# Useful tools
We provide lots of useful tools under the `tools/` directory. In addition, you can also quickly run other open source libraries of OpenMMLab through MIM.
Take MMDetection as an example. If you want to use [print_config.py](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/blob/3.x/tools/misc/print_config.py), you can directly use the following commands without copying the source code to the MMYOLO library.
```shell
mim run mmdet print_config [CONFIG]
```
**Note**: The MMDetection library must be installed through the MIM before the above command can succeed.
## Visualization
### Visualize COCO labels
`tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py` is a script that can visualization to display the COCO label in the picture.
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py ${DATA_ROOT} \
[--ann_file ${ANN_FILE}] \
[--img_dir ${IMG_DIR}] \
[--wait-time ${WAIT_TIME}] \
[--disp-all] [--category-names CATEGORY_NAMES [CATEGORY_NAMES ...]] \
[--shuffle]
```
E.g:
1. Visualize all categories of `COCO` and display all types of annotations such as `bbox` and `mask`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py './data/coco/' \
--ann_file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--img_dir 'train2017' \
--disp-all
```
2. Visualize all categories of `COCO`, and display only the `bbox` type labels, and shuffle the image to show:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py './data/coco/' \
--ann_file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--img_dir 'train2017' \
--shuffle
```
3. Only visualize the `bicycle` and `person` categories of `COCO` and only the `bbox` type labels are displayed:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py './data/coco/' \
--ann_file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--img_dir 'train2017' \
--category-names 'bicycle' 'person'
```
4. Visualize all categories of `COCO`, and display all types of label such as `bbox`, `mask`, and shuffle the image to show:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py './data/coco/' \
--ann_file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--img_dir 'train2017' \
--disp-all \
--shuffle
```
### Visualize Datasets
`tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py` helps the user to browse a detection dataset (both images and bounding box annotations) visually, or save the image to a designated directory.
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py ${CONFIG} \
[-h] \
[--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}] \
[--not-show] \
[--show-interval ${SHOW_INTERVAL}]
```
E,g:
1. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will pop up directly and be saved to the directory `work dir/browse_ dataset` at the same time:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--output-dir 'work-dir/browse_dataset'
```
2. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will pop up and display directly. Each picture lasts for `10` seconds. At the same time, it will be saved to the directory `work dir/browse_ dataset`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--output-dir 'work-dir/browse_dataset' \
--show-interval 10
```
3. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will pop up and display directly. Each picture lasts for `10` seconds and the picture will not be saved:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--show-interval 10
```
4. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will not pop up directly, but only saved to the directory `work dir/browse_ dataset`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--output-dir 'work-dir/browse_dataset' \
--not-show
```
### Visualize dataset analysis
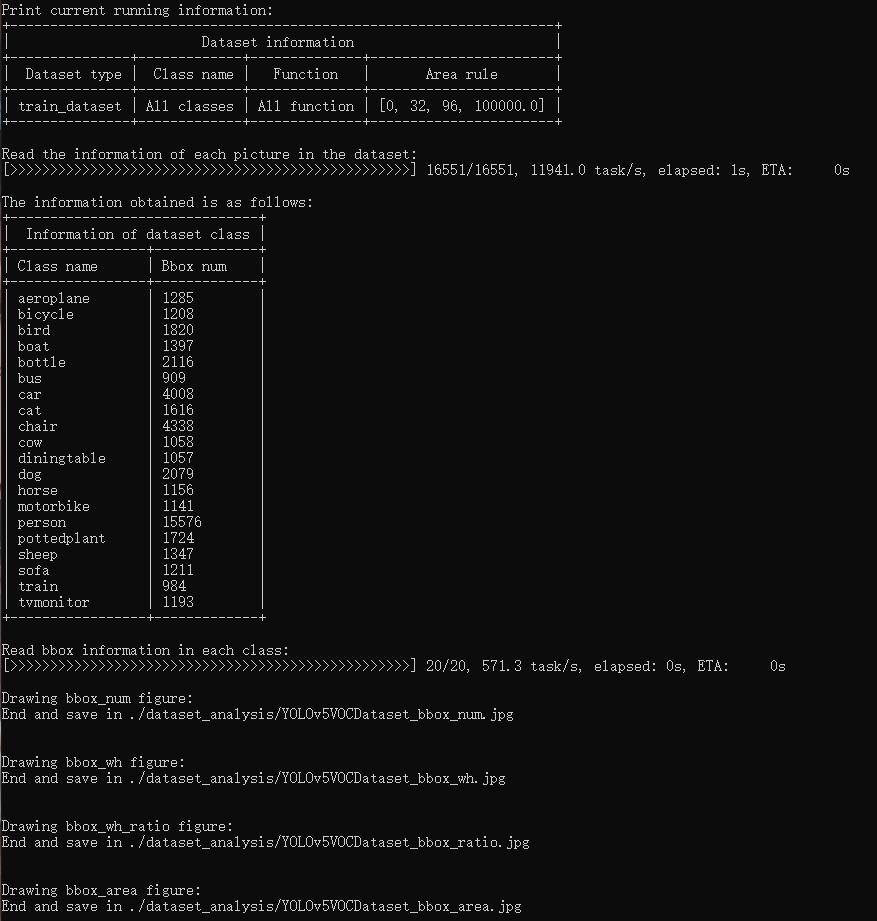
`tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py` help users get the renderings of the four functions, and save the pictures to the `dataset_analysis` folder under the current running directory.
Description of the script's functions:
The data required by each sub function is obtained through the data preparation of `main()`.
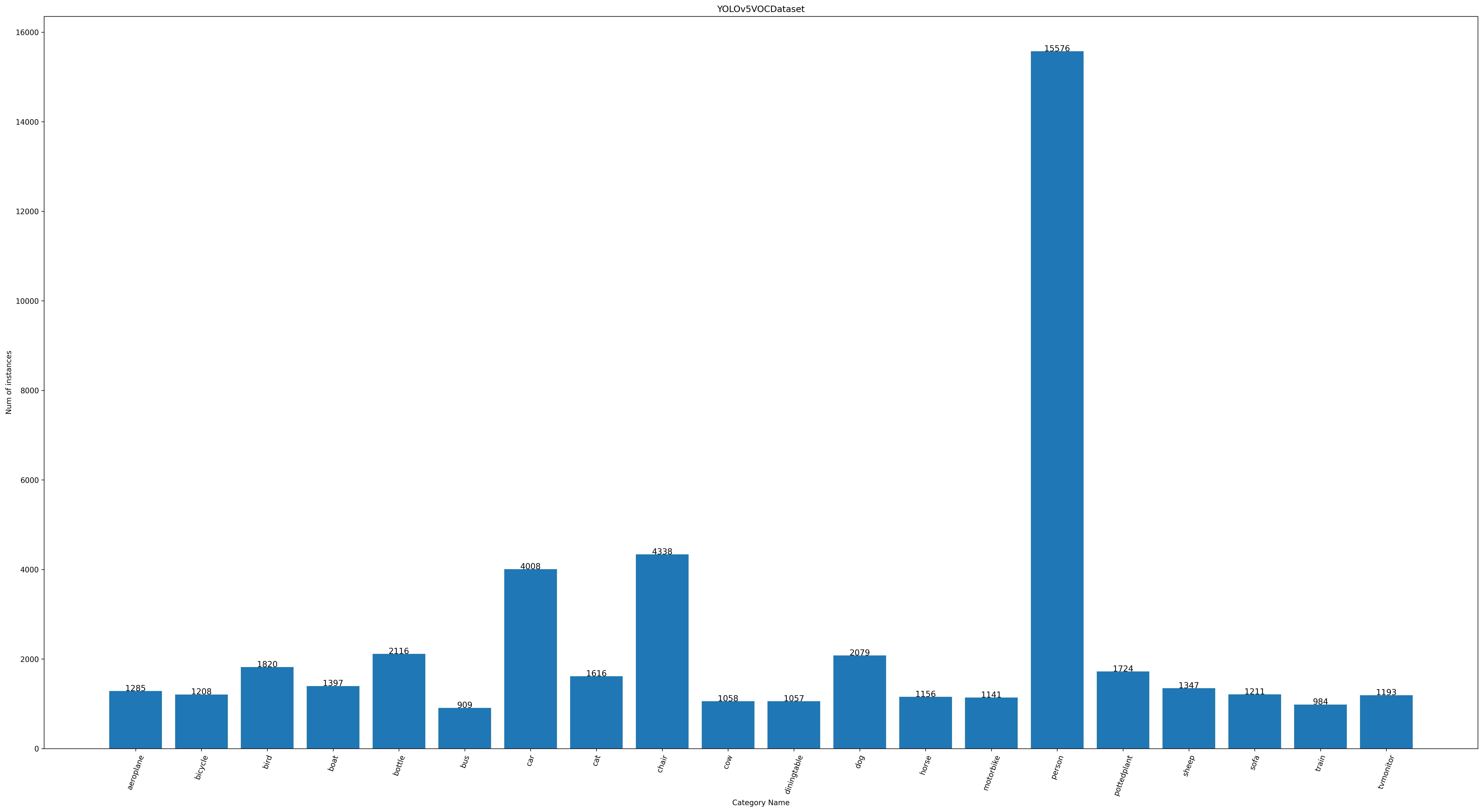
Function 1: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_num` to display the distribution of categories and bbox instances.
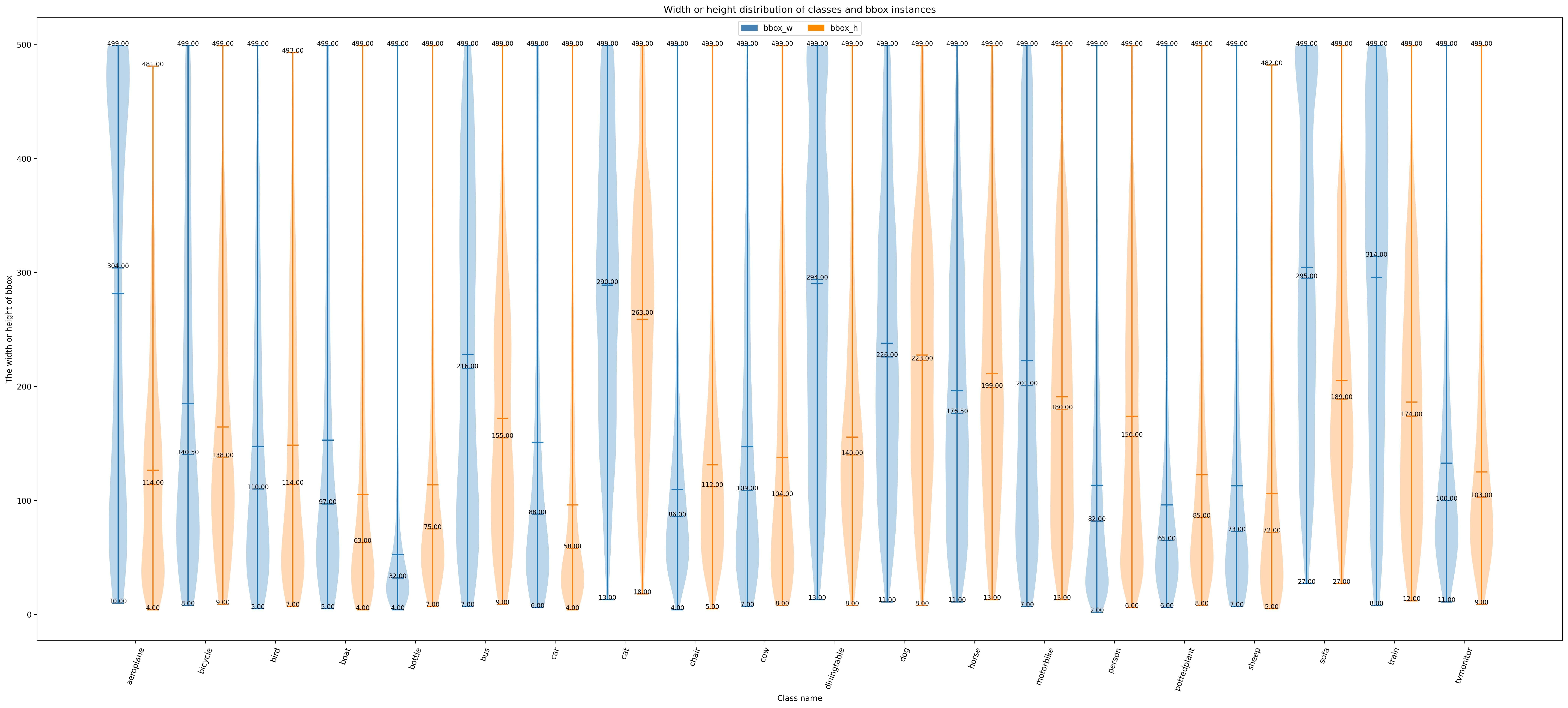
 Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
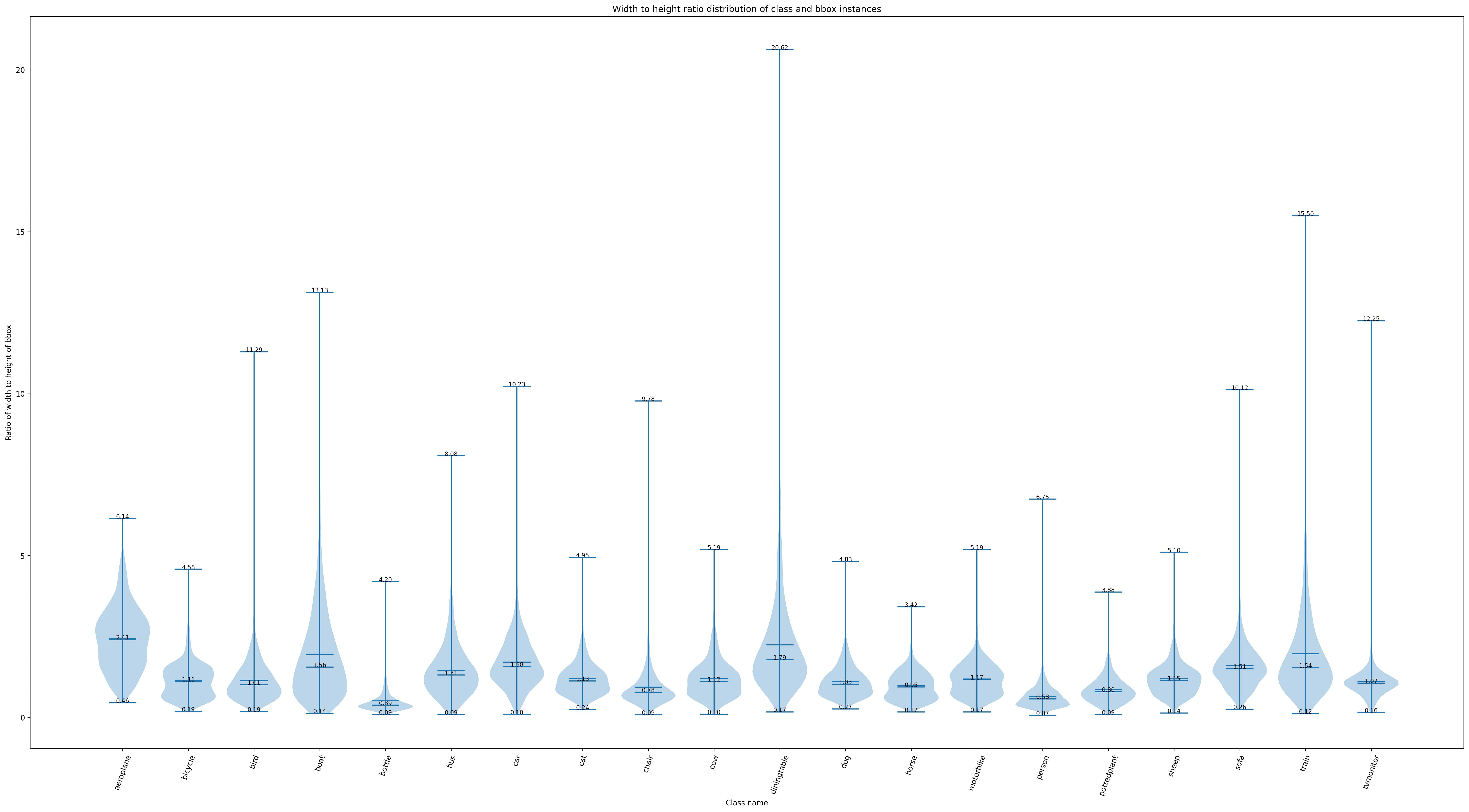
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
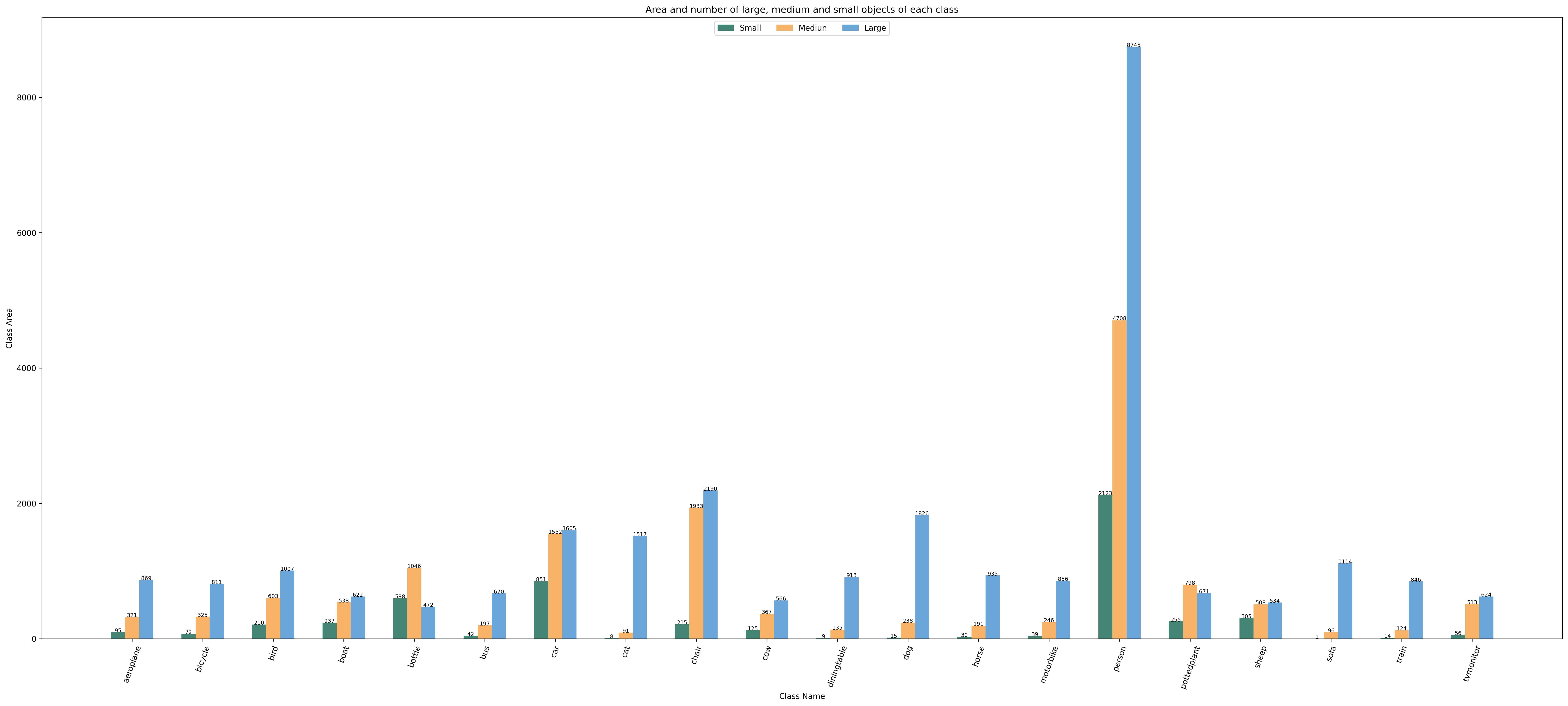
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
 Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
 ```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[-h] \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loadingt type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_ir/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--output-dir work_dir/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## optimize anchors size
script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `differential_evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### differential_evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm differential_evolution \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with yolov5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number of images. The user can use the `--num-img` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified number of images.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[-h] \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loadingt type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_ir/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--output-dir work_dir/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## optimize anchors size
script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `differential_evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### differential_evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm differential_evolution \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with yolov5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number of images. The user can use the `--num-img` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified number of images.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```
 Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
 Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
 ```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[-h] \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loadingt type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_ir/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--output-dir work_dir/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## optimize anchors size
script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `differential_evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### differential_evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm differential_evolution \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with yolov5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number of images. The user can use the `--num-img` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified number of images.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[-h] \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loadingt type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_ir/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--output-dir work_dir/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## optimize anchors size
script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `differential_evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### differential_evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm differential_evolution \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with yolov5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number of images. The user can use the `--num-img` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified number of images.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```