1.6 KiB
Utils
Config
Config class is used for manipulating config and config files. It supports
loading configs from multiple file formats including python, json and yaml.
It provides dict-like apis to get and set values.
Here is an example of the config file test.py.
a = 1
b = {'b1': [0, 1, 2], 'b2': None}
c = (1, 2)
d = 'string'
To load and use configs
cfg = Config.fromfile('test.py')
assert cfg.a == 1
assert cfg.b.b1 == [0, 1, 2]
cfg.c = None
assert cfg.c == None
ProgressBar
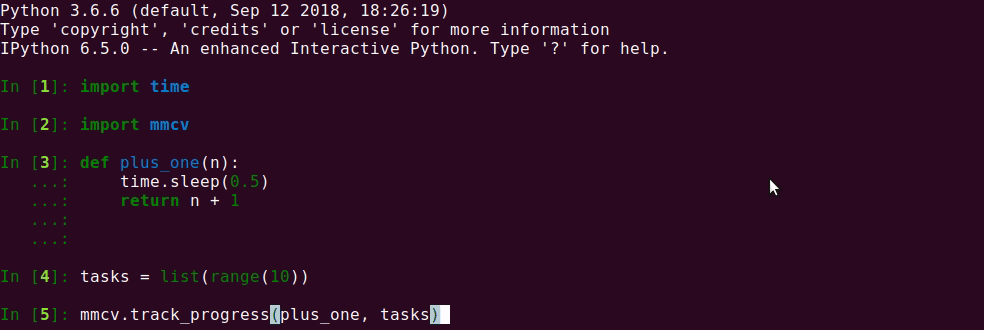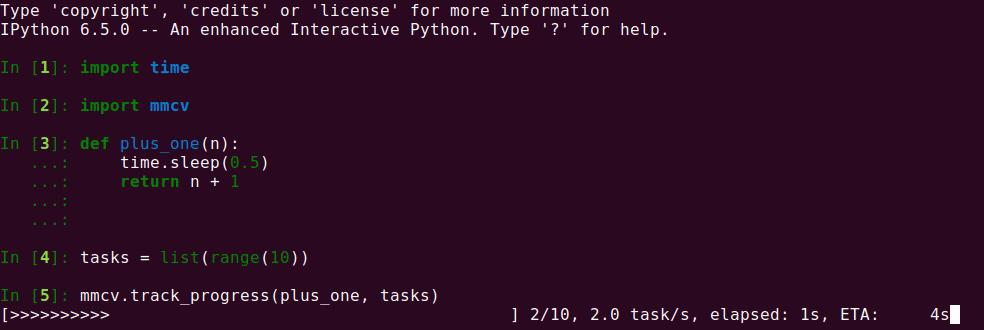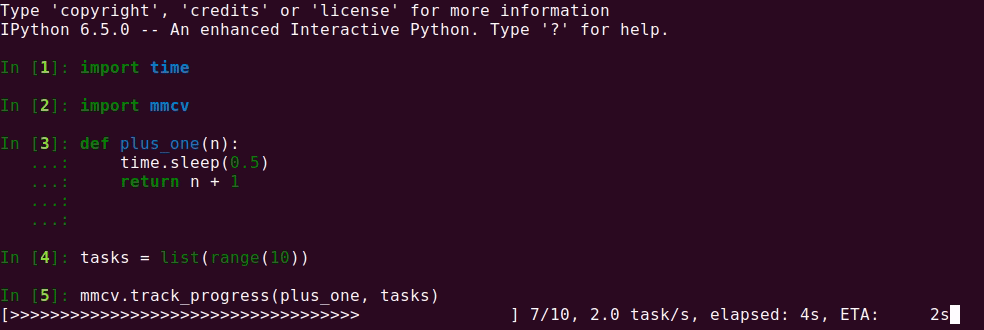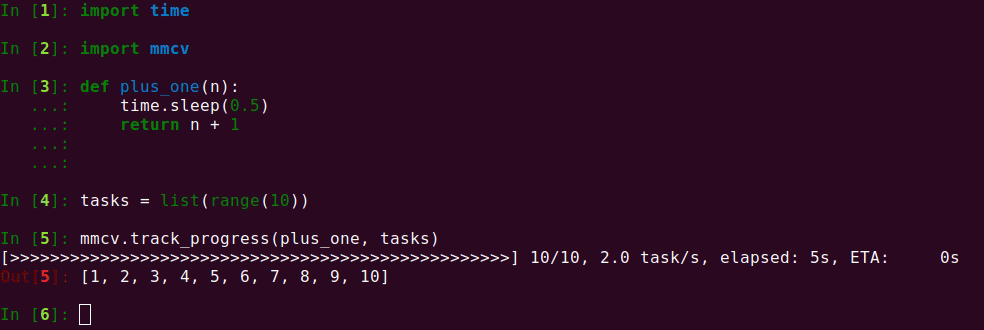
If you want to apply a method to a list of items and track the progress, track_progress
is a good choice. It will display a progress bar to tell the progress and ETA.
import mmcv
def func(item):
# do something
pass
tasks = [item_1, item_2, ..., item_n]
mmcv.track_progress(func, tasks)
The output is like the following.
There is another method track_parallel_progress, which wraps multiprocessing and
progress visualization.
mmcv.track_parallel_progress(func, tasks, 8) # 8 workers
Timer
It is convinient to compute the runtime of a code block with Timer.
import time
with mmcv.Timer():
# simulate some code block
time.sleep(1)
or try with since_start() and since_last_check(). This former can
return the runtime since the timer starts and the latter will return the time
since the last time checked.
timer = mmcv.Timer()
# code block 1 here
print(timer.since_start())
# code block 2 here
print(timer.since_last_check())
print(timer.since_start())
