __zero_table_end__
|
||||
* __etext
|
||||
* __data_start__
|
||||
* __preinit_array_start
|
||||
* __preinit_array_end
|
||||
* __init_array_start
|
||||
* __init_array_end
|
||||
* __fini_array_start
|
||||
* __fini_array_end
|
||||
* __data_end__
|
||||
* __bss_start__
|
||||
* __bss_end__
|
||||
* __end__
|
||||
* end
|
||||
* __HeapLimit
|
||||
* __StackLimit
|
||||
* __StackTop
|
||||
* __stack
|
||||
*/
|
||||
ENTRY(Reset_Handler)
|
||||
|
||||
SECTIONS
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* .ddr is placed before .text so that .rodata.tvm is encountered before .rodata* */
|
||||
.ddr :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN (16);
|
||||
*(.rodata.tvm)
|
||||
. = ALIGN (16);
|
||||
*(.data.tvm);
|
||||
. = ALIGN(16);
|
||||
} > DDR
|
||||
|
||||
.text :
|
||||
{
|
||||
KEEP(*(.vectors))
|
||||
*(.text*)
|
||||
|
||||
KEEP(*(.init))
|
||||
KEEP(*(.fini))
|
||||
|
||||
/* .ctors */
|
||||
*crtbegin.o(.ctors)
|
||||
*crtbegin?.o(.ctors)
|
||||
*(EXCLUDE_FILE(*crtend?.o *crtend.o) .ctors)
|
||||
*(SORT(.ctors.*))
|
||||
*(.ctors)
|
||||
|
||||
/* .dtors */
|
||||
*crtbegin.o(.dtors)
|
||||
*crtbegin?.o(.dtors)
|
||||
*(EXCLUDE_FILE(*crtend?.o *crtend.o) .dtors)
|
||||
*(SORT(.dtors.*))
|
||||
*(.dtors)
|
||||
|
||||
*(.rodata*)
|
||||
|
||||
KEEP(*(.eh_frame*))
|
||||
} > ITCM
|
||||
|
||||
.ARM.extab :
|
||||
{
|
||||
*(.ARM.extab* .gnu.linkonce.armextab.*)
|
||||
} > ITCM
|
||||
|
||||
__exidx_start = .;
|
||||
.ARM.exidx :
|
||||
{
|
||||
*(.ARM.exidx* .gnu.linkonce.armexidx.*)
|
||||
} > ITCM
|
||||
__exidx_end = .;
|
||||
|
||||
.copy.table :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
__copy_table_start__ = .;
|
||||
LONG (__etext)
|
||||
LONG (__data_start__)
|
||||
LONG (__data_end__ - __data_start__)
|
||||
/* Add each additional data section here */
|
||||
__copy_table_end__ = .;
|
||||
} > ITCM
|
||||
|
||||
.zero.table :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
__zero_table_start__ = .;
|
||||
__zero_table_end__ = .;
|
||||
} > ITCM
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Location counter can end up 2byte aligned with narrow Thumb code but
|
||||
* __etext is assumed by startup code to be the LMA of a section in DTCM
|
||||
* which must be 4byte aligned
|
||||
*/
|
||||
__etext = ALIGN (4);
|
||||
|
||||
.sram :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(16);
|
||||
} > SRAM AT > SRAM
|
||||
|
||||
.data : AT (__etext)
|
||||
{
|
||||
__data_start__ = .;
|
||||
*(vtable)
|
||||
*(.data)
|
||||
*(.data.*)
|
||||
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
/* preinit data */
|
||||
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__preinit_array_start = .);
|
||||
KEEP(*(.preinit_array))
|
||||
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__preinit_array_end = .);
|
||||
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
/* init data */
|
||||
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__init_array_start = .);
|
||||
KEEP(*(SORT(.init_array.*)))
|
||||
KEEP(*(.init_array))
|
||||
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__init_array_end = .);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
/* finit data */
|
||||
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__fini_array_start = .);
|
||||
KEEP(*(SORT(.fini_array.*)))
|
||||
KEEP(*(.fini_array))
|
||||
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__fini_array_end = .);
|
||||
|
||||
KEEP(*(.jcr*))
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
/* All data end */
|
||||
__data_end__ = .;
|
||||
|
||||
} > DTCM
|
||||
|
||||
.bss.noinit (NOLOAD):
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(16);
|
||||
*(.bss.noinit.*)
|
||||
. = ALIGN(16);
|
||||
} > SRAM AT > SRAM
|
||||
|
||||
.bss :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
__bss_start__ = .;
|
||||
*(.bss)
|
||||
*(.bss.*)
|
||||
*(COMMON)
|
||||
. = ALIGN(4);
|
||||
__bss_end__ = .;
|
||||
} > DTCM AT > DTCM
|
||||
|
||||
.data_sram :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(16);
|
||||
} > DATA_SRAM
|
||||
|
||||
.heap (COPY) :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(8);
|
||||
__end__ = .;
|
||||
PROVIDE(end = .);
|
||||
. = . + __HEAP_SIZE;
|
||||
. = ALIGN(8);
|
||||
__HeapLimit = .;
|
||||
} > DTCM
|
||||
|
||||
.stack (ORIGIN(DTCM) + LENGTH(DTCM) - __STACK_SIZE) (COPY) :
|
||||
{
|
||||
. = ALIGN(8);
|
||||
__StackLimit = .;
|
||||
. = . + __STACK_SIZE;
|
||||
. = ALIGN(8);
|
||||
__StackTop = .;
|
||||
} > DTCM
|
||||
PROVIDE(__stack = __StackTop);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Check if data + stack exceeds DTCM limit */
|
||||
ASSERT(__StackLimit >= __bss_end__, "region DTCM overflowed with stack")
|
||||
}
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 5.6 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 72 KiB |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
* distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
*
|
||||
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
* under the License.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TVM_RUNTIME_CRT_CONFIG_H_
|
||||
#define TVM_RUNTIME_CRT_CONFIG_H_
|
||||
|
||||
/*! Log level of the CRT runtime */
|
||||
#define TVM_CRT_LOG_LEVEL TVM_CRT_LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TVM_RUNTIME_CRT_CONFIG_H_
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
* distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
*
|
||||
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
* under the License.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdarg.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <tvm/runtime/c_runtime_api.h>
|
||||
#include <tvm/runtime/crt/stack_allocator.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
extern "C" {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
void __attribute__((noreturn)) TVMPlatformAbort(tvm_crt_error_t error_code) {
|
||||
printf("TVMPlatformAbort: %d\n", error_code);
|
||||
printf("EXITTHESIM\n");
|
||||
exit(-1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tvm_crt_error_t TVMPlatformMemoryAllocate(size_t num_bytes, DLDevice dev, void** out_ptr) {
|
||||
return kTvmErrorFunctionCallNotImplemented;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tvm_crt_error_t TVMPlatformMemoryFree(void* ptr, DLDevice dev) {
|
||||
return kTvmErrorFunctionCallNotImplemented;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void TVMLogf(const char* msg, ...) {
|
||||
va_list args;
|
||||
va_start(args, msg);
|
||||
vfprintf(stdout, msg, args);
|
||||
va_end(args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TVM_DLL int TVMFuncRegisterGlobal(const char* name, TVMFunctionHandle f, int override) { return 0; }
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
paddlepaddle
|
||||
numpy
|
||||
opencv-python
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
|||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
# distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
# under the License.
|
||||
set -e
|
||||
set -u
|
||||
set -o pipefail
|
||||
|
||||
# Show usage
|
||||
function show_usage() {
|
||||
cat <<EOF
|
||||
Usage: run_demo.sh
|
||||
-h, --help
|
||||
Display this help message.
|
||||
--cmsis_path CMSIS_PATH
|
||||
Set path to CMSIS.
|
||||
--ethosu_platform_path ETHOSU_PLATFORM_PATH
|
||||
Set path to Arm(R) Ethos(TM)-U core platform.
|
||||
--fvp_path FVP_PATH
|
||||
Set path to FVP.
|
||||
--cmake_path
|
||||
Set path to cmake.
|
||||
--enable_FVP
|
||||
Set 1 to run application on local Fixed Virtual Platforms (FVPs) executables.
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure environment variables
|
||||
FVP_enable=0
|
||||
export PATH=/opt/arm/gcc-arm-none-eabi/bin:$PATH
|
||||
|
||||
# Install python libraries
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mInstall python libraries\e[0m"
|
||||
sudo pip install -r ./requirements.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Parse arguments
|
||||
while (( $# )); do
|
||||
case "$1" in
|
||||
-h|--help)
|
||||
show_usage
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
--cmsis_path)
|
||||
if [ $# -gt 1 ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
export CMSIS_PATH="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo 'ERROR: --cmsis_path requires a non-empty argument' >&2
|
||||
show_usage >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
--ethosu_platform_path)
|
||||
if [ $# -gt 1 ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
export ETHOSU_PLATFORM_PATH="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo 'ERROR: --ethosu_platform_path requires a non-empty argument' >&2
|
||||
show_usage >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
--fvp_path)
|
||||
if [ $# -gt 1 ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
export PATH="$2/models/Linux64_GCC-6.4:$PATH"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo 'ERROR: --fvp_path requires a non-empty argument' >&2
|
||||
show_usage >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
--cmake_path)
|
||||
if [ $# -gt 1 ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
export CMAKE="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo 'ERROR: --cmake_path requires a non-empty argument' >&2
|
||||
show_usage >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
--enable_FVP)
|
||||
if [ $# -gt 1 ] && [ "$2" == "1" -o "$2" == "0" ];
|
||||
then
|
||||
FVP_enable="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo 'ERROR: --enable_FVP requires a right argument 1 or 0' >&2
|
||||
show_usage >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
-*|--*)
|
||||
echo "Error: Unknown flag: $1" >&2
|
||||
show_usage >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
;;
|
||||
esac
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose running environment: cloud(default) or local environment
|
||||
Platform="VHT_Corstone_SSE-300_Ethos-U55"
|
||||
if [ $FVP_enable == "1" ]; then
|
||||
Platform="FVP_Corstone_SSE-300_Ethos-U55"
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mRun application on local Fixed Virtual Platforms (FVPs)\e[0m"
|
||||
else
|
||||
if [ ! -d "/opt/arm/" ]; then
|
||||
sudo ./configure_avh.sh
|
||||
fi
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# Directories
|
||||
script_dir="$( cd "$( dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd )"
|
||||
|
||||
# Make build directory
|
||||
make cleanall
|
||||
mkdir -p build
|
||||
cd build
|
||||
|
||||
# Get PaddlePaddle inference model
|
||||
echo -e "\e[36mDownload PaddlePaddle inference model\e[0m"
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/tvm/ocr_en.tar
|
||||
tar -xf ocr_en.tar
|
||||
|
||||
# Compile model for Arm(R) Cortex(R)-M55 CPU and CMSIS-NN
|
||||
# An alternative to using "python3 -m tvm.driver.tvmc" is to call
|
||||
# "tvmc" directly once TVM has been pip installed.
|
||||
python3 -m tvm.driver.tvmc compile --target=cmsis-nn,c \
|
||||
--target-cmsis-nn-mcpu=cortex-m55 \
|
||||
--target-c-mcpu=cortex-m55 \
|
||||
--runtime=crt \
|
||||
--executor=aot \
|
||||
--executor-aot-interface-api=c \
|
||||
--executor-aot-unpacked-api=1 \
|
||||
--pass-config tir.usmp.enable=1 \
|
||||
--pass-config tir.usmp.algorithm=hill_climb \
|
||||
--pass-config tir.disable_storage_rewrite=1 \
|
||||
--pass-config tir.disable_vectorize=1 ocr_en/inference.pdmodel \
|
||||
--output-format=mlf \
|
||||
--model-format=paddle \
|
||||
--module-name=rec \
|
||||
--input-shapes x:[1,3,32,320] \
|
||||
--output=rec.tar
|
||||
tar -xf rec.tar
|
||||
|
||||
# Create C header files
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
python3 ./convert_image.py imgs_words_en/word_116.png
|
||||
|
||||
# Build demo executable
|
||||
cd ${script_dir}
|
||||
echo ${script_dir}
|
||||
make
|
||||
|
||||
# Run demo executable on the AVH
|
||||
$Platform -C cpu0.CFGDTCMSZ=15 \
|
||||
-C cpu0.CFGITCMSZ=15 -C mps3_board.uart0.out_file=\"-\" -C mps3_board.uart0.shutdown_tag=\"EXITTHESIM\" \
|
||||
-C mps3_board.visualisation.disable-visualisation=1 -C mps3_board.telnetterminal0.start_telnet=0 \
|
||||
-C mps3_board.telnetterminal1.start_telnet=0 -C mps3_board.telnetterminal2.start_telnet=0 -C mps3_board.telnetterminal5.start_telnet=0 \
|
||||
./build/demo --stat
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
|
||||
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
|
||||
* distributed with this work for additional information
|
||||
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
|
||||
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
|
||||
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
|
||||
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
*
|
||||
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
|
||||
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
|
||||
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
|
||||
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
|
||||
* under the License.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <tvm_runtime.h>
|
||||
#include <tvmgen_rec.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "uart.h"
|
||||
|
||||
// Header files generated by convert_image.py
|
||||
#include "inputs.h"
|
||||
#include "outputs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
char dict[]={"#0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~!\"#$%&'()*+,-./ "};
|
||||
int char_dict_nums = 97;
|
||||
uart_init();
|
||||
printf("Starting ocr rec inference\n");
|
||||
struct tvmgen_rec_outputs rec_outputs = {
|
||||
.output = output,
|
||||
};
|
||||
struct tvmgen_rec_inputs rec_inputs = {
|
||||
.x = input,
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
tvmgen_rec_run(&rec_inputs, &rec_outputs);
|
||||
|
||||
// post process
|
||||
int char_nums = output_len / char_dict_nums;
|
||||
|
||||
int last_index = 0;
|
||||
float score = 0.f;
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
printf("text: ");
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < char_nums; i++) {
|
||||
int argmax_idx = 0;
|
||||
float max_value = 0.0f;
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < char_dict_nums; j++){
|
||||
if (output[i * char_dict_nums + j] > max_value){
|
||||
max_value = output[i * char_dict_nums + j];
|
||||
argmax_idx = j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (argmax_idx > 0 && (!(i > 0 && argmax_idx == last_index))) {
|
||||
score += max_value;
|
||||
count += 1;
|
||||
// printf("%d,%f,%c\n", argmax_idx, max_value, dict[argmax_idx]);
|
||||
printf("%c", dict[argmax_idx]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
last_index = argmax_idx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
score /= count;
|
||||
printf(", score: %f\n", score);
|
||||
|
||||
// The FVP will shut down when it receives "EXITTHESIM" on the UART
|
||||
printf("EXITTHESIM\n");
|
||||
while (1 == 1)
|
||||
;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,5 @@ det_db_box_thresh 0.5
|
|||
det_db_unclip_ratio 1.6
|
||||
det_db_use_dilate 0
|
||||
det_use_polygon_score 1
|
||||
use_direction_classify 1
|
||||
use_direction_classify 1
|
||||
rec_image_height 32
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,24 +19,27 @@
|
|||
|
||||
const std::vector<int> rec_image_shape{3, 32, 320};
|
||||
|
||||
cv::Mat CrnnResizeImg(cv::Mat img, float wh_ratio) {
|
||||
cv::Mat CrnnResizeImg(cv::Mat img, float wh_ratio, int rec_image_height) {
|
||||
int imgC, imgH, imgW;
|
||||
imgC = rec_image_shape[0];
|
||||
imgH = rec_image_height;
|
||||
imgW = rec_image_shape[2];
|
||||
imgH = rec_image_shape[1];
|
||||
|
||||
imgW = int(32 * wh_ratio);
|
||||
imgW = int(imgH * wh_ratio);
|
||||
|
||||
float ratio = static_cast<float>(img.cols) / static_cast<float>(img.rows);
|
||||
float ratio = float(img.cols) / float(img.rows);
|
||||
int resize_w, resize_h;
|
||||
|
||||
if (ceilf(imgH * ratio) > imgW)
|
||||
resize_w = imgW;
|
||||
else
|
||||
resize_w = static_cast<int>(ceilf(imgH * ratio));
|
||||
resize_w = int(ceilf(imgH * ratio));
|
||||
cv::Mat resize_img;
|
||||
cv::resize(img, resize_img, cv::Size(resize_w, imgH), 0.f, 0.f,
|
||||
cv::INTER_LINEAR);
|
||||
|
||||
cv::copyMakeBorder(resize_img, resize_img, 0, 0, 0,
|
||||
int(imgW - resize_img.cols), cv::BORDER_CONSTANT,
|
||||
{127, 127, 127});
|
||||
return resize_img;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
|
|||
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
|
||||
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
cv::Mat CrnnResizeImg(cv::Mat img, float wh_ratio);
|
||||
cv::Mat CrnnResizeImg(cv::Mat img, float wh_ratio, int rec_image_height);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::string> ReadDict(std::string path);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -162,7 +162,8 @@ void RunRecModel(std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<int>>> boxes, cv::Mat img,
|
|||
std::vector<std::string> charactor_dict,
|
||||
std::shared_ptr<PaddlePredictor> predictor_cls,
|
||||
int use_direction_classify,
|
||||
std::vector<double> *times) {
|
||||
std::vector<double> *times,
|
||||
int rec_image_height) {
|
||||
std::vector<float> mean = {0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f};
|
||||
std::vector<float> scale = {1 / 0.5f, 1 / 0.5f, 1 / 0.5f};
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -183,7 +184,7 @@ void RunRecModel(std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<int>>> boxes, cv::Mat img,
|
|||
float wh_ratio =
|
||||
static_cast<float>(crop_img.cols) / static_cast<float>(crop_img.rows);
|
||||
|
||||
resize_img = CrnnResizeImg(crop_img, wh_ratio);
|
||||
resize_img = CrnnResizeImg(crop_img, wh_ratio, rec_image_height);
|
||||
resize_img.convertTo(resize_img, CV_32FC3, 1 / 255.f);
|
||||
|
||||
const float *dimg = reinterpret_cast<const float *>(resize_img.data);
|
||||
|
|
@ -444,7 +445,7 @@ void system(char **argv){
|
|||
//// load config from txt file
|
||||
auto Config = LoadConfigTxt(det_config_path);
|
||||
int use_direction_classify = int(Config["use_direction_classify"]);
|
||||
|
||||
int rec_image_height = int(Config["rec_image_height"]);
|
||||
auto charactor_dict = ReadDict(dict_path);
|
||||
charactor_dict.insert(charactor_dict.begin(), "#"); // blank char for ctc
|
||||
charactor_dict.push_back(" ");
|
||||
|
|
@ -473,7 +474,7 @@ void system(char **argv){
|
|||
|
||||
std::vector<double> rec_times;
|
||||
RunRecModel(boxes, srcimg, rec_predictor, rec_text, rec_text_score,
|
||||
charactor_dict, cls_predictor, use_direction_classify, &rec_times);
|
||||
charactor_dict, cls_predictor, use_direction_classify, &rec_times, rec_image_height);
|
||||
|
||||
//// visualization
|
||||
auto img_vis = Visualization(srcimg, boxes);
|
||||
|
|
@ -590,12 +591,16 @@ void rec(int argc, char **argv) {
|
|||
std::string batchsize = argv[6];
|
||||
std::string img_dir = argv[7];
|
||||
std::string dict_path = argv[8];
|
||||
std::string config_path = argv[9];
|
||||
|
||||
if (strcmp(argv[4], "FP32") != 0 && strcmp(argv[4], "INT8") != 0) {
|
||||
std::cerr << "Only support FP32 or INT8." << std::endl;
|
||||
exit(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto Config = LoadConfigTxt(config_path);
|
||||
int rec_image_height = int(Config["rec_image_height"]);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<cv::String> cv_all_img_names;
|
||||
cv::glob(img_dir, cv_all_img_names);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -630,7 +635,7 @@ void rec(int argc, char **argv) {
|
|||
std::vector<float> rec_text_score;
|
||||
std::vector<double> times;
|
||||
RunRecModel(boxes, srcimg, rec_predictor, rec_text, rec_text_score,
|
||||
charactor_dict, cls_predictor, 0, ×);
|
||||
charactor_dict, cls_predictor, 0, ×, rec_image_height);
|
||||
|
||||
//// print recognized text
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < rec_text.size(); i++) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ For the compilation process of different development environments, please refer
|
|||
### 1.2 Prepare Paddle-Lite library
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to obtain the Paddle-Lite library:
|
||||
- 1. Download directly, the download link of the Paddle-Lite library is as follows:
|
||||
- 1. [Recommended] Download directly, the download link of the Paddle-Lite library is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
| Platform | Paddle-Lite library download link |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|
|
@ -43,7 +43,9 @@ There are two ways to obtain the Paddle-Lite library:
|
|||
|
||||
Note: 1. The above Paddle-Lite library is compiled from the Paddle-Lite 2.10 branch. For more information about Paddle-Lite 2.10, please refer to [link](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/releases/tag/v2.10).
|
||||
|
||||
- 2. [Recommended] Compile Paddle-Lite to get the prediction library. The compilation method of Paddle-Lite is as follows:
|
||||
**Note: It is recommended to use paddlelite>=2.10 version of the prediction library, other prediction library versions [download link](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/tags)**
|
||||
|
||||
- 2. Compile Paddle-Lite to get the prediction library. The compilation method of Paddle-Lite is as follows:
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite.git
|
||||
cd Paddle-Lite
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,20 +106,16 @@ If you directly use the model in the above table for deployment, you can skip th
|
|||
|
||||
If the model to be deployed is not in the above table, you need to follow the steps below to obtain the optimized model.
|
||||
|
||||
The `opt` tool can be obtained by compiling Paddle Lite.
|
||||
- Step 1: Refer to [document](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/lite/v2.10/user_guides/opt/opt_python.html) to install paddlelite, which is used to convert paddle inference model to paddlelite required for running nb model
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite.git
|
||||
cd Paddle-Lite
|
||||
git checkout release/v2.10
|
||||
./lite/tools/build.sh build_optimize_tool
|
||||
pip install paddlelite==2.10 # The paddlelite version should be the same as the prediction library version
|
||||
```
|
||||
After installation, the following commands can view the help information
|
||||
```
|
||||
paddle_lite_opt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After the compilation is complete, the opt file is located under build.opt/lite/api/, You can view the operating options and usage of opt in the following ways:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd build.opt/lite/api/
|
||||
./opt
|
||||
```
|
||||
Introduction to paddle_lite_opt parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
|Options|Description|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|
|
@ -131,6 +129,8 @@ cd build.opt/lite/api/
|
|||
|
||||
`--model_dir` is suitable for the non-combined mode of the model to be optimized, and the inference model of PaddleOCR is the combined mode, that is, the model structure and model parameters are stored in a single file.
|
||||
|
||||
- Step 2: Use paddle_lite_opt to convert the inference model to the mobile model format.
|
||||
|
||||
The following takes the ultra-lightweight Chinese model of PaddleOCR as an example to introduce the use of the compiled opt file to complete the conversion of the inference model to the Paddle-Lite optimized model
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -240,6 +240,7 @@ det_db_thresh 0.3 # Used to filter the binarized image of DB prediction,
|
|||
det_db_box_thresh 0.5 # DDB post-processing filter box threshold, if there is a missing box detected, it can be reduced as appropriate
|
||||
det_db_unclip_ratio 1.6 # Indicates the compactness of the text box, the smaller the value, the closer the text box to the text
|
||||
use_direction_classify 0 # Whether to use the direction classifier, 0 means not to use, 1 means to use
|
||||
rec_image_height 32 # The height of the input image of the recognition model, the PP-OCRv3 model needs to be set to 48, and the PP-OCRv2 model needs to be set to 32
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Run Model on phone
|
||||
|
|
@ -258,8 +259,15 @@ After the above steps are completed, you can use adb to push the file to the pho
|
|||
cd /data/local/tmp/debug
|
||||
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PWD}:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
|
||||
# The use of ocr_db_crnn is:
|
||||
# ./ocr_db_crnn Detection model file Orientation classifier model file Recognition model file Test image path Dictionary file path
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn ch_PP-OCRv2_det_slim_opt.nb ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_slim_opt.nb ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_opt.nb ./11.jpg ppocr_keys_v1.txt
|
||||
# ./ocr_db_crnn Mode Detection model file Orientation classifier model file Recognition model file Hardware Precision Threads Batchsize Test image path Dictionary file path
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn system ch_PP-OCRv2_det_slim_opt.nb ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_slim_opt.nb ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_slim_opt.nb arm8 INT8 10 1 ./11.jpg config.txt ppocr_keys_v1.txt True
|
||||
# precision can be INT8 for quantitative model or FP32 for normal model.
|
||||
|
||||
# Only using detection model
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn det ch_PP-OCRv2_det_slim_opt.nb arm8 INT8 10 1 ./11.jpg config.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Only using recognition model
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn rec ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_slim_opt.nb arm8 INT8 10 1 word_1.jpg ppocr_keys_v1.txt config.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you modify the code, you need to recompile and push to the phone.
|
||||
|
|
@ -283,3 +291,7 @@ A2: Replace the .jpg test image under ./debug with the image you want to test, a
|
|||
Q3: How to package it into the mobile APP?
|
||||
|
||||
A3: This demo aims to provide the core algorithm part that can run OCR on mobile phones. Further, PaddleOCR/deploy/android_demo is an example of encapsulating this demo into a mobile app for reference.
|
||||
|
||||
Q4: When running the demo, an error is reported `Error: This model is not supported, because kernel for 'io_copy' is not supported by Paddle-Lite.`
|
||||
|
||||
A4: The problem is that the installed paddlelite version does not match the downloaded prediction library version. Make sure that the paddleliteopt tool matches your prediction library version, and try to switch to the nb model again.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
|||
- [2.1 模型优化](#21-模型优化)
|
||||
- [2.2 与手机联调](#22-与手机联调)
|
||||
- [FAQ](#faq)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本教程将介绍基于[Paddle Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) 在移动端部署PaddleOCR超轻量中文检测、识别模型的详细步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Paddle Lite是飞桨轻量化推理引擎,为手机、IOT端提供高效推理
|
|||
### 1.2 准备预测库
|
||||
|
||||
预测库有两种获取方式:
|
||||
- 1. 直接下载,预测库下载链接如下:
|
||||
- 1. [推荐]直接下载,预测库下载链接如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 平台 | 预测库下载链接 |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,9 @@ Paddle Lite是飞桨轻量化推理引擎,为手机、IOT端提供高效推理
|
|||
|
||||
注:1. 上述预测库为PaddleLite 2.10分支编译得到,有关PaddleLite 2.10 详细信息可参考 [链接](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/releases/tag/v2.10) 。
|
||||
|
||||
- 2. [推荐]编译Paddle-Lite得到预测库,Paddle-Lite的编译方式如下:
|
||||
**注:建议使用paddlelite>=2.10版本的预测库,其他预测库版本[下载链接](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/tags)**
|
||||
|
||||
- 2. 编译Paddle-Lite得到预测库,Paddle-Lite的编译方式如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite.git
|
||||
cd Paddle-Lite
|
||||
|
|
@ -102,22 +104,16 @@ Paddle-Lite 提供了多种策略来自动优化原始的模型,其中包括
|
|||
|
||||
如果要部署的模型不在上述表格中,则需要按照如下步骤获得优化后的模型。
|
||||
|
||||
模型优化需要Paddle-Lite的opt可执行文件,可以通过编译Paddle-Lite源码获得,编译步骤如下:
|
||||
- 步骤1:参考[文档](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/lite/v2.10/user_guides/opt/opt_python.html)安装paddlelite,用于转换paddle inference model为paddlelite运行所需的nb模型
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 如果准备环境时已经clone了Paddle-Lite,则不用重新clone Paddle-Lite
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite.git
|
||||
cd Paddle-Lite
|
||||
git checkout release/v2.10
|
||||
# 启动编译
|
||||
./lite/tools/build.sh build_optimize_tool
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
编译完成后,opt文件位于`build.opt/lite/api/`下,可通过如下方式查看opt的运行选项和使用方式;
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd build.opt/lite/api/
|
||||
./opt
|
||||
pip install paddlelite==2.10 # paddlelite版本要与预测库版本一致
|
||||
```
|
||||
安装完后,如下指令可以查看帮助信息
|
||||
```
|
||||
paddle_lite_opt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
paddle_lite_opt 参数介绍:
|
||||
|选项|说明|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|--model_dir|待优化的PaddlePaddle模型(非combined形式)的路径|
|
||||
|
|
@ -130,6 +126,8 @@ cd build.opt/lite/api/
|
|||
|
||||
`--model_dir`适用于待优化的模型是非combined方式,PaddleOCR的inference模型是combined方式,即模型结构和模型参数使用单独一个文件存储。
|
||||
|
||||
- 步骤2:使用paddle_lite_opt将inference模型转换成移动端模型格式。
|
||||
|
||||
下面以PaddleOCR的超轻量中文模型为例,介绍使用编译好的opt文件完成inference模型到Paddle-Lite优化模型的转换。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -148,7 +146,7 @@ wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/slim/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls
|
|||
|
||||
转换成功后,inference模型目录下会多出`.nb`结尾的文件,即是转换成功的模型文件。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:使用paddle-lite部署时,需要使用opt工具优化后的模型。 opt 工具的输入模型是paddle保存的inference模型
|
||||
注意:使用paddle-lite部署时,需要使用opt工具优化后的模型。 opt工具的输入模型是paddle保存的inference模型
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2.2与手机联调"></a>
|
||||
### 2.2 与手机联调
|
||||
|
|
@ -234,13 +232,14 @@ ppocr_keys_v1.txt # 中文字典
|
|||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. `config.txt` 包含了检测器、分类器的超参数,如下:
|
||||
2. `config.txt` 包含了检测器、分类器、识别器的超参数,如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
max_side_len 960 # 输入图像长宽大于960时,等比例缩放图像,使得图像最长边为960
|
||||
det_db_thresh 0.3 # 用于过滤DB预测的二值化图像,设置为0.-0.3对结果影响不明显
|
||||
det_db_box_thresh 0.5 # DB后处理过滤box的阈值,如果检测存在漏框情况,可酌情减小
|
||||
det_db_box_thresh 0.5 # 检测器后处理过滤box的阈值,如果检测存在漏框情况,可酌情减小
|
||||
det_db_unclip_ratio 1.6 # 表示文本框的紧致程度,越小则文本框更靠近文本
|
||||
use_direction_classify 0 # 是否使用方向分类器,0表示不使用,1表示使用
|
||||
rec_image_height 32 # 识别模型输入图像的高度,PP-OCRv3模型设置为48,PP-OCRv2模型需要设置为32
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. 启动调试
|
||||
|
|
@ -259,8 +258,14 @@ use_direction_classify 0 # 是否使用方向分类器,0表示不使用,1
|
|||
cd /data/local/tmp/debug
|
||||
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PWD}:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
|
||||
# 开始使用,ocr_db_crnn可执行文件的使用方式为:
|
||||
# ./ocr_db_crnn 检测模型文件 方向分类器模型文件 识别模型文件 测试图像路径 字典文件路径
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn ch_PP-OCRv2_det_slim_opt.nb ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_slim_opt.nb ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_slim_opt.nb ./11.jpg ppocr_keys_v1.txt
|
||||
# ./ocr_db_crnn 预测模式 检测模型文件 方向分类器模型文件 识别模型文件 运行硬件 运行精度 线程数 batchsize 测试图像路径 参数配置路径 字典文件路径 是否使用benchmark参数
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn system ch_PP-OCRv2_det_slim_opt.nb ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_slim_opt.nb ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_slim_opt.nb arm8 INT8 10 1 ./11.jpg config.txt ppocr_keys_v1.txt True
|
||||
|
||||
# 仅使用文本检测模型,使用方式如下:
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn det ch_PP-OCRv2_det_slim_opt.nb arm8 INT8 10 1 ./11.jpg config.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# 仅使用文本识别模型,使用方式如下:
|
||||
./ocr_db_crnn rec ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_slim_opt.nb arm8 INT8 10 1 word_1.jpg ppocr_keys_v1.txt config.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果对代码做了修改,则需要重新编译并push到手机上。
|
||||
|
|
@ -284,3 +289,7 @@ A2:替换debug下的.jpg测试图像为你想要测试的图像,adb push 到
|
|||
Q3:如何封装到手机APP中?
|
||||
|
||||
A3:此demo旨在提供能在手机上运行OCR的核心算法部分,PaddleOCR/deploy/android_demo是将这个demo封装到手机app的示例,供参考
|
||||
|
||||
Q4:运行demo时遇到报错`Error: This model is not supported, because kernel for 'io_copy' is not supported by Paddle-Lite.`
|
||||
|
||||
A4:问题是安装的paddlelite版本和下载的预测库版本不匹配,确保paddleliteopt工具和你的预测库版本匹配,重新转nb模型试试。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,252 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3 文本检测模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 简介](#1)
|
||||
- [2. PPOCRv3检测训练](#2)
|
||||
- [3. 基于PPOCRv3检测的finetune训练](#3)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. 简介
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3在PP-OCRv2的基础上进一步升级。本节介绍PP-OCRv3检测模型的训练步骤。有关PPOCRv3策略介绍参考[文档](./PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. 检测训练
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3检测模型是对PP-OCRv2中的[CML](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2109.03144.pdf)(Collaborative Mutual Learning) 协同互学习文本检测蒸馏策略进行了升级。PP-OCRv3分别针对检测教师模型和学生模型进行进一步效果优化。其中,在对教师模型优化时,提出了大感受野的PAN结构LK-PAN和引入了DML(Deep Mutual Learning)蒸馏策略;在对学生模型优化时,提出了残差注意力机制的FPN结构RSE-FPN。
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3检测训练包括两个步骤:
|
||||
- 步骤1:采用DML蒸馏方法训练检测教师模型
|
||||
- 步骤2:使用步骤1得到的教师模型采用CML方法训练出轻量学生模型
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.1 准备数据和运行环境
|
||||
|
||||
训练数据采用icdar2015数据,准备训练集步骤参考[ocr_dataset](./dataset/ocr_datasets.md).
|
||||
|
||||
运行环境准备参考[文档](./installation.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 训练教师模型
|
||||
|
||||
教师模型训练的配置文件是[ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release%2F2.5/configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml)。教师模型模型结构的Backbone、Neck、Head分别为Resnet50, LKPAN, DBHead,采用DML的蒸馏方法训练。有关配置文件的详细介绍参考[文档](./knowledge_distillation)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下载ImageNet预训练模型:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 下载ResNet50_vd的预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrain_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pretrained/ResNet50_vd_ssld_pretrained.pdparams
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**启动训练**
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 单卡训练
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Models.Student.pretrained=./pretrain_models/ResNet50_vd_ssld_pretrained \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Student2.pretrained=./pretrain_models/ResNet50_vd_ssld_pretrained \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
# 如果要使用多GPU分布式训练,请使用如下命令:
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Models.Student.pretrained=./pretrain_models/ResNet50_vd_ssld_pretrained \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Student2.pretrained=./pretrain_models/ResNet50_vd_ssld_pretrained \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练过程中保存的模型在output目录下,包含以下文件:
|
||||
```
|
||||
best_accuracy.states
|
||||
best_accuracy.pdparams # 默认保存最优精度的模型参数
|
||||
best_accuracy.pdopt # 默认保存最优精度的优化器相关参数
|
||||
latest.states
|
||||
latest.pdparams # 默认保存的最新模型参数
|
||||
latest.pdopt # 默认保存的最新模型的优化器相关参数
|
||||
```
|
||||
其中,best_accuracy是保存的精度最高的模型参数,可以直接使用该模型评估。
|
||||
|
||||
模型评估命令如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml -o Global.checkpoints=./output/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练的教师模型结构更大,精度更高,用于提升学生模型的精度。
|
||||
|
||||
**提取教师模型参数**
|
||||
best_accuracy包含两个模型的参数,分别对应配置文件中的Student,Student2。提取Student的参数方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("output/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("Student."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Student." in key}
|
||||
# 查看模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "./pretrain_models/dml_teacher.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
提取出来的模型参数可以用于模型进一步的finetune训练或者蒸馏训练。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.3 训练学生模型
|
||||
|
||||
训练学生模型的配置文件是[ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release%2F2.5/configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml)
|
||||
上一节训练得到的教师模型作为监督,采用CML方式训练得到轻量的学生模型。
|
||||
|
||||
下载学生模型的ImageNet预训练模型:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 下载MobileNetV3的预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrain_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pretrained/MobileNetV3_large_x0_5_pretrained.pdparams
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**启动训练**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 单卡训练
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Models.Student.pretrained=./pretrain_models/MobileNetV3_large_x0_5_pretrained \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Student2.pretrained=./pretrain_models/MobileNetV3_large_x0_5_pretrained \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Teacher.pretrained=./pretrain_models/dml_teacher \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
# 如果要使用多GPU分布式训练,请使用如下命令:
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Models.Student.pretrained=./pretrain_models/MobileNetV3_large_x0_5_pretrained \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Student2.pretrained=./pretrain_models/MobileNetV3_large_x0_5_pretrained \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Teacher.pretrained=./pretrain_models/dml_teacher \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练过程中保存的模型在output目录下,
|
||||
模型评估命令如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.checkpoints=./output/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
best_accuracy包含三个模型的参数,分别对应配置文件中的Student,Student2,Teacher。提取Student参数的方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("output/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("Student."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Student." in key}
|
||||
# 查看模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "./pretrain_models/cml_student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
提取出来的Student的参数可用于模型部署或者做进一步的finetune训练。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. 基于PPOCRv3检测finetune训练
|
||||
|
||||
本节介绍如何使用PPOCRv3检测模型在其他场景上的finetune训练。
|
||||
|
||||
finetune训练适用于三种场景:
|
||||
- 基于CML蒸馏方法的finetune训练,适用于教师模型在使用场景上精度高于PPOCRv3检测模型,且希望得到一个轻量检测模型。
|
||||
- 基于PPOCRv3轻量检测模型的finetune训练,无需训练教师模型,希望在PPOCRv3检测模型基础上提升使用场景上的精度。
|
||||
- 基于DML蒸馏方法的finetune训练,适用于采用DML方法进一步提升精度的场景。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**基于CML蒸馏方法的finetune训练**
|
||||
|
||||
下载PPOCRv3训练模型:
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy.pdparams包含CML配置文件中Student、Student2、Teacher模型的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 单卡训练
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
# 如果要使用多GPU分布式训练,请使用如下命令:
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**基于PPOCRv3轻量检测模型的finetune训练**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下载PPOCRv3训练模型,并提取Student结构的模型参数:
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
提取Student参数的方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("output/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("Student."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Student." in key}
|
||||
# 查看模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "./student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用配置文件[ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release%2F2.5/configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml)训练。
|
||||
|
||||
**启动训练**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 单卡训练
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./student \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
# 如果要使用多GPU分布式训练,请使用如下命令:
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./student \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**基于DML蒸馏方法的finetune训练**
|
||||
|
||||
以ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train中的Teacher模型为例,首先提取Teacher结构的参数,方法如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("Teacher."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Teacher." in key}
|
||||
# 查看模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "./teacher.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**启动训练**
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 单卡训练
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Models.Student.pretrained=./teacher \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Student2.pretrained=./teacher \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
# 如果要使用多GPU分布式训练,请使用如下命令:
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Models.Student.pretrained=./teacher \
|
||||
Architecture.Models.Student2.pretrained=./teacher \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=./output/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,9 +5,10 @@ PaddleOCR将**持续新增**支持OCR领域前沿算法与模型,已支持的
|
|||
- [文本检测算法](./algorithm_overview.md#11-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E6%A3%80%E6%B5%8B%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95)
|
||||
- [文本识别算法](./algorithm_overview.md#12-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95)
|
||||
- [端到端算法](./algorithm_overview.md#2-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95)
|
||||
- [表格识别]](./algorithm_overview.md#3-%E8%A1%A8%E6%A0%BC%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95)
|
||||
|
||||
**欢迎广大开发者合作共建,贡献更多算法,合入有奖🎁!具体可查看[社区常规赛](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/issues/4982)。**
|
||||
|
||||
新增算法可参考如下教程:
|
||||
|
||||
- [使用PaddleOCR架构添加新算法](./add_new_algorithm.md)
|
||||
- [使用PaddleOCR架构添加新算法](./add_new_algorithm.md)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# DB
|
||||
# DB与DB++
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 算法简介](#1)
|
||||
- [2. 环境配置](#2)
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,12 +21,24 @@
|
|||
> Liao, Minghui and Wan, Zhaoyi and Yao, Cong and Chen, Kai and Bai, Xiang
|
||||
> AAAI, 2020
|
||||
|
||||
> [Real-Time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization and Adaptive Scale Fusion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.10304)
|
||||
> Liao, Minghui and Zou, Zhisheng and Wan, Zhaoyi and Yao, Cong and Bai, Xiang
|
||||
> TPAMI, 2022
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在ICDAR2015文本检测公开数据集上,算法复现效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型|骨干网络|配置文件|precision|recall|Hmean|下载链接|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|DB|ResNet50_vd|[configs/det/det_r50_vd_db.yml](../../configs/det/det_r50_vd_db.yml)|86.41%|78.72%|82.38%|[训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/en/det_r50_vd_db_v2.0_train.tar)|
|
||||
|DB|MobileNetV3|[configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml](../../configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml)|77.29%|73.08%|75.12%|[训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/en/det_mv3_db_v2.0_train.tar)|
|
||||
|DB++|ResNet50|[configs/det/det_r50_db++_ic15.yml](../../configs/det/det_r50_db++_ic15.yml)|90.89%|82.66%|86.58%|[合成数据预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/en_det/ResNet50_dcn_asf_synthtext_pretrained.pdparams)/[训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/en_det/det_r50_db%2B%2B_icdar15_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
在TD_TR文本检测公开数据集上,算法复现效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型|骨干网络|配置文件|precision|recall|Hmean|下载链接|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|DB++|ResNet50|[configs/det/det_r50_db++_td_tr.yml](../../configs/det/det_r50_db++_td_tr.yml)|92.92%|86.48%|89.58%|[合成数据预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/en_det/ResNet50_dcn_asf_synthtext_pretrained.pdparams)/[训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/en_det/det_r50_db%2B%2B_td_tr_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,7 +66,7 @@ python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/det/det_r50_vd_db.yml -o Global.pretrai
|
|||
DB文本检测模型推理,可以执行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_det.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_en/img_10.jpg" --det_model_dir="./inference/det_db/"
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_det.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_en/img_10.jpg" --det_model_dir="./inference/det_db/" --det_algorithm="DB"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可视化文本检测结果默认保存到`./inference_results`文件夹里面,结果文件的名称前缀为'det_res'。结果示例如下:
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,4 +108,12 @@ DB模型还支持以下推理部署方式:
|
|||
pages={11474--11481},
|
||||
year={2020}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@article{liao2022real,
|
||||
title={Real-Time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization and Adaptive Scale Fusion},
|
||||
author={Liao, Minghui and Zou, Zhisheng and Wan, Zhaoyi and Yao, Cong and Bai, Xiang},
|
||||
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
|
||||
year={2022},
|
||||
publisher={IEEE}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,17 +1,15 @@
|
|||
# FCENet
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 算法简介](#1)
|
||||
- [2. 环境配置](#2)
|
||||
- [3. 模型训练、评估、预测](#3)
|
||||
- [3.1 训练](#3-1)
|
||||
- [3.2 评估](#3-2)
|
||||
- [3.3 预测](#3-3)
|
||||
- [4. 推理部署](#4)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python推理](#4-1)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++推理](#4-2)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving服务化部署](#4-3)
|
||||
- [4.4 更多推理部署](#4-4)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5)
|
||||
- [1. 算法简介](#1-算法简介)
|
||||
- [2. 环境配置](#2-环境配置)
|
||||
- [3. 模型训练、评估、预测](#3-模型训练评估预测)
|
||||
- [4. 推理部署](#4-推理部署)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python推理](#41-python推理)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++推理](#42-c推理)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving服务化部署](#43-serving服务化部署)
|
||||
- [4.4 更多推理部署](#44-更多推理部署)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5-faq)
|
||||
- [引用](#引用)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. 算法简介
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
|||
# OCR算法
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 两阶段算法](#1-两阶段算法)
|
||||
- [1.1 文本检测算法](#11-文本检测算法)
|
||||
- [1.2 文本识别算法](#12-文本识别算法)
|
||||
- [2. 端到端算法](#2-端到端算法)
|
||||
- [1. 两阶段算法](#1)
|
||||
- [1.1 文本检测算法](#11)
|
||||
- [1.2 文本识别算法](#12)
|
||||
- [2. 端到端算法](#2)
|
||||
- [3. 表格识别算法](#3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本文给出了PaddleOCR已支持的OCR算法列表,以及每个算法在**英文公开数据集**上的模型和指标,主要用于算法简介和算法性能对比,更多包括中文在内的其他数据集上的模型请参考[PP-OCR v2.0 系列模型下载](./models_list.md)。
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,6 +67,8 @@
|
|||
- [x] [SAR](./algorithm_rec_sar.md)
|
||||
- [x] [SEED](./algorithm_rec_seed.md)
|
||||
- [x] [SVTR](./algorithm_rec_svtr.md)
|
||||
- [x] [ViTSTR](./algorithm_rec_vitstr.md)
|
||||
- [x] [ABINet](./algorithm_rec_abinet.md)
|
||||
- [x] [SPIN](./algorithm_rec_spin.md)
|
||||
|
||||
参考[DTRB](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01906)[3]文字识别训练和评估流程,使用MJSynth和SynthText两个文字识别数据集训练,在IIIT, SVT, IC03, IC13, IC15, SVTP, CUTE数据集上进行评估,算法效果如下:
|
||||
|
|
@ -85,7 +88,12 @@
|
|||
|SAR|Resnet31| 87.20% | rec_r31_sar | [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/rec/rec_r31_sar_train.tar) |
|
||||
|SEED|Aster_Resnet| 85.35% | rec_resnet_stn_bilstm_att | [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/rec/rec_resnet_stn_bilstm_att.tar) |
|
||||
|SVTR|SVTR-Tiny| 89.25% | rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_en | [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_en_train.tar) |
|
||||
<<<<<<< HEAD
|
||||
|SPIN|ResNet32| 90.00% | rec_r32_gaspin_bilstm_att | coming soon |
|
||||
=======
|
||||
|ViTSTR|ViTSTR| 79.82% | rec_vitstr_none_ce | [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_vitstr_none_ce_train.tar) |
|
||||
|ABINet|Resnet45| 90.75% | rec_r45_abinet | [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_r45_abinet_train.tar) |
|
||||
>>>>>>> b6982b7fc720a1c9346838978b9228025f26c42b
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
|
|
@ -94,3 +102,16 @@
|
|||
|
||||
已支持的端到端OCR算法列表(戳链接获取使用教程):
|
||||
- [x] [PGNet](./algorithm_e2e_pgnet.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 表格识别算法
|
||||
|
||||
已支持的表格识别算法列表(戳链接获取使用教程):
|
||||
- [x] [TableMaster](./algorithm_table_master.md)
|
||||
|
||||
在PubTabNet表格识别公开数据集上,算法效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型|骨干网络|配置文件|acc|下载链接|
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|TableMaster|TableResNetExtra|[configs/table/table_master.yml](../../configs/table/table_master.yml)|77.47%|[训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_train.tar) / [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_infer.tar)|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
|||
# 场景文本识别算法-ABINet
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 算法简介](#1)
|
||||
- [2. 环境配置](#2)
|
||||
- [3. 模型训练、评估、预测](#3)
|
||||
- [3.1 训练](#3-1)
|
||||
- [3.2 评估](#3-2)
|
||||
- [3.3 预测](#3-3)
|
||||
- [4. 推理部署](#4)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python推理](#4-1)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++推理](#4-2)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving服务化部署](#4-3)
|
||||
- [4.4 更多推理部署](#4-4)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. 算法简介
|
||||
|
||||
论文信息:
|
||||
> [ABINet: Read Like Humans: Autonomous, Bidirectional and Iterative Language Modeling for Scene Text Recognition](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2021/papers/Fang_Read_Like_Humans_Autonomous_Bidirectional_and_Iterative_Language_Modeling_for_CVPR_2021_paper.pdf)
|
||||
> Shancheng Fang and Hongtao Xie and Yuxin Wang and Zhendong Mao and Yongdong Zhang
|
||||
> CVPR, 2021
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="model"></a>
|
||||
`ABINet`使用MJSynth和SynthText两个文字识别数据集训练,在IIIT, SVT, IC03, IC13, IC15, SVTP, CUTE数据集上进行评估,算法复现效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型|骨干网络|配置文件|Acc|下载链接|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|ABINet|ResNet45|[rec_r45_abinet.yml](../../configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml)|90.75%|[预训练、训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_r45_abinet_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. 环境配置
|
||||
请先参考[《运行环境准备》](./environment.md)配置PaddleOCR运行环境,参考[《项目克隆》](./clone.md)克隆项目代码。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. 模型训练、评估、预测
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3-1"></a>
|
||||
### 3.1 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
请参考[文本识别训练教程](./recognition.md)。PaddleOCR对代码进行了模块化,训练`ABINet`识别模型时需要**更换配置文件**为`ABINet`的[配置文件](../../configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 启动训练
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
具体地,在完成数据准备后,便可以启动训练,训练命令如下:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
#单卡训练(训练周期长,不建议)
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml
|
||||
|
||||
#多卡训练,通过--gpus参数指定卡号
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3-2"></a>
|
||||
### 3.2 评估
|
||||
|
||||
可下载已训练完成的[模型文件](#model),使用如下命令进行评估:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 注意将pretrained_model的路径设置为本地路径。
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0' tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_r45_abinet_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3-3"></a>
|
||||
### 3.3 预测
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令进行单张图片预测:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 注意将pretrained_model的路径设置为本地路径。
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml -o Global.infer_img='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' Global.pretrained_model=./rec_r45_abinet_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
# 预测文件夹下所有图像时,可修改infer_img为文件夹,如 Global.infer_img='./doc/imgs_words_en/'。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||
## 4. 推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-1"></a>
|
||||
### 4.1 Python推理
|
||||
首先将训练得到best模型,转换成inference model。这里以训练完成的模型为例([模型下载地址](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_r45_abinet_train.tar) ),可以使用如下命令进行转换:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 注意将pretrained_model的路径设置为本地路径。
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_r45_abinet_train/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/rec_r45_abinet/
|
||||
```
|
||||
**注意:**
|
||||
- 如果您是在自己的数据集上训练的模型,并且调整了字典文件,请注意修改配置文件中的`character_dict_path`是否是所需要的字典文件。
|
||||
- 如果您修改了训练时的输入大小,请修改`tools/export_model.py`文件中的对应ABINet的`infer_shape`。
|
||||
|
||||
转换成功后,在目录下有三个文件:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/inference/rec_r45_abinet/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams # 识别inference模型的参数文件
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info # 识别inference模型的参数信息,可忽略
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel # 识别inference模型的program文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行如下命令进行模型推理:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' --rec_model_dir='./inference/rec_r45_abinet/' --rec_algorithm='ABINet' --rec_image_shape='3,32,128' --rec_char_dict_path='./ppocr/utils/ic15_dict.txt'
|
||||
# 预测文件夹下所有图像时,可修改image_dir为文件夹,如 --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/'。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
执行命令后,上面图像的预测结果(识别的文本和得分)会打印到屏幕上,示例如下:
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9999995231628418)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 训练上述模型采用的图像分辨率是[3,32,128],需要通过参数`rec_image_shape`设置为您训练时的识别图像形状。
|
||||
- 在推理时需要设置参数`rec_char_dict_path`指定字典,如果您修改了字典,请修改该参数为您的字典文件。
|
||||
- 如果您修改了预处理方法,需修改`tools/infer/predict_rec.py`中ABINet的预处理为您的预处理方法。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-2"></a>
|
||||
### 4.2 C++推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
由于C++预处理后处理还未支持ABINet,所以暂未支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-3"></a>
|
||||
### 4.3 Serving服务化部署
|
||||
|
||||
暂不支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-4"></a>
|
||||
### 4.4 更多推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
暂不支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||
## 5. FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
1. MJSynth和SynthText两种数据集来自于[ABINet源repo](https://github.com/FangShancheng/ABINet) 。
|
||||
2. 我们使用ABINet作者提供的预训练模型进行finetune训练。
|
||||
|
||||
## 引用
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{Fang2021ABINet,
|
||||
title = {ABINet: Read Like Humans: Autonomous, Bidirectional and Iterative Language Modeling for Scene Text Recognition},
|
||||
author = {Shancheng Fang and Hongtao Xie and Yuxin Wang and Zhendong Mao and Yongdong Zhang},
|
||||
booktitle = {CVPR},
|
||||
year = {2021},
|
||||
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06495},
|
||||
pages = {7098-7107}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,6 +12,7 @@
|
|||
- [4.3 Serving服务化部署](#4-3)
|
||||
- [4.4 更多推理部署](#4-4)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5)
|
||||
- [6. 发行公告](#6)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. 算法简介
|
||||
|
|
@ -110,7 +111,7 @@ python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png'
|
|||
执行命令后,上面图像的预测结果(识别的文本和得分)会打印到屏幕上,示例如下:
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9265879392623901)
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9465042352676392)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:
|
||||
|
|
@ -140,12 +141,147 @@ Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9265879392623901)
|
|||
|
||||
1. `NRTR`论文中使用Beam搜索进行解码字符,但是速度较慢,这里默认未使用Beam搜索,以贪婪搜索进行解码字符。
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="6"></a>
|
||||
## 6. 发行公告
|
||||
|
||||
1. release/2.6更新NRTR代码结构,新版NRTR可加载旧版(release/2.5及之前)模型参数,使用下面示例代码将旧版模型参数转换为新版模型参数:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
params = paddle.load('path/' + '.pdparams') # 旧版本参数
|
||||
state_dict = model.state_dict() # 新版模型参数
|
||||
new_state_dict = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for k1, v1 in state_dict.items():
|
||||
|
||||
k = k1
|
||||
if 'encoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q[:, :, 0, 0], k[:, :, 0, 0], v[:, :, 0, 0]], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')]
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')]
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')]
|
||||
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q, k, v], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'out_proj' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'norm3' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para.replace('norm3', 'norm2')]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'norm1' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q[:, :, 0, 0], k[:, :, 0, 0], v[:, :, 0, 0]], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')]
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')]
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q, k, v], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'out_proj' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'q' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('q', 'conv1')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = q[:, :, 0, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'q' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('q', 'conv1')]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = q
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'kv' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv2')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv3')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([k[:, :, 0, 0], v[:, :, 0, 0]], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'kv' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv2')]
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv3')]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([k, v], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'out_proj' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'norm' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
elif 'mlp' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('fc', 'conv')
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('mlp.', '')
|
||||
w = params[k_para].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = w[:, :, 0, 0]
|
||||
elif 'mlp' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('fc', 'conv')
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('mlp.', '')
|
||||
w = params[k_para]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = w
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k1]
|
||||
|
||||
if list(new_state_dict[k1].shape) != list(v1.shape):
|
||||
print(k1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for k, v1 in state_dict.items():
|
||||
if k not in new_state_dict.keys():
|
||||
print(1, k)
|
||||
elif list(new_state_dict[k].shape) != list(v1.shape):
|
||||
print(2, k)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model.set_state_dict(new_state_dict)
|
||||
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), 'nrtrnew_from_old_params.pdparams')
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 新版相比与旧版,代码结构简洁,推理速度有所提高。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 引用
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{Sheng2019NRTR,
|
||||
title = {NRTR: A No-Recurrence Sequence-to-Sequence Model For Scene Text Recognition},
|
||||
author = {Fenfen Sheng and Zhineng Chen andBo Xu},
|
||||
author = {Fenfen Sheng and Zhineng Chen and Bo Xu},
|
||||
booktitle = {ICDAR},
|
||||
year = {2019},
|
||||
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1806.00926},
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,6 @@ python3 tools/export_model.py -c ./rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_en_train/rec_svtr_tiny
|
|||
|
||||
**注意:**
|
||||
- 如果您是在自己的数据集上训练的模型,并且调整了字典文件,请注意修改配置文件中的`character_dict_path`是否为所正确的字典文件。
|
||||
- 如果您修改了训练时的输入大小,请修改`tools/export_model.py`文件中的对应SVTR的`infer_shape`。
|
||||
|
||||
转换成功后,在目录下有三个文件:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
|||
# 场景文本识别算法-ViTSTR
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 算法简介](#1)
|
||||
- [2. 环境配置](#2)
|
||||
- [3. 模型训练、评估、预测](#3)
|
||||
- [3.1 训练](#3-1)
|
||||
- [3.2 评估](#3-2)
|
||||
- [3.3 预测](#3-3)
|
||||
- [4. 推理部署](#4)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python推理](#4-1)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++推理](#4-2)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving服务化部署](#4-3)
|
||||
- [4.4 更多推理部署](#4-4)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. 算法简介
|
||||
|
||||
论文信息:
|
||||
> [Vision Transformer for Fast and Efficient Scene Text Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.08582)
|
||||
> Rowel Atienza
|
||||
> ICDAR, 2021
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="model"></a>
|
||||
`ViTSTR`使用MJSynth和SynthText两个文字识别数据集训练,在IIIT, SVT, IC03, IC13, IC15, SVTP, CUTE数据集上进行评估,算法复现效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型|骨干网络|配置文件|Acc|下载链接|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|ViTSTR|ViTSTR|[rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml](../../configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml)|79.82%|[训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_vitstr_none_ce_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. 环境配置
|
||||
请先参考[《运行环境准备》](./environment.md)配置PaddleOCR运行环境,参考[《项目克隆》](./clone.md)克隆项目代码。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. 模型训练、评估、预测
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3-1"></a>
|
||||
### 3.1 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
请参考[文本识别训练教程](./recognition.md)。PaddleOCR对代码进行了模块化,训练`ViTSTR`识别模型时需要**更换配置文件**为`ViTSTR`的[配置文件](../../configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 启动训练
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
具体地,在完成数据准备后,便可以启动训练,训练命令如下:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
#单卡训练(训练周期长,不建议)
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml
|
||||
|
||||
#多卡训练,通过--gpus参数指定卡号
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3-2"></a>
|
||||
### 3.2 评估
|
||||
|
||||
可下载已训练完成的[模型文件](#model),使用如下命令进行评估:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 注意将pretrained_model的路径设置为本地路径。
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0' tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_vitstr_none_ce_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3-3"></a>
|
||||
### 3.3 预测
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令进行单张图片预测:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 注意将pretrained_model的路径设置为本地路径。
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml -o Global.infer_img='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' Global.pretrained_model=./rec_vitstr_none_ce_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
# 预测文件夹下所有图像时,可修改infer_img为文件夹,如 Global.infer_img='./doc/imgs_words_en/'。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||
## 4. 推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-1"></a>
|
||||
### 4.1 Python推理
|
||||
首先将训练得到best模型,转换成inference model。这里以训练完成的模型为例([模型下载地址](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_vitstr_none_ce_train.tar) ),可以使用如下命令进行转换:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 注意将pretrained_model的路径设置为本地路径。
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_vitstr_none_ce_train/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/rec_vitstr/
|
||||
```
|
||||
**注意:**
|
||||
- 如果您是在自己的数据集上训练的模型,并且调整了字典文件,请注意修改配置文件中的`character_dict_path`是否是所需要的字典文件。
|
||||
- 如果您修改了训练时的输入大小,请修改`tools/export_model.py`文件中的对应ViTSTR的`infer_shape`。
|
||||
|
||||
转换成功后,在目录下有三个文件:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/inference/rec_vitstr/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams # 识别inference模型的参数文件
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info # 识别inference模型的参数信息,可忽略
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel # 识别inference模型的program文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行如下命令进行模型推理:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' --rec_model_dir='./inference/rec_vitstr/' --rec_algorithm='ViTSTR' --rec_image_shape='1,224,224' --rec_char_dict_path='./ppocr/utils/EN_symbol_dict.txt'
|
||||
# 预测文件夹下所有图像时,可修改image_dir为文件夹,如 --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/'。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
执行命令后,上面图像的预测结果(识别的文本和得分)会打印到屏幕上,示例如下:
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9998350143432617)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 训练上述模型采用的图像分辨率是[1,224,224],需要通过参数`rec_image_shape`设置为您训练时的识别图像形状。
|
||||
- 在推理时需要设置参数`rec_char_dict_path`指定字典,如果您修改了字典,请修改该参数为您的字典文件。
|
||||
- 如果您修改了预处理方法,需修改`tools/infer/predict_rec.py`中ViTSTR的预处理为您的预处理方法。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-2"></a>
|
||||
### 4.2 C++推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
由于C++预处理后处理还未支持ViTSTR,所以暂未支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-3"></a>
|
||||
### 4.3 Serving服务化部署
|
||||
|
||||
暂不支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-4"></a>
|
||||
### 4.4 更多推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
暂不支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||
## 5. FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在`ViTSTR`论文中,使用在ImageNet1k上的预训练权重进行初始化训练,我们在训练未采用预训练权重,最终精度没有变化甚至有所提高。
|
||||
2. 我们仅仅复现了`ViTSTR`中的tiny版本,如果需要使用small、base版本,可将[ViTSTR源repo](https://github.com/roatienza/deep-text-recognition-benchmark) 中的预训练权重转为Paddle权重使用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 引用
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{Atienza2021ViTSTR,
|
||||
title = {Vision Transformer for Fast and Efficient Scene Text Recognition},
|
||||
author = {Rowel Atienza},
|
||||
booktitle = {ICDAR},
|
||||
year = {2021},
|
||||
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.08582}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
|
|||
# 表格识别算法-TableMASTER
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 算法简介](#1-算法简介)
|
||||
- [2. 环境配置](#2-环境配置)
|
||||
- [3. 模型训练、评估、预测](#3-模型训练评估预测)
|
||||
- [4. 推理部署](#4-推理部署)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python推理](#41-python推理)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++推理部署](#42-c推理部署)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving服务化部署](#43-serving服务化部署)
|
||||
- [4.4 更多推理部署](#44-更多推理部署)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5-faq)
|
||||
- [引用](#引用)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. 算法简介
|
||||
|
||||
论文信息:
|
||||
> [TableMaster: PINGAN-VCGROUP’S SOLUTION FOR ICDAR 2021 COMPETITION ON SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE PARSING TASK B: TABLE RECOGNITION TO HTML](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.01848.pdf)
|
||||
> Ye, Jiaquan and Qi, Xianbiao and He, Yelin and Chen, Yihao and Gu, Dengyi and Gao, Peng and Xiao, Rong
|
||||
> 2021
|
||||
|
||||
在PubTabNet表格识别公开数据集上,算法复现效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型|骨干网络|配置文件|acc|下载链接|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|TableMaster|TableResNetExtra|[configs/table/table_master.yml](../../configs/table/table_master.yml)|77.47%|[训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_train.tar)/[推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_infer.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. 环境配置
|
||||
请先参考[《运行环境准备》](./environment.md)配置PaddleOCR运行环境,参考[《项目克隆》](./clone.md)克隆项目代码。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. 模型训练、评估、预测
|
||||
|
||||
上述TableMaster模型使用PubTabNet表格识别公开数据集训练得到,数据集下载可参考 [table_datasets](./dataset/table_datasets.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
数据下载完成后,请参考[文本识别教程](./recognition.md)进行训练。PaddleOCR对代码进行了模块化,训练不同的模型只需要**更换配置文件**即可。
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||
## 4. 推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-1"></a>
|
||||
### 4.1 Python推理
|
||||
首先将训练得到best模型,转换成inference model。以基于TableResNetExtra骨干网络,在PubTabNet数据集训练的模型为例([模型下载地址](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/contribution/table_master.tar)),可以使用如下命令进行转换:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 注意将pretrained_model的路径设置为本地路径。
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/table/table_master.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=output/table_master/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/table_master
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:**
|
||||
- 如果您是在自己的数据集上训练的模型,并且调整了字典文件,请注意修改配置文件中的`character_dict_path`是否为所正确的字典文件。
|
||||
|
||||
转换成功后,在目录下有三个文件:
|
||||
```
|
||||
./inference/table_master/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams # 识别inference模型的参数文件
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info # 识别inference模型的参数信息,可忽略
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel # 识别inference模型的program文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
执行如下命令进行模型推理:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd ppstructure/
|
||||
python3.7 table/predict_structure.py --table_model_dir=../output/table_master/table_structure_tablemaster_infer/ --table_algorithm=TableMaster --table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_master_structure_dict.txt --table_max_len=480 --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg
|
||||
# 预测文件夹下所有图像时,可修改image_dir为文件夹,如 --image_dir='docs/table'。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行命令后,上面图像的预测结果(结构信息和表格中每个单元格的坐标)会打印到屏幕上,同时会保存单元格坐标的可视化结果。示例如下:
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
[2022/06/16 13:06:54] ppocr INFO: result: ['<html>', '<body>', '<table>', '<thead>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '</thead>', '<tbody>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '</tbody>', '</table>', '</body>', '</html>'], [[72.17591094970703, 10.759100914001465, 60.29658508300781, 16.6805362701416], [161.85562133789062, 10.884308815002441, 14.9495210647583, 16.727018356323242], [277.79876708984375, 29.54340362548828, 31.490320205688477, 18.143272399902344],
|
||||
...
|
||||
[336.11724853515625, 280.3601989746094, 39.456939697265625, 18.121286392211914]]
|
||||
[2022/06/16 13:06:54] ppocr INFO: save vis result to ./output/table.jpg
|
||||
[2022/06/16 13:06:54] ppocr INFO: Predict time of docs/table/table.jpg: 17.36806297302246
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:
|
||||
|
||||
- TableMaster在推理时比较慢,建议使用GPU进行使用。
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-2"></a>
|
||||
### 4.2 C++推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
由于C++预处理后处理还未支持TableMaster,所以暂未支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-3"></a>
|
||||
### 4.3 Serving服务化部署
|
||||
|
||||
暂不支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-4"></a>
|
||||
### 4.4 更多推理部署
|
||||
|
||||
暂不支持
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||
## 5. FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
## 引用
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{ye2021pingan,
|
||||
title={PingAn-VCGroup's Solution for ICDAR 2021 Competition on Scientific Literature Parsing Task B: Table Recognition to HTML},
|
||||
author={Ye, Jiaquan and Qi, Xianbiao and He, Yelin and Chen, Yihao and Gu, Dengyi and Gao, Peng and Xiao, Rong},
|
||||
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.01848},
|
||||
year={2021}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
|||
# 场景应用
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR场景应用覆盖通用,制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用,在PP-OCR、PP-Structure的通用能力基础之上,以notebook的形式展示利用场景数据微调、模型优化方法、数据增广等内容,为开发者快速落地OCR应用提供示范与启发。
|
||||
|
||||
> 如需下载全部垂类模型,可以扫描下方二维码,关注公众号填写问卷后,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取20G OCR学习大礼包(内含《动手学OCR》电子书、课程回放视频、前沿论文等重磅资料)
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果您是企业开发者且未在下述场景中找到合适的方案,可以填写[OCR应用合作调研问卷](https://paddle.wjx.cn/vj/QwF7GKw.aspx),免费与官方团队展开不同层次的合作,包括但不限于问题抽象、确定技术方案、项目答疑、共同研发等。如果您已经使用PaddleOCR落地项目,也可以填写此问卷,与飞桨平台共同宣传推广,提升企业技术品宣。期待您的提交!
|
||||
|
||||
## 通用
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | -------- | ---------- | ------------ |
|
||||
| 高精度中文识别模型SVTR | 新增模型 | 手写体识别 | 新增字形支持 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 制造
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| -------------- | ------------------------------ | -------------- | -------------------- |
|
||||
| 数码管识别 | 数码管数据合成、漏识别调优 | 电表识别 | 大分辨率图像检测调优 |
|
||||
| 液晶屏读数识别 | 检测模型蒸馏、Serving部署 | PCB文字识别 | 小尺寸文本检测与识别 |
|
||||
| 包装生产日期 | 点阵字符合成、过曝过暗文字识别 | 液晶屏缺陷检测 | 非文字形态识别 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 金融
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| -------------- | ------------------------ | ------------ | --------------------- |
|
||||
| 表单VQA | 多模态通用表单结构化提取 | 通用卡证识别 | 通用结构化提取 |
|
||||
| 增值税发票 | 尽请期待 | 身份证识别 | 结构化提取、图像阴影 |
|
||||
| 印章检测与识别 | 端到端弯曲文本识别 | 合同比对 | 密集文本检测、NLP串联 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 交通
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 类别 | 亮点 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------------------ | ---------- | -------- |
|
||||
| 车牌识别 | 多角度图像、轻量模型、端侧部署 | 快递单识别 | 尽请期待 |
|
||||
| 驾驶证/行驶证识别 | 尽请期待 | | |
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,6 +34,7 @@ json.dumps编码前的图像标注信息是包含多个字典的list,字典中
|
|||
| ICDAR 2015 |https://rrc.cvc.uab.es/?ch=4&com=downloads| [train](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/train_icdar2015_label.txt) / [test](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/test_icdar2015_label.txt) |
|
||||
| ctw1500 |https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/ctw1500.zip| 图片下载地址中已包含 |
|
||||
| total text |https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/total_text.tar| 图片下载地址中已包含 |
|
||||
| td tr |https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/TD_TR.tar| 图片下载地址中已包含 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.2.1 ICDAR 2015
|
||||
ICDAR 2015 数据集包含1000张训练图像和500张测试图像。ICDAR 2015 数据集可以从上表中链接下载,首次下载需注册。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,7 +7,8 @@
|
|||
- [1. 文本检测模型推理](#1-文本检测模型推理)
|
||||
- [2. 文本识别模型推理](#2-文本识别模型推理)
|
||||
- [2.1 超轻量中文识别模型推理](#21-超轻量中文识别模型推理)
|
||||
- [2.2 多语言模型的推理](#22-多语言模型的推理)
|
||||
- [2.2 英文识别模型推理](#22-英文识别模型推理)
|
||||
- [2.3 多语言模型的推理](#23-多语言模型的推理)
|
||||
- [3. 方向分类模型推理](#3-方向分类模型推理)
|
||||
- [4. 文本检测、方向分类和文字识别串联推理](#4-文本检测方向分类和文字识别串联推理)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,9 +79,29 @@ python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_4.jpg"
|
|||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_4.jpg:('实力活力', 0.9956803321838379)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="英文识别模型推理"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 英文识别模型推理
|
||||
|
||||
英文识别模型推理,可以执行如下命令, 注意修改字典路径:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 下载英文数字识别模型:
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
tar xf en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_words/en/word_1.png" --rec_model_dir="./en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer/" --rec_char_dict_path="ppocr/utils/en_dict.txt"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
执行命令后,上图的预测结果为:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words/en/word_1.png: ('JOINT', 0.998160719871521)
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a name="多语言模型的推理"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 多语言模型的推理
|
||||
### 2.3 多语言模型的推理
|
||||
|
||||
如果您需要预测的是其他语言模型,可以在[此链接](./models_list.md#%E5%A4%9A%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B)中找到对应语言的inference模型,在使用inference模型预测时,需要通过`--rec_char_dict_path`指定使用的字典路径, 同时为了得到正确的可视化结果,需要通过 `--vis_font_path` 指定可视化的字体路径,`doc/fonts/` 路径下有默认提供的小语种字体,例如韩文识别:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -30,11 +30,11 @@ PP-OCR系统pipeline如下:
|
|||
|
||||
PP-OCR系统在持续迭代优化,目前已发布PP-OCR和PP-OCRv2两个版本:
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCR从骨干网络选择和调整、预测头部的设计、数据增强、学习率变换策略、正则化参数选择、预训练模型使用以及模型自动裁剪量化8个方面,采用19个有效策略,对各个模块的模型进行效果调优和瘦身(如绿框所示),最终得到整体大小为3.5M的超轻量中英文OCR和2.8M的英文数字OCR。更多细节请参考PP-OCR技术方案 https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.09941
|
||||
PP-OCR从骨干网络选择和调整、预测头部的设计、数据增强、学习率变换策略、正则化参数选择、预训练模型使用以及模型自动裁剪量化8个方面,采用19个有效策略,对各个模块的模型进行效果调优和瘦身(如绿框所示),最终得到整体大小为3.5M的超轻量中英文OCR和2.8M的英文数字OCR。更多细节请参考[PP-OCR技术报告](https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.09941)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### PP-OCRv2
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv2在PP-OCR的基础上,进一步在5个方面重点优化,检测模型采用CML协同互学习知识蒸馏策略和CopyPaste数据增广策略;识别模型采用LCNet轻量级骨干网络、UDML 改进知识蒸馏策略和[Enhanced CTC loss](./enhanced_ctc_loss.md)损失函数改进(如上图红框所示),进一步在推理速度和预测效果上取得明显提升。更多细节请参考PP-OCRv2[技术报告](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03144)。
|
||||
PP-OCRv2在PP-OCR的基础上,进一步在5个方面重点优化,检测模型采用CML协同互学习知识蒸馏策略和CopyPaste数据增广策略;识别模型采用LCNet轻量级骨干网络、UDML 改进知识蒸馏策略和[Enhanced CTC loss](./enhanced_ctc_loss.md)损失函数改进(如上图红框所示),进一步在推理速度和预测效果上取得明显提升。更多细节请参考[PP-OCRv2技术报告](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03144)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### PP-OCRv3
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ PP-OCRv3系统pipeline如下:
|
|||
<img src="../ppocrv3_framework.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
更多细节请参考PP-OCRv3[技术报告](./PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)。
|
||||
更多细节请参考[PP-OCRv3技术报告](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.03001v2) 👉[中文简洁版](./PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,5 +6,6 @@ PaddleOCR will add cutting-edge OCR algorithms and models continuously. Check ou
|
|||
- [text detection algorithms](./algorithm_overview_en.md#11)
|
||||
- [text recognition algorithms](./algorithm_overview_en.md#12)
|
||||
- [end-to-end algorithms](./algorithm_overview_en.md#2)
|
||||
- [table recognition algorithms](./algorithm_overview_en.md#3)
|
||||
|
||||
Developers are welcome to contribute more algorithms! Please refer to [add new algorithm](./add_new_algorithm_en.md) guideline.
|
||||
Developers are welcome to contribute more algorithms! Please refer to [add new algorithm](./add_new_algorithm_en.md) guideline.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
|||
# OCR Algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. Two-stage Algorithms](#1)
|
||||
* [1.1 Text Detection Algorithms](#11)
|
||||
* [1.2 Text Recognition Algorithms](#12)
|
||||
- [1.1 Text Detection Algorithms](#11)
|
||||
- [1.2 Text Recognition Algorithms](#12)
|
||||
- [2. End-to-end Algorithms](#2)
|
||||
- [3. Table Recognition Algorithms](#3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial lists the OCR algorithms supported by PaddleOCR, as well as the models and metrics of each algorithm on **English public datasets**. It is mainly used for algorithm introduction and algorithm performance comparison. For more models on other datasets including Chinese, please refer to [PP-OCR v2.0 models list](./models_list_en.md).
|
||||
|
|
@ -65,7 +66,12 @@ Supported text recognition algorithms (Click the link to get the tutorial):
|
|||
- [x] [SAR](./algorithm_rec_sar_en.md)
|
||||
- [x] [SEED](./algorithm_rec_seed_en.md)
|
||||
- [x] [SVTR](./algorithm_rec_svtr_en.md)
|
||||
<<<<<<< HEAD
|
||||
- [x] [SPIN](./algorithm_rec_spin_en.md)
|
||||
=======
|
||||
- [x] [ViTSTR](./algorithm_rec_vitstr_en.md)
|
||||
- [x] [ABINet](./algorithm_rec_abinet_en.md)
|
||||
>>>>>>> b6982b7fc720a1c9346838978b9228025f26c42b
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [DTRB](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01906), the training and evaluation result of these above text recognition (using MJSynth and SynthText for training, evaluate on IIIT, SVT, IC03, IC13, IC15, SVTP, CUTE) is as follow:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,6 +90,8 @@ Refer to [DTRB](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01906), the training and evaluation r
|
|||
|SAR|Resnet31| 87.20% | rec_r31_sar | [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/rec/rec_r31_sar_train.tar) |
|
||||
|SEED|Aster_Resnet| 85.35% | rec_resnet_stn_bilstm_att | [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.1/rec/rec_resnet_stn_bilstm_att.tar) |
|
||||
|SVTR|SVTR-Tiny| 89.25% | rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_en | [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_en_train.tar) |
|
||||
|ViTSTR|ViTSTR| 79.82% | rec_vitstr_none_ce | [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_vitstr_none_none_train.tar) |
|
||||
|ABINet|Resnet45| 90.75% | rec_r45_abinet | [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_r45_abinet_train.tar) |
|
||||
|SPIN|ResNet32| 90.00% | rec_r32_gaspin_bilstm_att | coming soon |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,3 +101,15 @@ Refer to [DTRB](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01906), the training and evaluation r
|
|||
|
||||
Supported end-to-end algorithms (Click the link to get the tutorial):
|
||||
- [x] [PGNet](./algorithm_e2e_pgnet_en.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. Table Recognition Algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
Supported table recognition algorithms (Click the link to get the tutorial):
|
||||
- [x] [TableMaster](./algorithm_table_master_en.md)
|
||||
|
||||
On the PubTabNet dataset, the algorithm result is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|Model|Backbone|Config|Acc|Download link|
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|TableMaster|TableResNetExtra|[configs/table/table_master.yml](../../configs/table/table_master.yml)|77.47%|[trained](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_train.tar) / [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_infer.tar)|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
|||
# ABINet
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. Introduction](#1)
|
||||
- [2. Environment](#2)
|
||||
- [3. Model Training / Evaluation / Prediction](#3)
|
||||
- [3.1 Training](#3-1)
|
||||
- [3.2 Evaluation](#3-2)
|
||||
- [3.3 Prediction](#3-3)
|
||||
- [4. Inference and Deployment](#4)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python Inference](#4-1)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++ Inference](#4-2)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving](#4-3)
|
||||
- [4.4 More](#4-4)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Paper:
|
||||
> [ABINet: Read Like Humans: Autonomous, Bidirectional and Iterative Language Modeling for Scene Text Recognition](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2021/papers/Fang_Read_Like_Humans_Autonomous_Bidirectional_and_Iterative_Language_Modeling_for_CVPR_2021_paper.pdf)
|
||||
> Shancheng Fang and Hongtao Xie and Yuxin Wang and Zhendong Mao and Yongdong Zhang
|
||||
> CVPR, 2021
|
||||
|
||||
Using MJSynth and SynthText two text recognition datasets for training, and evaluating on IIIT, SVT, IC03, IC13, IC15, SVTP, CUTE datasets, the algorithm reproduction effect is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|Model|Backbone|config|Acc|Download link|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|ABINet|ResNet45|[rec_r45_abinet.yml](../../configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml)|90.75%|[pretrained & trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_r45_abinet_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. Environment
|
||||
Please refer to ["Environment Preparation"](./environment_en.md) to configure the PaddleOCR environment, and refer to ["Project Clone"](./clone_en.md) to clone the project code.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. Model Training / Evaluation / Prediction
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to [Text Recognition Tutorial](./recognition_en.md). PaddleOCR modularizes the code, and training different recognition models only requires **changing the configuration file**.
|
||||
|
||||
Training:
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, after the data preparation is completed, the training can be started. The training command is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#Single GPU training (long training period, not recommended)
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml
|
||||
|
||||
#Multi GPU training, specify the gpu number through the --gpus parameter
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Evaluation:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# GPU evaluation
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0' tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml -o Global.pretrained_model={path/to/weights}/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Prediction:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# The configuration file used for prediction must match the training
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml -o Global.infer_img='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' Global.pretrained_model=./rec_r45_abinet_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||
## 4. Inference and Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-1"></a>
|
||||
### 4.1 Python Inference
|
||||
First, the model saved during the ABINet text recognition training process is converted into an inference model. ( [Model download link](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_r45_abinet_train.tar)) ), you can use the following command to convert:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/rec_r45_abinet.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_r45_abinet_train/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/rec_r45_abinet
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:**
|
||||
- If you are training the model on your own dataset and have modified the dictionary file, please pay attention to modify the `character_dict_path` in the configuration file to the modified dictionary file.
|
||||
- If you modified the input size during training, please modify the `infer_shape` corresponding to ABINet in the `tools/export_model.py` file.
|
||||
|
||||
After the conversion is successful, there are three files in the directory:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/inference/rec_r45_abinet/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For ABINet text recognition model inference, the following commands can be executed:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' --rec_model_dir='./inference/rec_r45_abinet/' --rec_algorithm='ABINet' --rec_image_shape='3,32,128' --rec_char_dict_path='./ppocr/utils/ic15_dict.txt'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After executing the command, the prediction result (recognized text and score) of the image above is printed to the screen, an example is as follows:
|
||||
The result is as follows:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9999995231628418)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-2"></a>
|
||||
### 4.2 C++ Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-3"></a>
|
||||
### 4.3 Serving
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-4"></a>
|
||||
### 4.4 More
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||
## 5. FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
1. Note that the MJSynth and SynthText datasets come from [ABINet repo](https://github.com/FangShancheng/ABINet).
|
||||
2. We use the pre-trained model provided by the ABINet authors for finetune training.
|
||||
|
||||
## Citation
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{Fang2021ABINet,
|
||||
title = {ABINet: Read Like Humans: Autonomous, Bidirectional and Iterative Language Modeling for Scene Text Recognition},
|
||||
author = {Shancheng Fang and Hongtao Xie and Yuxin Wang and Zhendong Mao and Yongdong Zhang},
|
||||
booktitle = {CVPR},
|
||||
year = {2021},
|
||||
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06495},
|
||||
pages = {7098-7107}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,6 +12,7 @@
|
|||
- [4.3 Serving](#4-3)
|
||||
- [4.4 More](#4-4)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5)
|
||||
- [6. Release Note](#6)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. Introduction
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,7 +26,7 @@ Using MJSynth and SynthText two text recognition datasets for training, and eval
|
|||
|
||||
|Model|Backbone|config|Acc|Download link|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|NRTR|MTB|[rec_mtb_nrtr.yml](../../configs/rec/rec_mtb_nrtr.yml)|84.21%|[train model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/en/rec_mtb_nrtr_train.tar)|
|
||||
|NRTR|MTB|[rec_mtb_nrtr.yml](../../configs/rec/rec_mtb_nrtr.yml)|84.21%|[trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/en/rec_mtb_nrtr_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. Environment
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,7 +99,7 @@ python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png'
|
|||
After executing the command, the prediction result (recognized text and score) of the image above is printed to the screen, an example is as follows:
|
||||
The result is as follows:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9265879392623901)
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9465042352676392)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-2"></a>
|
||||
|
|
@ -121,12 +122,146 @@ Not supported
|
|||
|
||||
1. In the `NRTR` paper, Beam search is used to decode characters, but the speed is slow. Beam search is not used by default here, and greedy search is used to decode characters.
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="6"></a>
|
||||
## 6. Release Note
|
||||
|
||||
1. The release/2.6 version updates the NRTR code structure. The new version of NRTR can load the model parameters of the old version (release/2.5 and before), and you may use the following code to convert the old version model parameters to the new version model parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
params = paddle.load('path/' + '.pdparams') # the old version parameters
|
||||
state_dict = model.state_dict() # the new version model parameters
|
||||
new_state_dict = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for k1, v1 in state_dict.items():
|
||||
|
||||
k = k1
|
||||
if 'encoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q[:, :, 0, 0], k[:, :, 0, 0], v[:, :, 0, 0]], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')]
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')]
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')]
|
||||
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q, k, v], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'out_proj' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'norm3' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para.replace('norm3', 'norm2')]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'encoder' in k and 'norm1' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q[:, :, 0, 0], k[:, :, 0, 0], v[:, :, 0, 0]], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'qkv' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv1')]
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv2')]
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('qkv', 'conv3')]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([q, k, v], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'self_attn' in k and 'out_proj' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'q' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('q', 'conv1')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = q[:, :, 0, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'q' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
q = params[k_para.replace('q', 'conv1')]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = q
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'kv' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv2')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv3')].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([k[:, :, 0, 0], v[:, :, 0, 0]], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'kv' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
k = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv2')]
|
||||
v = params[k_para.replace('kv', 'conv3')]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = np.concatenate([k, v], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'cross_attn' in k and 'out_proj' in k:
|
||||
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('cross_attn', 'multihead_attn')
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
elif 'decoder' in k and 'norm' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k_para]
|
||||
elif 'mlp' in k and 'weight' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('fc', 'conv')
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('mlp.', '')
|
||||
w = params[k_para].transpose((1, 0, 2, 3))
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = w[:, :, 0, 0]
|
||||
elif 'mlp' in k and 'bias' in k:
|
||||
k_para = k[:13] + 'layers.' + k[13:]
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('fc', 'conv')
|
||||
k_para = k_para.replace('mlp.', '')
|
||||
w = params[k_para]
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = w
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
new_state_dict[k1] = params[k1]
|
||||
|
||||
if list(new_state_dict[k1].shape) != list(v1.shape):
|
||||
print(k1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for k, v1 in state_dict.items():
|
||||
if k not in new_state_dict.keys():
|
||||
print(1, k)
|
||||
elif list(new_state_dict[k].shape) != list(v1.shape):
|
||||
print(2, k)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model.set_state_dict(new_state_dict)
|
||||
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), 'nrtrnew_from_old_params.pdparams')
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. The new version has a clean code structure and improved inference speed compared with the old version.
|
||||
|
||||
## Citation
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{Sheng2019NRTR,
|
||||
title = {NRTR: A No-Recurrence Sequence-to-Sequence Model For Scene Text Recognition},
|
||||
author = {Fenfen Sheng and Zhineng Chen andBo Xu},
|
||||
author = {Fenfen Sheng and Zhineng Chen and Bo Xu},
|
||||
booktitle = {ICDAR},
|
||||
year = {2019},
|
||||
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1806.00926},
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -88,7 +88,6 @@ python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/rec_svtrnet.yml -o Global.pretraine
|
|||
|
||||
**Note:**
|
||||
- If you are training the model on your own dataset and have modified the dictionary file, please pay attention to modify the `character_dict_path` in the configuration file to the modified dictionary file.
|
||||
- If you modified the input size during training, please modify the `infer_shape` corresponding to SVTR in the `tools/export_model.py` file.
|
||||
|
||||
After the conversion is successful, there are three files in the directory:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
|||
# ViTSTR
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. Introduction](#1)
|
||||
- [2. Environment](#2)
|
||||
- [3. Model Training / Evaluation / Prediction](#3)
|
||||
- [3.1 Training](#3-1)
|
||||
- [3.2 Evaluation](#3-2)
|
||||
- [3.3 Prediction](#3-3)
|
||||
- [4. Inference and Deployment](#4)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python Inference](#4-1)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++ Inference](#4-2)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving](#4-3)
|
||||
- [4.4 More](#4-4)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Paper:
|
||||
> [Vision Transformer for Fast and Efficient Scene Text Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.08582)
|
||||
> Rowel Atienza
|
||||
> ICDAR, 2021
|
||||
|
||||
Using MJSynth and SynthText two text recognition datasets for training, and evaluating on IIIT, SVT, IC03, IC13, IC15, SVTP, CUTE datasets, the algorithm reproduction effect is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|Model|Backbone|config|Acc|Download link|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|ViTSTR|ViTSTR|[rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml](../../configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml)|79.82%|[trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_vitstr_none_none_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. Environment
|
||||
Please refer to ["Environment Preparation"](./environment_en.md) to configure the PaddleOCR environment, and refer to ["Project Clone"](./clone_en.md) to clone the project code.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. Model Training / Evaluation / Prediction
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to [Text Recognition Tutorial](./recognition_en.md). PaddleOCR modularizes the code, and training different recognition models only requires **changing the configuration file**.
|
||||
|
||||
Training:
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, after the data preparation is completed, the training can be started. The training command is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#Single GPU training (long training period, not recommended)
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml
|
||||
|
||||
#Multi GPU training, specify the gpu number through the --gpus parameter
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Evaluation:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# GPU evaluation
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0' tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml -o Global.pretrained_model={path/to/weights}/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Prediction:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# The configuration file used for prediction must match the training
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml -o Global.infer_img='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' Global.pretrained_model=./rec_vitstr_none_ce_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||
## 4. Inference and Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-1"></a>
|
||||
### 4.1 Python Inference
|
||||
First, the model saved during the ViTSTR text recognition training process is converted into an inference model. ( [Model download link](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/rec_vitstr_none_none_train.tar)) ), you can use the following command to convert:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/rec_vitstr_none_ce.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_vitstr_none_ce_train/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/rec_vitstr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:**
|
||||
- If you are training the model on your own dataset and have modified the dictionary file, please pay attention to modify the `character_dict_path` in the configuration file to the modified dictionary file.
|
||||
- If you modified the input size during training, please modify the `infer_shape` corresponding to ViTSTR in the `tools/export_model.py` file.
|
||||
|
||||
After the conversion is successful, there are three files in the directory:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/inference/rec_vitstr/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For ViTSTR text recognition model inference, the following commands can be executed:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir='./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png' --rec_model_dir='./inference/rec_vitstr/' --rec_algorithm='ViTSTR' --rec_image_shape='1,224,224' --rec_char_dict_path='./ppocr/utils/EN_symbol_dict.txt'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After executing the command, the prediction result (recognized text and score) of the image above is printed to the screen, an example is as follows:
|
||||
The result is as follows:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('pain', 0.9998350143432617)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-2"></a>
|
||||
### 4.2 C++ Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-3"></a>
|
||||
### 4.3 Serving
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-4"></a>
|
||||
### 4.4 More
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||
## 5. FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
1. In the `ViTSTR` paper, using pre-trained weights on ImageNet1k for initial training, we did not use pre-trained weights in training, and the final accuracy did not change or even improved.
|
||||
|
||||
## Citation
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{Atienza2021ViTSTR,
|
||||
title = {Vision Transformer for Fast and Efficient Scene Text Recognition},
|
||||
author = {Rowel Atienza},
|
||||
booktitle = {ICDAR},
|
||||
year = {2021},
|
||||
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.08582}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
|
|||
# Table Recognition Algorithm-TableMASTER
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. Introduction](#1-introduction)
|
||||
- [2. Environment](#2-environment)
|
||||
- [3. Model Training / Evaluation / Prediction](#3-model-training--evaluation--prediction)
|
||||
- [4. Inference and Deployment](#4-inference-and-deployment)
|
||||
- [4.1 Python Inference](#41-python-inference)
|
||||
- [4.2 C++ Inference](#42-c-inference)
|
||||
- [4.3 Serving](#43-serving)
|
||||
- [4.4 More](#44-more)
|
||||
- [5. FAQ](#5-faq)
|
||||
- [Citation](#citation)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
## 1. Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Paper:
|
||||
> [TableMaster: PINGAN-VCGROUP’S SOLUTION FOR ICDAR 2021 COMPETITION ON SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE PARSING TASK B: TABLE RECOGNITION TO HTML](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.01848.pdf)
|
||||
> Ye, Jiaquan and Qi, Xianbiao and He, Yelin and Chen, Yihao and Gu, Dengyi and Gao, Peng and Xiao, Rong
|
||||
> 2021
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
On the PubTabNet table recognition public data set, the algorithm reproduction acc is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|Model|Backbone|Cnnfig|Acc|Download link|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|TableMaster|TableResNetExtra|[configs/table/table_master.yml](../../configs/table/table_master.yml)|77.47%|[trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_train.tar)/[inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/tablemaster/table_structure_tablemaster_infer.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. Environment
|
||||
Please refer to ["Environment Preparation"](./environment_en.md) to configure the PaddleOCR environment, and refer to ["Project Clone"](./clone_en.md) to clone the project code.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||
## 3. Model Training / Evaluation / Prediction
|
||||
|
||||
The above TableMaster model is trained using the PubTabNet table recognition public dataset. For the download of the dataset, please refer to [table_datasets](./dataset/table_datasets_en.md).
|
||||
|
||||
After the data download is complete, please refer to [Text Recognition Training Tutorial](./recognition_en.md) for training. PaddleOCR has modularized the code structure, so that you only need to **replace the configuration file** to train different models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||
## 4. Inference and Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-1"></a>
|
||||
### 4.1 Python Inference
|
||||
|
||||
First, convert the model saved in the TableMaster table recognition training process into an inference model. Taking the model based on the TableResNetExtra backbone network and trained on the PubTabNet dataset as example ([model download link](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/contribution/table_master.tar)), you can use the following command to convert:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py -c configs/table/table_master.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=output/table_master/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/table_master
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: **
|
||||
- If you trained the model on your own dataset and adjusted the dictionary file, please pay attention to whether the `character_dict_path` in the modified configuration file is the correct dictionary file
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Execute the following command for model inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd ppstructure/
|
||||
# When predicting all images in a folder, you can modify image_dir to a folder, such as --image_dir='docs/table'.
|
||||
python3.7 table/predict_structure.py --table_model_dir=../output/table_master/table_structure_tablemaster_infer/ --table_algorithm=TableMaster --table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_master_structure_dict.txt --table_max_len=480 --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After executing the command, the prediction results of the above image (structural information and the coordinates of each cell in the table) are printed to the screen, and the visualization of the cell coordinates is also saved. An example is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
result:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
[2022/06/16 13:06:54] ppocr INFO: result: ['<html>', '<body>', '<table>', '<thead>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '</thead>', '<tbody>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '<tr>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '<td></td>', '</tr>', '</tbody>', '</table>', '</body>', '</html>'], [[72.17591094970703, 10.759100914001465, 60.29658508300781, 16.6805362701416], [161.85562133789062, 10.884308815002441, 14.9495210647583, 16.727018356323242], [277.79876708984375, 29.54340362548828, 31.490320205688477, 18.143272399902344],
|
||||
...
|
||||
[336.11724853515625, 280.3601989746094, 39.456939697265625, 18.121286392211914]]
|
||||
[2022/06/16 13:06:54] ppocr INFO: save vis result to ./output/table.jpg
|
||||
[2022/06/16 13:06:54] ppocr INFO: Predict time of docs/table/table.jpg: 17.36806297302246
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**:
|
||||
|
||||
- TableMaster is relatively slow during inference, and it is recommended to use GPU for use.
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-2"></a>
|
||||
### 4.2 C++ Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Since the post-processing is not written in CPP, the TableMaster does not support CPP inference.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-3"></a>
|
||||
### 4.3 Serving
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="4-4"></a>
|
||||
### 4.4 More
|
||||
|
||||
Not supported
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||
## 5. FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
## Citation
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{ye2021pingan,
|
||||
title={PingAn-VCGroup's Solution for ICDAR 2021 Competition on Scientific Literature Parsing Task B: Table Recognition to HTML},
|
||||
author={Ye, Jiaquan and Qi, Xianbiao and He, Yelin and Chen, Yihao and Gu, Dengyi and Gao, Peng and Xiao, Rong},
|
||||
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.01848},
|
||||
year={2021}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,8 @@ This article introduces the use of the Python inference engine for the PP-OCR mo
|
|||
- [Text Detection Model Inference](#text-detection-model-inference)
|
||||
- [Text Recognition Model Inference](#text-recognition-model-inference)
|
||||
- [1. Lightweight Chinese Recognition Model Inference](#1-lightweight-chinese-recognition-model-inference)
|
||||
- [2. Multilingual Model Inference](#2-multilingual-model-inference)
|
||||
- [2. English Recognition Model Inference](#2-english-recognition-model-inference)
|
||||
- [3. Multilingual Model Inference](#3-multilingual-model-inference)
|
||||
- [Angle Classification Model Inference](#angle-classification-model-inference)
|
||||
- [Text Detection Angle Classification and Recognition Inference Concatenation](#text-detection-angle-classification-and-recognition-inference-concatenation)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -76,10 +77,31 @@ After executing the command, the prediction results (recognized text and score)
|
|||
```bash
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words_en/word_10.png:('PAIN', 0.988671)
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a name="2-english-recognition-model-inference"></a>
|
||||
### 2. English Recognition Model Inference
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="MULTILINGUAL_MODEL_INFERENCE"></a>
|
||||
For English recognition model inference, you can execute the following commands,you need to specify the dictionary path used by `--rec_char_dict_path`:
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Multilingual Model Inference
|
||||
```
|
||||
# download en model:
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
tar xf en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_words/en/word_1.png" --rec_model_dir="./en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer/" --rec_char_dict_path="ppocr/utils/en_dict.txt"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
After executing the command, the prediction result of the above figure is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Predicts of ./doc/imgs_words/en/word_1.png: ('JOINT', 0.998160719871521)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="3-multilingual-model-inference"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Multilingual Model Inference
|
||||
If you need to predict [other language models](./models_list_en.md#Multilingual), when using inference model prediction, you need to specify the dictionary path used by `--rec_char_dict_path`. At the same time, in order to get the correct visualization results,
|
||||
You need to specify the visual font path through `--vis_font_path`. There are small language fonts provided by default under the `doc/fonts` path, such as Korean recognition:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -29,10 +29,10 @@ PP-OCR pipeline is as follows:
|
|||
|
||||
PP-OCR system is in continuous optimization. At present, PP-OCR and PP-OCRv2 have been released:
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCR adopts 19 effective strategies from 8 aspects including backbone network selection and adjustment, prediction head design, data augmentation, learning rate transformation strategy, regularization parameter selection, pre-training model use, and automatic model tailoring and quantization to optimize and slim down the models of each module (as shown in the green box above). The final results are an ultra-lightweight Chinese and English OCR model with an overall size of 3.5M and a 2.8M English digital OCR model. For more details, please refer to the PP-OCR technical article (https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.09941).
|
||||
PP-OCR adopts 19 effective strategies from 8 aspects including backbone network selection and adjustment, prediction head design, data augmentation, learning rate transformation strategy, regularization parameter selection, pre-training model use, and automatic model tailoring and quantization to optimize and slim down the models of each module (as shown in the green box above). The final results are an ultra-lightweight Chinese and English OCR model with an overall size of 3.5M and a 2.8M English digital OCR model. For more details, please refer to [PP-OCR technical report](https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.09941).
|
||||
|
||||
#### PP-OCRv2
|
||||
On the basis of PP-OCR, PP-OCRv2 is further optimized in five aspects. The detection model adopts CML(Collaborative Mutual Learning) knowledge distillation strategy and CopyPaste data expansion strategy. The recognition model adopts LCNet lightweight backbone network, U-DML knowledge distillation strategy and enhanced CTC loss function improvement (as shown in the red box above), which further improves the inference speed and prediction effect. For more details, please refer to the technical report of PP-OCRv2 (https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03144).
|
||||
On the basis of PP-OCR, PP-OCRv2 is further optimized in five aspects. The detection model adopts CML(Collaborative Mutual Learning) knowledge distillation strategy and CopyPaste data expansion strategy. The recognition model adopts LCNet lightweight backbone network, U-DML knowledge distillation strategy and enhanced CTC loss function improvement (as shown in the red box above), which further improves the inference speed and prediction effect. For more details, please refer to [PP-OCRv2 technical report](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03144).
|
||||
|
||||
#### PP-OCRv3
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ PP-OCRv3 pipeline is as follows:
|
|||
<img src="../ppocrv3_framework.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, please refer to [PP-OCRv3 technical report](./PP-OCRv3_introduction_en.md).
|
||||
For more details, please refer to [PP-OCRv3 technical report](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.03001v2).
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
## 2. Features
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,9 +22,11 @@ from .make_shrink_map import MakeShrinkMap
|
|||
from .random_crop_data import EastRandomCropData, RandomCropImgMask
|
||||
from .make_pse_gt import MakePseGt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from .rec_img_aug import BaseDataAugmentation, RecAug, RecConAug, RecResizeImg, ClsResizeImg, \
|
||||
SRNRecResizeImg, NRTRRecResizeImg, SARRecResizeImg, PRENResizeImg, \
|
||||
SPINRecResizeImg
|
||||
SRNRecResizeImg, GrayRecResizeImg, SARRecResizeImg, PRENResizeImg, \
|
||||
ABINetRecResizeImg, SVTRRecResizeImg, ABINetRecAug, SPINRecResizeImg
|
||||
from .ssl_img_aug import SSLRotateResize
|
||||
from .randaugment import RandAugment
|
||||
from .copy_paste import CopyPaste
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,7 +37,7 @@ from .label_ops import *
|
|||
from .east_process import *
|
||||
from .sast_process import *
|
||||
from .pg_process import *
|
||||
from .gen_table_mask import *
|
||||
from .table_ops import *
|
||||
|
||||
from .vqa import *
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,407 @@
|
|||
# copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This code is refer from:
|
||||
https://github.com/FangShancheng/ABINet/blob/main/transforms.py
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import numbers
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from paddle.vision.transforms import Compose, ColorJitter
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sample_asym(magnitude, size=None):
|
||||
return np.random.beta(1, 4, size) * magnitude
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sample_sym(magnitude, size=None):
|
||||
return (np.random.beta(4, 4, size=size) - 0.5) * 2 * magnitude
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sample_uniform(low, high, size=None):
|
||||
return np.random.uniform(low, high, size=size)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_interpolation(type='random'):
|
||||
if type == 'random':
|
||||
choice = [
|
||||
cv2.INTER_NEAREST, cv2.INTER_LINEAR, cv2.INTER_CUBIC, cv2.INTER_AREA
|
||||
]
|
||||
interpolation = choice[random.randint(0, len(choice) - 1)]
|
||||
elif type == 'nearest':
|
||||
interpolation = cv2.INTER_NEAREST
|
||||
elif type == 'linear':
|
||||
interpolation = cv2.INTER_LINEAR
|
||||
elif type == 'cubic':
|
||||
interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC
|
||||
elif type == 'area':
|
||||
interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise TypeError(
|
||||
'Interpolation types only nearest, linear, cubic, area are supported!'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return interpolation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVRandomRotation(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, degrees=15):
|
||||
assert isinstance(degrees,
|
||||
numbers.Number), "degree should be a single number."
|
||||
assert degrees >= 0, "degree must be positive."
|
||||
self.degrees = degrees
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def get_params(degrees):
|
||||
return sample_sym(degrees)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
angle = self.get_params(self.degrees)
|
||||
src_h, src_w = img.shape[:2]
|
||||
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(
|
||||
center=(src_w / 2, src_h / 2), angle=angle, scale=1.0)
|
||||
abs_cos, abs_sin = abs(M[0, 0]), abs(M[0, 1])
|
||||
dst_w = int(src_h * abs_sin + src_w * abs_cos)
|
||||
dst_h = int(src_h * abs_cos + src_w * abs_sin)
|
||||
M[0, 2] += (dst_w - src_w) / 2
|
||||
M[1, 2] += (dst_h - src_h) / 2
|
||||
|
||||
flags = get_interpolation()
|
||||
return cv2.warpAffine(
|
||||
img,
|
||||
M, (dst_w, dst_h),
|
||||
flags=flags,
|
||||
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVRandomAffine(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, degrees, translate=None, scale=None, shear=None):
|
||||
assert isinstance(degrees,
|
||||
numbers.Number), "degree should be a single number."
|
||||
assert degrees >= 0, "degree must be positive."
|
||||
self.degrees = degrees
|
||||
|
||||
if translate is not None:
|
||||
assert isinstance(translate, (tuple, list)) and len(translate) == 2, \
|
||||
"translate should be a list or tuple and it must be of length 2."
|
||||
for t in translate:
|
||||
if not (0.0 <= t <= 1.0):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"translation values should be between 0 and 1")
|
||||
self.translate = translate
|
||||
|
||||
if scale is not None:
|
||||
assert isinstance(scale, (tuple, list)) and len(scale) == 2, \
|
||||
"scale should be a list or tuple and it must be of length 2."
|
||||
for s in scale:
|
||||
if s <= 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError("scale values should be positive")
|
||||
self.scale = scale
|
||||
|
||||
if shear is not None:
|
||||
if isinstance(shear, numbers.Number):
|
||||
if shear < 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"If shear is a single number, it must be positive.")
|
||||
self.shear = [shear]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert isinstance(shear, (tuple, list)) and (len(shear) == 2), \
|
||||
"shear should be a list or tuple and it must be of length 2."
|
||||
self.shear = shear
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.shear = shear
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_inverse_affine_matrix(self, center, angle, translate, scale,
|
||||
shear):
|
||||
# https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/v0.4.0/torchvision/transforms/functional.py#L717
|
||||
from numpy import sin, cos, tan
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(shear, numbers.Number):
|
||||
shear = [shear, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
if not isinstance(shear, (tuple, list)) and len(shear) == 2:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Shear should be a single value or a tuple/list containing " +
|
||||
"two values. Got {}".format(shear))
|
||||
|
||||
rot = math.radians(angle)
|
||||
sx, sy = [math.radians(s) for s in shear]
|
||||
|
||||
cx, cy = center
|
||||
tx, ty = translate
|
||||
|
||||
# RSS without scaling
|
||||
a = cos(rot - sy) / cos(sy)
|
||||
b = -cos(rot - sy) * tan(sx) / cos(sy) - sin(rot)
|
||||
c = sin(rot - sy) / cos(sy)
|
||||
d = -sin(rot - sy) * tan(sx) / cos(sy) + cos(rot)
|
||||
|
||||
# Inverted rotation matrix with scale and shear
|
||||
# det([[a, b], [c, d]]) == 1, since det(rotation) = 1 and det(shear) = 1
|
||||
M = [d, -b, 0, -c, a, 0]
|
||||
M = [x / scale for x in M]
|
||||
|
||||
# Apply inverse of translation and of center translation: RSS^-1 * C^-1 * T^-1
|
||||
M[2] += M[0] * (-cx - tx) + M[1] * (-cy - ty)
|
||||
M[5] += M[3] * (-cx - tx) + M[4] * (-cy - ty)
|
||||
|
||||
# Apply center translation: C * RSS^-1 * C^-1 * T^-1
|
||||
M[2] += cx
|
||||
M[5] += cy
|
||||
return M
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def get_params(degrees, translate, scale_ranges, shears, height):
|
||||
angle = sample_sym(degrees)
|
||||
if translate is not None:
|
||||
max_dx = translate[0] * height
|
||||
max_dy = translate[1] * height
|
||||
translations = (np.round(sample_sym(max_dx)),
|
||||
np.round(sample_sym(max_dy)))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
translations = (0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
if scale_ranges is not None:
|
||||
scale = sample_uniform(scale_ranges[0], scale_ranges[1])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
scale = 1.0
|
||||
|
||||
if shears is not None:
|
||||
if len(shears) == 1:
|
||||
shear = [sample_sym(shears[0]), 0.]
|
||||
elif len(shears) == 2:
|
||||
shear = [sample_sym(shears[0]), sample_sym(shears[1])]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
shear = 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
return angle, translations, scale, shear
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
src_h, src_w = img.shape[:2]
|
||||
angle, translate, scale, shear = self.get_params(
|
||||
self.degrees, self.translate, self.scale, self.shear, src_h)
|
||||
|
||||
M = self._get_inverse_affine_matrix((src_w / 2, src_h / 2), angle,
|
||||
(0, 0), scale, shear)
|
||||
M = np.array(M).reshape(2, 3)
|
||||
|
||||
startpoints = [(0, 0), (src_w - 1, 0), (src_w - 1, src_h - 1),
|
||||
(0, src_h - 1)]
|
||||
project = lambda x, y, a, b, c: int(a * x + b * y + c)
|
||||
endpoints = [(project(x, y, *M[0]), project(x, y, *M[1]))
|
||||
for x, y in startpoints]
|
||||
|
||||
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(np.array(endpoints))
|
||||
bbox = cv2.boxPoints(rect).astype(dtype=np.int)
|
||||
max_x, max_y = bbox[:, 0].max(), bbox[:, 1].max()
|
||||
min_x, min_y = bbox[:, 0].min(), bbox[:, 1].min()
|
||||
|
||||
dst_w = int(max_x - min_x)
|
||||
dst_h = int(max_y - min_y)
|
||||
M[0, 2] += (dst_w - src_w) / 2
|
||||
M[1, 2] += (dst_h - src_h) / 2
|
||||
|
||||
# add translate
|
||||
dst_w += int(abs(translate[0]))
|
||||
dst_h += int(abs(translate[1]))
|
||||
if translate[0] < 0: M[0, 2] += abs(translate[0])
|
||||
if translate[1] < 0: M[1, 2] += abs(translate[1])
|
||||
|
||||
flags = get_interpolation()
|
||||
return cv2.warpAffine(
|
||||
img,
|
||||
M, (dst_w, dst_h),
|
||||
flags=flags,
|
||||
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVRandomPerspective(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, distortion=0.5):
|
||||
self.distortion = distortion
|
||||
|
||||
def get_params(self, width, height, distortion):
|
||||
offset_h = sample_asym(
|
||||
distortion * height / 2, size=4).astype(dtype=np.int)
|
||||
offset_w = sample_asym(
|
||||
distortion * width / 2, size=4).astype(dtype=np.int)
|
||||
topleft = (offset_w[0], offset_h[0])
|
||||
topright = (width - 1 - offset_w[1], offset_h[1])
|
||||
botright = (width - 1 - offset_w[2], height - 1 - offset_h[2])
|
||||
botleft = (offset_w[3], height - 1 - offset_h[3])
|
||||
|
||||
startpoints = [(0, 0), (width - 1, 0), (width - 1, height - 1),
|
||||
(0, height - 1)]
|
||||
endpoints = [topleft, topright, botright, botleft]
|
||||
return np.array(
|
||||
startpoints, dtype=np.float32), np.array(
|
||||
endpoints, dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
height, width = img.shape[:2]
|
||||
startpoints, endpoints = self.get_params(width, height, self.distortion)
|
||||
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(startpoints, endpoints)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: more robust way to crop image
|
||||
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(endpoints)
|
||||
bbox = cv2.boxPoints(rect).astype(dtype=np.int)
|
||||
max_x, max_y = bbox[:, 0].max(), bbox[:, 1].max()
|
||||
min_x, min_y = bbox[:, 0].min(), bbox[:, 1].min()
|
||||
min_x, min_y = max(min_x, 0), max(min_y, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
flags = get_interpolation()
|
||||
img = cv2.warpPerspective(
|
||||
img,
|
||||
M, (max_x, max_y),
|
||||
flags=flags,
|
||||
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
|
||||
img = img[min_y:, min_x:]
|
||||
return img
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVRescale(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, factor=4, base_size=(128, 512)):
|
||||
""" Define image scales using gaussian pyramid and rescale image to target scale.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
factor: the decayed factor from base size, factor=4 keeps target scale by default.
|
||||
base_size: base size the build the bottom layer of pyramid
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(factor, numbers.Number):
|
||||
self.factor = round(sample_uniform(0, factor))
|
||||
elif isinstance(factor, (tuple, list)) and len(factor) == 2:
|
||||
self.factor = round(sample_uniform(factor[0], factor[1]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise Exception('factor must be number or list with length 2')
|
||||
# assert factor is valid
|
||||
self.base_h, self.base_w = base_size[:2]
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
if self.factor == 0: return img
|
||||
src_h, src_w = img.shape[:2]
|
||||
cur_w, cur_h = self.base_w, self.base_h
|
||||
scale_img = cv2.resize(
|
||||
img, (cur_w, cur_h), interpolation=get_interpolation())
|
||||
for _ in range(self.factor):
|
||||
scale_img = cv2.pyrDown(scale_img)
|
||||
scale_img = cv2.resize(
|
||||
scale_img, (src_w, src_h), interpolation=get_interpolation())
|
||||
return scale_img
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVGaussianNoise(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, mean=0, var=20):
|
||||
self.mean = mean
|
||||
if isinstance(var, numbers.Number):
|
||||
self.var = max(int(sample_asym(var)), 1)
|
||||
elif isinstance(var, (tuple, list)) and len(var) == 2:
|
||||
self.var = int(sample_uniform(var[0], var[1]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise Exception('degree must be number or list with length 2')
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
noise = np.random.normal(self.mean, self.var**0.5, img.shape)
|
||||
img = np.clip(img + noise, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
return img
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVMotionBlur(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, degrees=12, angle=90):
|
||||
if isinstance(degrees, numbers.Number):
|
||||
self.degree = max(int(sample_asym(degrees)), 1)
|
||||
elif isinstance(degrees, (tuple, list)) and len(degrees) == 2:
|
||||
self.degree = int(sample_uniform(degrees[0], degrees[1]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise Exception('degree must be number or list with length 2')
|
||||
self.angle = sample_uniform(-angle, angle)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((self.degree // 2, self.degree // 2),
|
||||
self.angle, 1)
|
||||
motion_blur_kernel = np.zeros((self.degree, self.degree))
|
||||
motion_blur_kernel[self.degree // 2, :] = 1
|
||||
motion_blur_kernel = cv2.warpAffine(motion_blur_kernel, M,
|
||||
(self.degree, self.degree))
|
||||
motion_blur_kernel = motion_blur_kernel / self.degree
|
||||
img = cv2.filter2D(img, -1, motion_blur_kernel)
|
||||
img = np.clip(img, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
return img
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVGeometry(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
degrees=15,
|
||||
translate=(0.3, 0.3),
|
||||
scale=(0.5, 2.),
|
||||
shear=(45, 15),
|
||||
distortion=0.5,
|
||||
p=0.5):
|
||||
self.p = p
|
||||
type_p = random.random()
|
||||
if type_p < 0.33:
|
||||
self.transforms = CVRandomRotation(degrees=degrees)
|
||||
elif type_p < 0.66:
|
||||
self.transforms = CVRandomAffine(
|
||||
degrees=degrees, translate=translate, scale=scale, shear=shear)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.transforms = CVRandomPerspective(distortion=distortion)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
if random.random() < self.p:
|
||||
return self.transforms(img)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return img
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVDeterioration(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, var, degrees, factor, p=0.5):
|
||||
self.p = p
|
||||
transforms = []
|
||||
if var is not None:
|
||||
transforms.append(CVGaussianNoise(var=var))
|
||||
if degrees is not None:
|
||||
transforms.append(CVMotionBlur(degrees=degrees))
|
||||
if factor is not None:
|
||||
transforms.append(CVRescale(factor=factor))
|
||||
|
||||
random.shuffle(transforms)
|
||||
transforms = Compose(transforms)
|
||||
self.transforms = transforms
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
if random.random() < self.p:
|
||||
|
||||
return self.transforms(img)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return img
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CVColorJitter(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
brightness=0.5,
|
||||
contrast=0.5,
|
||||
saturation=0.5,
|
||||
hue=0.1,
|
||||
p=0.5):
|
||||
self.p = p
|
||||
self.transforms = ColorJitter(
|
||||
brightness=brightness,
|
||||
contrast=contrast,
|
||||
saturation=saturation,
|
||||
hue=hue)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, img):
|
||||
if random.random() < self.p: return self.transforms(img)
|
||||
else: return img
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue