mirror of https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmocr.git
[Docs] Data Transforms (#1392)
* init * reorder * update * fix comments * update * update images * updatepull/1415/head
parent
77ab13b3ff
commit
22283b4acd
docs
en/basic_concepts
zh_cn
basic_concepts
migration
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,229 @@
|
|||
# Data Transforms
|
||||
# Data Transforms and Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Coming Soon!
|
||||
In the design of MMOCR, dataset construction and preparation are decoupled. That is, dataset construction classes such as [`OCRDataset`](mmocr.datasets.ocr_dataset.OCRDataset) are responsible for loading and parsing annotation files; while data transforms further apply data preprocessing, augmentation, formatting, and other related functions. Currently, there are five types of data transforms implemented in MMOCR, as shown in the following table.
|
||||
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| -------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Transforms Type | File | Description |
|
||||
| Data Loading | loading.py | Implemented the data loading functions. |
|
||||
| Data Formatting | formatting.py | Formatting the data required by different tasks. |
|
||||
| Cross Project Data Adapter | adapters.py | Converting the data format between other OpenMMLab projects and MMOCR. |
|
||||
| Data Augmentation Functions | ocr_transforms.py<br>textdet_transforms.py<br>textrecog_transforms.py | Various built-in data augmentation methods designed for different tasks. |
|
||||
| Wrappers of Third Party Packages | wrappers.py | Wrapping the transforms implemented in popular third party packages such as [ImgAug](https://github.com/aleju/imgaug), and adapting them to MMOCR format. |
|
||||
|
||||
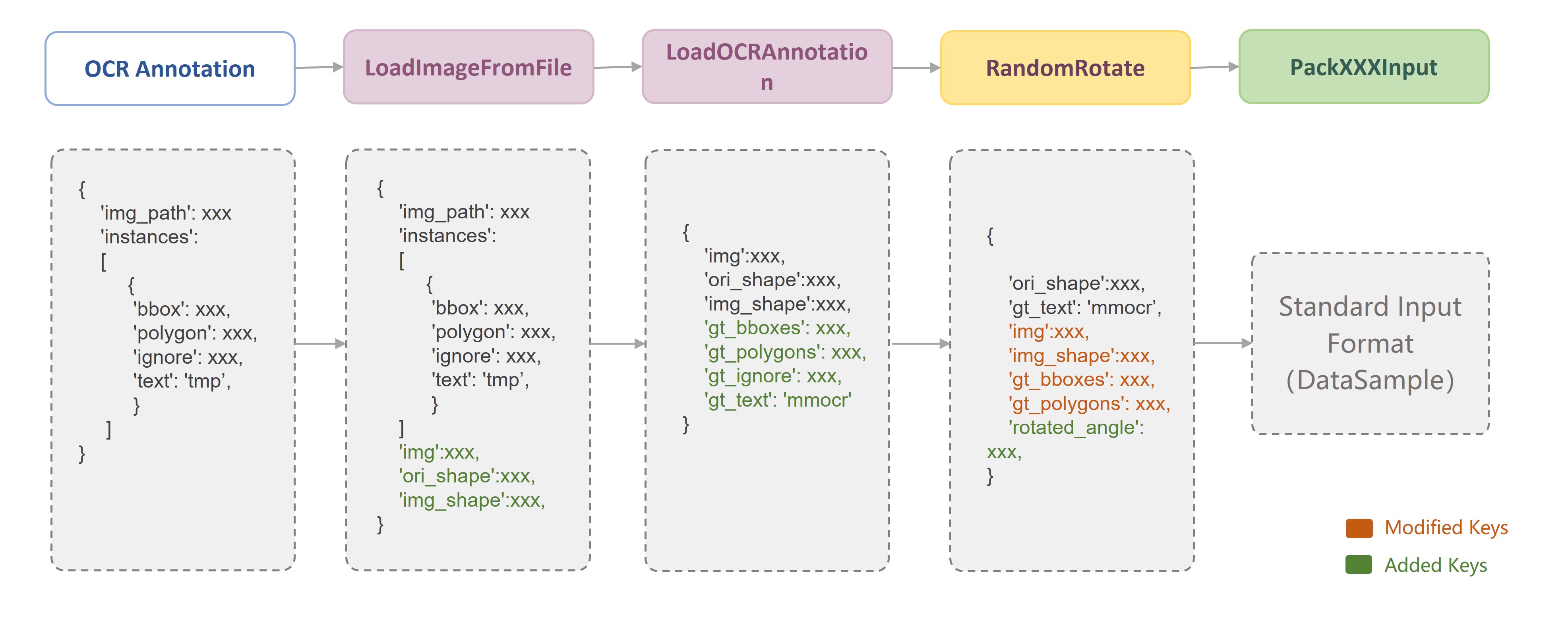
Since each data transform class is independent of each other, we can easily combine any data transforms to build a data pipeline after we have defined the data fields. As shown in the following figure, in MMOCR, a typical training data pipeline consists of three stages: **data loading**, **data augmentation**, and **data formatting**. Users only need to define the data pipeline list in the configuration file and specify the specific data transform class and its parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
train_pipeline_r18 = [
|
||||
# Loading images
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='LoadImageFromFile',
|
||||
file_client_args=file_client_args,
|
||||
color_type='color_ignore_orientation'),
|
||||
# Loading annotations
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
|
||||
with_polygon=True,
|
||||
with_bbox=True,
|
||||
with_label=True,
|
||||
),
|
||||
# Data augmentation
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='ImgAugWrapper',
|
||||
args=[['Fliplr', 0.5],
|
||||
dict(cls='Affine', rotate=[-10, 10]), ['Resize', [0.5, 3.0]]]),
|
||||
dict(type='RandomCrop', min_side_ratio=0.1),
|
||||
dict(type='Resize', scale=(640, 640), keep_ratio=True),
|
||||
dict(type='Pad', size=(640, 640)),
|
||||
# Data formatting
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='PackTextDetInputs',
|
||||
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```{tip}
|
||||
More tutorials about data pipeline configuration can be found in the [Config Doc](../user_guides/config.md#data-pipeline-configuration). Next, we will briefly introduce the data transforms supported in MMOCR according to their categories.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For each data transform, MMOCR provides a detailed docstring. For example, in the header of each data transform class, we annotate `Required Keys`, `Modified Keys` and `Added Keys`. The `Required Keys` represent the mandatory fields that should be included in the input required by the data transform, while the `Modified Keys` and `Added Keys` indicate that the transform may modify or add the fields into the original data. For example, `LoadImageFromFile` implements the image loading function, whose `Required Keys` is the image path `img_path`, and the `Modified Keys` includes the loaded image `img`, the current size of the image `img_shape`, the original size of the image `ori_shape`, and other image attributes.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@TRANSFORMS.register_module()
|
||||
class LoadImageFromFile(MMCV_LoadImageFromFile):
|
||||
# We provide detailed docstring for each data transform.
|
||||
"""Load an image from file.
|
||||
|
||||
Required Keys:
|
||||
|
||||
- img_path
|
||||
|
||||
Modified Keys:
|
||||
|
||||
- img
|
||||
- img_shape
|
||||
- ori_shape
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```{note}
|
||||
In the data pipeline of MMOCR, the image and label information are saved in a dictionary. By using the unified fields, the data can be freely transferred between different data transforms. Therefore, it is very important to understand the conventional fields used in MMOCR.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For your convenience, the following table lists the conventional keys used in MMOCR data transforms.
|
||||
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| ---------------- | --------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Key | Type | Description |
|
||||
| img | `np.array(dtype=np.uint8)` | Image array, shape of `(h, w, c)`. |
|
||||
| img_shape | `tuple(int, int)` | Current image size `(h, w)`. |
|
||||
| ori_shape | `tuple(int, int)` | Original image size `(h, w)`. |
|
||||
| scale | `tuple(int, int)` | Stores the target image size `(h, w)` specified by the user in the `Resize` data transform series. Note: This value may not correspond to the actual image size after the transformation. |
|
||||
| scale_factor | `tuple(float, float)` | Stores the target image scale factor `(w_scale, h_scale)` specified by the user in the `Resize` data transform series. Note: This value may not correspond to the actual image size after the transformation. |
|
||||
| keep_ratio | `bool` | Boolean flag determines whether to keep the aspect ratio while scaling images. |
|
||||
| flip | `bool` | Boolean flags to indicate whether the image has been flipped. |
|
||||
| flip_direction | `str` | Flipping direction, options are `horizontal`, `vertical`, `diagonal`. |
|
||||
| gt_bboxes | `np.array(dtype=np.float32)` | Ground-truth bounding boxes. |
|
||||
| gt_polygons | `list[np.array(dtype=np.float32)` | Ground-truth polygons. |
|
||||
| gt_bboxes_labels | `np.array(dtype=np.int64)` | Category label of bounding boxes. By default, MMOCR uses `0` to represent "text" instances. |
|
||||
| gt_texts | `list[str]` | Ground-truth text content of the instance. |
|
||||
| gt_ignored | `np.array(dtype=np.bool_)` | Boolean flag indicating whether ignoring the instance (used in text detection). |
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Loading
|
||||
|
||||
Data loading transforms mainly implement the functions of loading data from different formats and backends. Currently, the following data loading transforms are implemented in MMOCR:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
|
||||
| LoadImageFromFile | `img_path` | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`ori_shape` | Load image from the specified path,supporting different file storage backends (e.g. `disk`, `http`, `petrel`) and decoding backends (e.g. `cv2`, `turbojpeg`, `pillow`, `tifffile`). |
|
||||
| LoadOCRAnnotations | `bbox`<br>`bbox_label`<br>`polygon`<br>`ignore`<br>`text` | `gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored`<br>`gt_texts` | Parse the annotation required by OCR task. |
|
||||
| LoadKIEAnnotations | `bboxes` `bbox_labels` `edge_labels`<br>`texts` | `gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_edge_labels`<br>`gt_texts`<br>`ori_shape` | Parse the annotation required by KIE task. |
|
||||
| LoadImageFromLMDB | `img_path` | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`ori_shape` | Load images from LMDB. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Augmentation
|
||||
|
||||
Data augmentation is an indispensable process in text detection and recognition tasks. Currently, MMOCR has implemented dozens of data augmentation modules commonly used in OCR fields, which are classified into [ocr_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/ocr_transforms.py), [textdet_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/textdet_transforms.py), and [textrecog_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/textrecog_transforms.py).
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, `ocr_transforms.py` implements generic OCR data augmentation modules such as `RandomCrop` and `RandomRotate`:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
|
||||
| RandomCrop | `img`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored`<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored`<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | Randomly crop the image and make sure the cropped image contains at least one text instance. The optional parameter is `min_side_ratio`, which controls the ratio of the short side of the cropped image to the original image, the default value is `0.4`. |
|
||||
| RandomRotate | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional)<br>`gt_polygons` (optional) | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional)<br>`gt_polygons` (optional)<br>`rotated_angle` | Randomly rotate the image and optionally fill the blank areas of the rotated image. |
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
`textdet_transforms.py` implements text detection related data augmentation modules:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
|
||||
| RandomFlip | `img`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_polygons` | `img`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`flip`<br>`flip_direction` | Random flip, support `horizontal`, `vertical` and `diagonal` modes. Defaults to `horizontal`. |
|
||||
| FixInvalidPolygon | `gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | `gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | Automatically fixing the invalid polygons included in the annotations. |
|
||||
|
||||
`textrecog_transforms.py` implements text recognition related data augmentation modules:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
|
||||
| RescaleToHeight | `img` | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`scale`<br>`scale_factor`<br>`keep_ratio` | Scales the image to the specified height while keeping the aspect ratio. When `min_width` and `max_width` are specified, the aspect ratio may be changed. |
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
```{warning}
|
||||
The above table only briefly introduces some selected data augmentation methods, for more information please refer to the [API documentation](../api.rst) or the code docstrings.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
Data formatting transforms are responsible for packaging images, ground truth labels, and other information into a dictionary. Different tasks usually rely on different formatting transforms. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ------------- | ------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
|
||||
| PackTextDetInputs | - | - | Pack the inputs required by text detection. |
|
||||
| PackTextRecogInputs | - | - | Pack the inputs required by text recognition. |
|
||||
| PackKIEInputs | - | - | Pack the inputs required by KIE. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Cross Project Data Adapters
|
||||
|
||||
The cross-project data adapters bridge the data formats between MMOCR and other OpenMMLab libraries such as [MMDetection](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection), making it possible to call models implemented in other OpenMMLab projects. Currently, MMOCR has implemented [`MMDet2MMOCR`](mmocr.datasets.transforms.MMDet2MMOCR) and [`MMOCR2MMDet`](mmocr.datasets.transforms.MMOCR2MMDet), allowing data to be converted between MMDetection and MMOCR formats; with these adapters, users can easily train any detectors supported by MMDetection in MMOCR. For example, we provide a [tutorial](#todo) to show how to train Mask R-CNN as a text detector in MMOCR.
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| --------------- | -------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
|
||||
| MMDet2MMOCR | `gt_masks` `gt_ignore_flags` | `gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | Convert the fields used in MMDet to MMOCR. |
|
||||
| MMOCR2MMDet | `img_shape`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | `gt_masks` `gt_ignore_flags` | Convert the fields used in MMOCR to MMDet. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Wrappers
|
||||
|
||||
To facilitate the use of popular third-party CV libraries in MMOCR, we provide wrappers in `wrappers.py` to unify the data format between MMOCR and other third-party libraries. Users can directly configure the data transforms provided by these libraries in the configuration file of MMOCR. The supported wrappers are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
|
||||
| ImgAugWrapper | `img`<br>`gt_polygons` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes_labels` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_ignored` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | `img`<br>`gt_polygons` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes_labels` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_ignored` (optional for text recognition)<br>`img_shape` (optional)<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | [ImgAug](https://github.com/aleju/imgaug) wrapper, which bridges the data format and configuration between ImgAug and MMOCR, allowing users to config the data augmentation methods supported by ImgAug in MMOCR. |
|
||||
| TorchVisionWrapper | `img` | `img`<br>`img_shape` | [TorchVision](https://github.com/pytorch/vision) wrapper, which bridges the data format and configuration between TorchVision and MMOCR, allowing users to config the data transforms supported by `torchvision.transforms` in MMOCR. |
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
### `ImgAugWrapper` Example
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in the original ImgAug, we can define a `Sequential` type data augmentation pipeline as follows to perform random flipping, random rotation and random scaling on the image:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
|
||||
|
||||
aug = iaa.Sequential(
|
||||
iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # horizontally flip 50% of all images
|
||||
iaa.Affine(rotate=(-10, 10)), # rotate by -10 to +10 degrees
|
||||
iaa.Resize((0.5, 3.0)) # scale images to 50-300% of their size
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In MMOCR, we can directly configure the above data augmentation pipeline in `train_pipeline` as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='ImgAugWrapper',
|
||||
args=[
|
||||
['Fliplr', 0.5],
|
||||
dict(cls='Affine', rotate=[-10, 10]),
|
||||
['Resize', [0.5, 3.0]],
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, the `args` parameter accepts a list, and each element in the list can be a list or a dictionary. If it is a list, the first element of the list is the class name in `imgaug.augmenters`, and the following elements are the initialization parameters of the class; if it is a dictionary, the `cls` key corresponds to the class name in `imgaug.augmenters`, and the other key-value pairs correspond to the initialization parameters of the class.
|
||||
|
||||
### `TorchVisionWrapper` Example
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in the original TorchVision, we can define a `Compose` type data transformation pipeline as follows to perform color jittering on the image:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
|
||||
|
||||
aug = transforms.Compose([
|
||||
transforms.ColorJitter(
|
||||
brightness=32.0 / 255, # brightness jittering range
|
||||
saturation=0.5) # saturation jittering range
|
||||
])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In MMOCR, we can directly configure the above data transformation pipeline in `train_pipeline` as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='TorchVisionWrapper',
|
||||
op='ColorJitter',
|
||||
brightness=32.0 / 255,
|
||||
saturation=0.5
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, the `op` parameter is the class name in `torchvision.transforms`, and the following parameters correspond to the initialization parameters of the class.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,230 @@
|
|||
# 数据变换
|
||||
# 数据变换与流水线
|
||||
|
||||
待更新
|
||||
在 MMOCR 的设计中,数据集的构建与数据准备是相互解耦的。也就是说,[`OCRDataset`](mmocr.datasets.ocr_dataset.OCRDataset) 等数据集构建类负责完成标注文件的读取与解析功能;而数据变换方法(Data Transforms)则进一步实现了数据预处理、数据增强、数据格式化等相关功能。目前,如下表所示,MMOCR 中共实现了 5 类数据变换方法:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| -------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 数据变换类型 | 对应文件 | 功能说明 |
|
||||
| 数据读取 | loading.py | 实现了不同格式数据的读取功能。 |
|
||||
| 数据格式化 | formatting.py | 完成不同任务所需数据的格式化功能。 |
|
||||
| 跨库数据适配器 | adapters.py | 负责 OpenMMLab 项目内跨库调用的数据格式转换功能。 |
|
||||
| 数据增强 | ocr_transforms.py<br>textdet_transforms.py<br>textrecog_transforms.py | 实现了不同任务下的各类数据增强方法。 |
|
||||
| 包装类 | wrappers.py | 实现了对 ImgAug 等常用算法库的包装,使其适配 MMOCR 的内部数据格式。 |
|
||||
|
||||
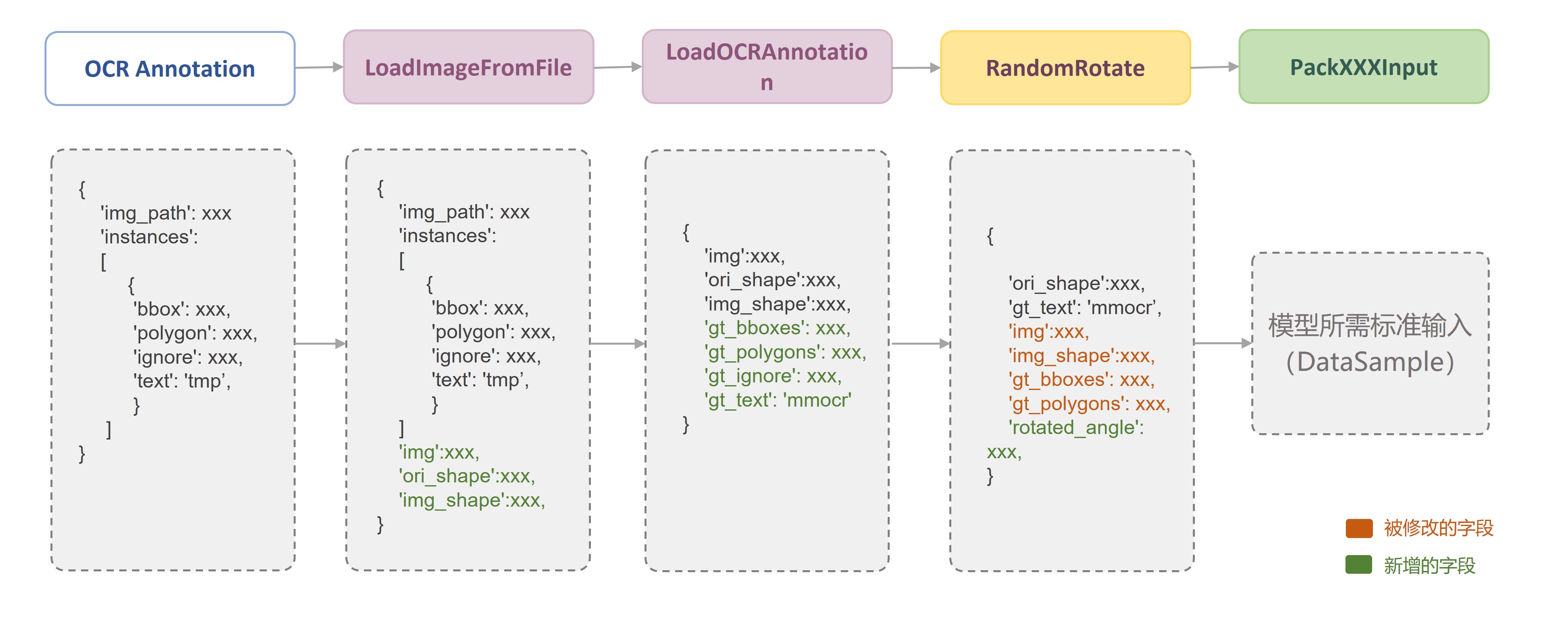
由于每一个数据变换类之间都是相互独立的,因此,在约定好固定的数据存储字段后,我们可以便捷地采用任意的数据变换组合来构建数据流水线(Pipeline)。如下图所示,在 MMOCR 中,一个典型的训练数据流水线主要由**数据读取**、**图像增强**以及**数据格式化**三部分构成,用户只需要在配置文件中定义相关的数据流水线列表,并指定具体所需的数据变换类及其参数即可:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
train_pipeline_r18 = [
|
||||
# 数据读取(图像)
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='LoadImageFromFile',
|
||||
file_client_args=file_client_args,
|
||||
color_type='color_ignore_orientation'),
|
||||
# 数据读取(标注)
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
|
||||
with_polygon=True,
|
||||
with_bbox=True,
|
||||
with_label=True,
|
||||
),
|
||||
# 使用 ImgAug 作数据增强
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='ImgAugWrapper',
|
||||
args=[['Fliplr', 0.5],
|
||||
dict(cls='Affine', rotate=[-10, 10]), ['Resize', [0.5, 3.0]]]),
|
||||
# 使用 MMOCR 内置的图像增强
|
||||
dict(type='RandomCrop', min_side_ratio=0.1),
|
||||
dict(type='Resize', scale=(640, 640), keep_ratio=True),
|
||||
dict(type='Pad', size=(640, 640)),
|
||||
# 数据格式化
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='PackTextDetInputs',
|
||||
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```{tip}
|
||||
更多有关数据流水线配置的教程可见[配置文档](../user_guides/config.md#数据流水线配置)。下面,我们将简单介绍 MMOCR 中已支持的数据变换类型。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于每一个数据变换方法,MMOCR 都严格按照文档字符串(docstring)规范在源码中提供了详细的代码注释。例如,每一个数据转换类的头部我们都注释了 “需求字段”(`Required keys`), “修改字段”(`Modified Keys`)与 “添加字段”(`Added Keys`)。其中,“需求字段”代表该数据转换方法对于输入数据所需包含字段的强制需求,而“修改字段”与“添加字段”则表明该方法可能会在原有数据基础之上修改或添加的字段。例如,`LoadImageFromFile` 实现了图片的读取功能,其需求字段为图像的存储路径 `img_path`,而修改字段则包括了读入的图像信息 `img`,以及图片当前尺寸 `img_shape`,图片原始尺寸 `ori_shape` 等图片属性。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@TRANSFORMS.register_module()
|
||||
class LoadImageFromFile(MMCV_LoadImageFromFile):
|
||||
# 在每一个数据变换方法的头部,我们都提供了详细的代码注释。
|
||||
"""Load an image from file.
|
||||
|
||||
Required Keys:
|
||||
|
||||
- img_path
|
||||
|
||||
Modified Keys:
|
||||
|
||||
- img
|
||||
- img_shape
|
||||
- ori_shape
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```{note}
|
||||
在 MMOCR 的数据流水线中,图像及标签等信息被统一保存在字典中。通过统一的字段名,我们可以在不同的数据变换方法间灵活地传递数据。因此,了解 MMOCR 中常用的约定字段名是非常重要的。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为方便用户查询,下表列出了 MMOCR 中各数据转换(Data Transform)类常用的字段约定和说明。
|
||||
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| ---------------- | --------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 字段 | 类型 | 说明 |
|
||||
| img | `np.array(dtype=np.uint8)` | 图像信息,形状为 `(h, w, c)`。 |
|
||||
| img_shape | `tuple(int, int)` | 当前图像尺寸 `(h, w)`。 |
|
||||
| ori_shape | `tuple(int, int)` | 图像在初始化时的尺寸 `(h, w)`。 |
|
||||
| scale | `tuple(int, int)` | 存放用户在 Resize 系列数据变换(Transform)中指定的目标图像尺寸 `(h, w)`。注意:该值未必与变换后的实际图像尺寸相符。 |
|
||||
| scale_factor | `tuple(float, float)` | 存放用户在 Resize 系列数据变换(Transform)中指定的目标图像缩放因子 `(w_scale, h_scale)`。注意:该值未必与变换后的实际图像尺寸相符。 |
|
||||
| keep_ratio | `bool` | 是否按等比例对图像进行缩放。 |
|
||||
| flip | `bool` | 图像是否被翻转。 |
|
||||
| flip_direction | `str` | 翻转方向。可选项为 `horizontal`, `vertical`, `diagonal`。 |
|
||||
| gt_bboxes | `np.array(dtype=np.float32)` | 文本实例边界框的真实标签。 |
|
||||
| gt_polygons | `list[np.array(dtype=np.float32)` | 文本实例边界多边形的真实标签。 |
|
||||
| gt_bboxes_labels | `np.array(dtype=np.int64)` | 文本实例对应的类别标签。在 MMOCR 中通常为 0,代指 "text" 类别。 |
|
||||
| gt_texts | `list[str]` | 与文本实例对应的字符串标注。 |
|
||||
| gt_ignored | `np.array(dtype=np.bool_)` | 是否要在计算目标时忽略该实例(用于检测任务中)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据读取 - loading.py
|
||||
|
||||
数据读取类主要实现了不同文件格式、后端读取图片及加载标注信息的功能。目前,MMOCR 内部共实现了以下数据读取类的 Data Transforms:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 数据转换类名称 | 需求字段 | 修改/添加字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| LoadImageFromFile | `img_path` | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`ori_shape` | 从图片路径读取图片,支持多种文件存储后端(如 `disk`, `http`, `petrel` 等)及图片解码后端(如 `cv2`, `turbojpeg`, `pillow`, `tifffile`等)。 |
|
||||
| LoadOCRAnnotations | `bbox`<br>`bbox_label`<br>`polygon`<br>`ignore`<br>`text` | `gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored`<br>`gt_texts` | 解析 OCR 任务所需的标注信息。 |
|
||||
| LoadKIEAnnotations | `bboxes` `bbox_labels` `edge_labels`<br>`texts` | `gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_edge_labels`<br>`gt_texts`<br>`ori_shape` | 解析 KIE 任务所需的标注信息。 |
|
||||
| LoadImageFromLMDB | `img_path` | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`ori_shape` | 从 LMDB 格式标注文件中读取图片。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据增强 - xxx_transforms.py
|
||||
|
||||
数据增强是文本检测、识别等任务中必不可少的流程之一。目前,MMOCR 中共实现了数十种文本领域内常用的数据增强模块,依据其任务类型,分别为通用 OCR 数据增强模块 [ocr_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/ocr_transforms.py),文本检测数据增强模块 [textdet_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/textdet_transforms.py),以及文本识别数据增强模块 [textrecog_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/textrecog_transforms.py)。
|
||||
|
||||
具体而言,`ocr_transforms.py` 中实现了随机剪裁、随机旋转等各任务通用的数据增强模块:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| -------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 数据转换类名称 | 需求字段 | 修改/添加字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| RandomCrop | `img`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored`<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_bboxes_labels`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored`<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | 随机裁剪,并确保裁剪后的图片至少包含一个文本实例。可选参数为 `min_side_ratio`,用以控制裁剪图片的短边占原始图片的比例,默认值为 `0.4`。 |
|
||||
| RandomRotate | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional)<br>`gt_polygons` (optional) | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional)<br>`gt_polygons` (optional)<br>`rotated_angle` | 随机旋转,并可选择对旋转后图像的黑边进行填充。 |
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
`textdet_transforms.py` 则实现了文本检测任务中常用的数据增强模块:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 数据转换类名称 | 需求字段 | 修改/添加字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| RandomFlip | `img`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_polygons` | `img`<br>`gt_bboxes`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`flip`<br>`flip_direction` | 随机翻转,支持水平、垂直和对角三种方向的图像翻转。默认使用水平翻转。 |
|
||||
| FixInvalidPolygon | `gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | `gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | 自动修复或忽略非法多边形标注。 |
|
||||
|
||||
`textrecog_transforms.py` 中实现了文本识别任务中常用的数据增强模块:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| --------------- | -------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 数据转换类名称 | 需求字段 | 修改/添加字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| RescaleToHeight | `img` | `img`<br>`img_shape`<br>`scale`<br>`scale_factor`<br>`keep_ratio` | 缩放图像至指定高度,并尽可能保持长宽比不变。当 `min_width` 及 `max_width` 被指定时,长宽比则可能会被改变。 |
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
```{warning}
|
||||
以上表格仅选择性地对部分数据增强方法作简要介绍,更多数据增强方法介绍请参考[API 文档](../api.rst)或阅读代码内的文档注释。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据格式化 - formatting.py
|
||||
|
||||
数据格式化负责将图像、真实标签以及其它常用信息等打包成一个字典。不同的任务通常依赖于不同的数据格式化数据变换类。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ------------------- | -------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 数据转换类名称 | 需求字段 | 修改/添加字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| PackTextDetInputs | - | - | 用于打包文本检测任务所需要的输入信息。 |
|
||||
| PackTextRecogInputs | - | - | 用于打包文本识别任务所需要的输入信息。 |
|
||||
| PackKIEInputs | - | - | 用于打包关键信息抽取任务所需要的输入信息。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 跨库数据适配器 - adapters.py
|
||||
|
||||
跨库数据适配器打通了 MMOCR 与其他 OpenMMLab 系列算法库如 [MMDetection](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection) 之间的数据格式,使得跨项目调用其它开源算法库的配置文件及算法成为了可能。目前,MMOCR 实现了 `MMDet2MMOCR` 以及 `MMOCR2MMDet`,使得数据可以在 MMDetection 与 MMOCR 的格式之间自由转换;借助这些适配转换器,用户可以在 MMOCR 算法库内部轻松调用任何 MMDetection 已支持的检测算法,并在 OCR 相关数据集上进行训练。例如,我们以 Mask R-CNN 为例提供了[教程](#todo),展示了如何在 MMOCR 中使用 MMDetection 的检测算法训练文本检测器。
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| -------------- | -------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 数据转换类名称 | 需求字段 | 修改/添加字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| MMDet2MMOCR | `gt_masks` `gt_ignore_flags` | `gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | 将 MMDet 中采用的字段转换为对应的 MMOCR 字段。 |
|
||||
| MMOCR2MMDet | `img_shape`<br>`gt_polygons`<br>`gt_ignored` | `gt_masks` `gt_ignore_flags` | 将 MMOCR 中采用的字段转换为对应的 MMDet 字段。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 包装类 - wrappers.py
|
||||
|
||||
为了方便用户在 MMOCR 内部无缝调用常用的 CV 算法库,我们在 wrappers.py 中提供了相应的包装类。其主要打通了 MMOCR 与其它第三方算法库之间的数据格式和转换标准,使得用户可以在 MMOCR 的配置文件内直接配置使用这些第三方库提供的数据变换方法。目前支持的包装类有:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 数据转换类名称 | 需求字段 | 修改/添加字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ImgAugWrapper | `img`<br>`gt_polygons` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes_labels` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_ignored` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | `img`<br>`gt_polygons` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_bboxes_labels` (optional for text recognition)<br>`gt_ignored` (optional for text recognition)<br>`img_shape` (optional)<br>`gt_texts` (optional) | [ImgAug](https://github.com/aleju/imgaug) 包装类,用于打通 ImgAug 与 MMOCR 的数据格式及配置,方便用户调用 ImgAug 实现的一系列数据增强方法。 |
|
||||
| TorchVisionWrapper | `img` | `img`<br>`img_shape` | [TorchVision](https://github.com/pytorch/vision) 包装类,用于打通 TorchVision 与 MMOCR 的数据格式及配置,方便用户调用 `torchvision.transforms` 中实现的一系列数据变换方法。 |
|
||||
| | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
### `ImgAugWrapper` 示例
|
||||
|
||||
例如,在原生的 ImgAug 中,我们可以按照如下代码定义一个 `Sequential` 类型的数据增强流程,对图像分别进行随机翻转、随机旋转和随机缩放:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
|
||||
|
||||
aug = iaa.Sequential(
|
||||
iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # 以概率 0.5 进行水平翻转
|
||||
iaa.Affine(rotate=(-10, 10)), # 随机旋转 -10 到 10 度
|
||||
iaa.Resize((0.5, 3.0)) # 随机缩放到 50% 到 300% 的尺寸
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
而在 MMOCR 中,我们可以通过 `ImgAugWrapper` 包装类,将上述数据增强流程直接配置到 `train_pipeline` 中:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='ImgAugWrapper',
|
||||
args=[
|
||||
['Fliplr', 0.5],
|
||||
dict(cls='Affine', rotate=[-10, 10]),
|
||||
['Resize', [0.5, 3.0]],
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中,`args` 参数接收一个列表,列表中的每个元素可以是一个列表,也可以是一个字典。如果是列表,则列表的第一个元素为 `imgaug.augmenters` 中的类名,后面的元素为该类的初始化参数;如果是字典,则字典的 `cls` 键对应 `imgaug.augmenters` 中的类名,其他键值对则对应该类的初始化参数。
|
||||
|
||||
### `TorchVisionWrapper` 示例
|
||||
|
||||
例如,在原生的 TorchVision 中,我们可以按照如下代码定义一个 `Compose` 类型的数据变换流程,对图像进行色彩抖动:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
|
||||
|
||||
aug = transforms.Compose([
|
||||
transforms.ColorJitter(
|
||||
brightness=32.0 / 255, # 亮度抖动范围
|
||||
saturation=0.5) # 饱和度抖动范围
|
||||
])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
而在 MMOCR 中,我们可以通过 `TorchVisionWrapper` 包装类,将上述数据变换流程直接配置到 `train_pipeline` 中:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
type='TorchVisionWrapper',
|
||||
op='ColorJitter',
|
||||
brightness=32.0 / 255,
|
||||
saturation=0.5
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中,`op` 参数为 `torchvision.transforms` 中的类名,后面的参数则对应该类的初始化参数。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ img2.jpg MMOCR
|
|||
"bbox": [0, 0, 10, 20],
|
||||
"bbox_label": 0,
|
||||
"ignore": False
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue