# Useful tools
We provide lots of useful tools under the `tools/` directory. In addition, you can also quickly run other open source libraries of OpenMMLab through MIM.
Take MMDetection as an example. If you want to use [print_config.py](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/blob/3.x/tools/misc/print_config.py), you can directly use the following commands without copying the source code to the MMYOLO library.
```shell
mim run mmdet print_config ${CONFIG}
```
## Visualization
### Visualize COCO labels
`tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py` is a script that can visualization to display the COCO label in the picture.
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py [--data-root ${DATA_ROOT}] \
[--img-dir ${IMG_DIR}] \
[--ann-file ${ANN_FILE}] \
[--wait-time ${WAIT_TIME}] \
[--disp-all] [--category-names CATEGORY_NAMES [CATEGORY_NAMES ...]] \
[--shuffle]
```
If images and labels are in the same folder, you can specify `--data-root` to the folder, and then `--img-dir` and `--ann-file` to specify the relative path of the folder. The code will be automatically spliced.
If the image and label files are not in the same folder, you do not need to specify `--data-root`, but directly specify `--img-dir` and `--ann-file` of the absolute path.
E.g:
1. Visualize all categories of `COCO` and display all types of annotations such as `bbox` and `mask`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py --data-root './data/coco' \
--img-dir 'train2017' \
--ann-file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--disp-all
```
If images and labels are not in the same folder, you can use a absolutely path:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py --img-dir '/dataset/image/coco/train2017' \
--ann-file '/label/instances_train2017.json' \
--disp-all
```
2. Visualize all categories of `COCO`, and display only the `bbox` type labels, and shuffle the image to show:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py --data-root './data/coco' \
--img-dir 'train2017' \
--ann-file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--shuffle
```
3. Only visualize the `bicycle` and `person` categories of `COCO` and only the `bbox` type labels are displayed:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py --data-root './data/coco' \
--img-dir 'train2017' \
--ann-file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--category-names 'bicycle' 'person'
```
4. Visualize all categories of `COCO`, and display all types of label such as `bbox`, `mask`, and shuffle the image to show:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_coco_json.py --data-root './data/coco' \
--img-dir 'train2017' \
--ann-file 'annotations/instances_train2017.json' \
--disp-all \
--shuffle
```
### Visualize Datasets
`tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py` helps the user to browse a detection dataset (both images and bounding box annotations) visually, or save the image to a designated directory.
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py ${CONFIG} \
[--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}] \
[--not-show] \
[--show-interval ${SHOW_INTERVAL}]
```
E,g:
1. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will pop up directly and be saved to the directory `work_dirs/browse_ dataset` at the same time:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--out-dir 'work_dirs/browse_dataset'
```
2. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will pop up and display directly. Each picture lasts for `10` seconds. At the same time, it will be saved to the directory `work_dirs/browse_ dataset`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--out-dir 'work_dirs/browse_dataset' \
--show-interval 10
```
3. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will pop up and display directly. Each picture lasts for `10` seconds and the picture will not be saved:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--show-interval 10
```
4. Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py` to visualize the picture. The picture will not pop up directly, but only saved to the directory `work_dirs/browse_ dataset`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/browse_dataset.py 'configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py' \
--out-dir 'work_dirs/browse_dataset' \
--not-show
```
### Visualize dataset analysis
`tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py` help users get the renderings of the four functions, and save the pictures to the `dataset_analysis` folder under the current running directory.
Description of the script's functions:
The data required by each sub function is obtained through the data preparation of `main()`.
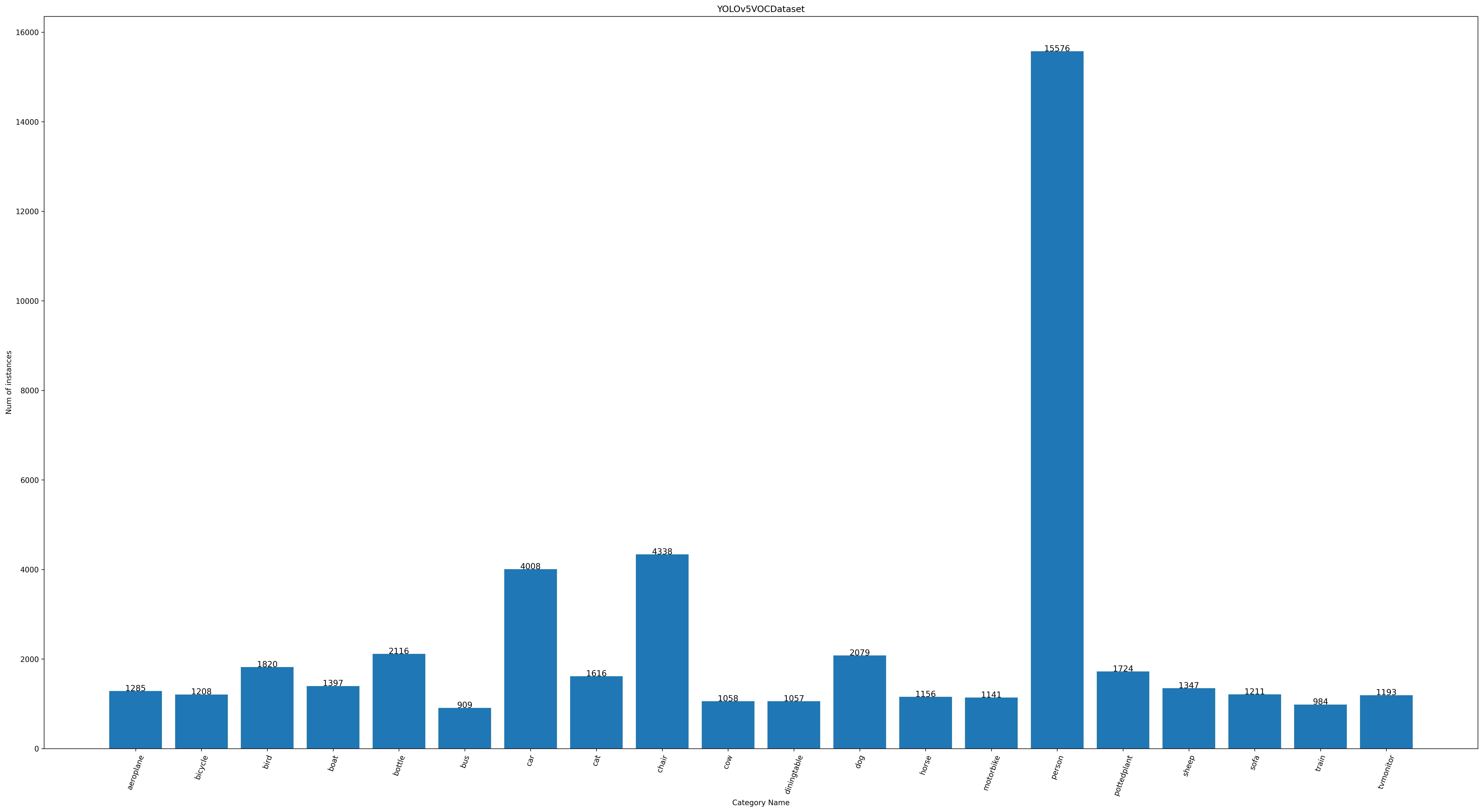
Function 1: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_num` to display the distribution of categories and bbox instances.
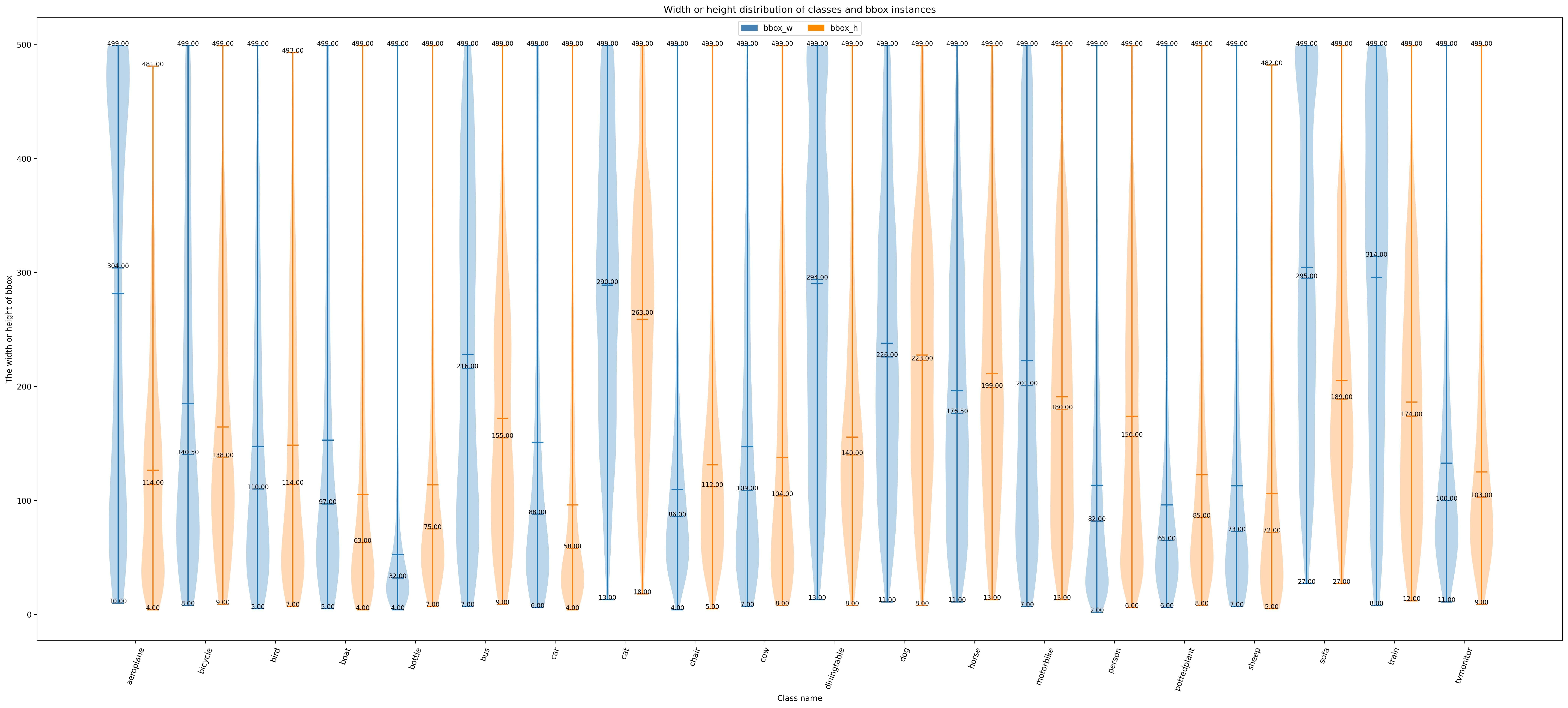
 Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
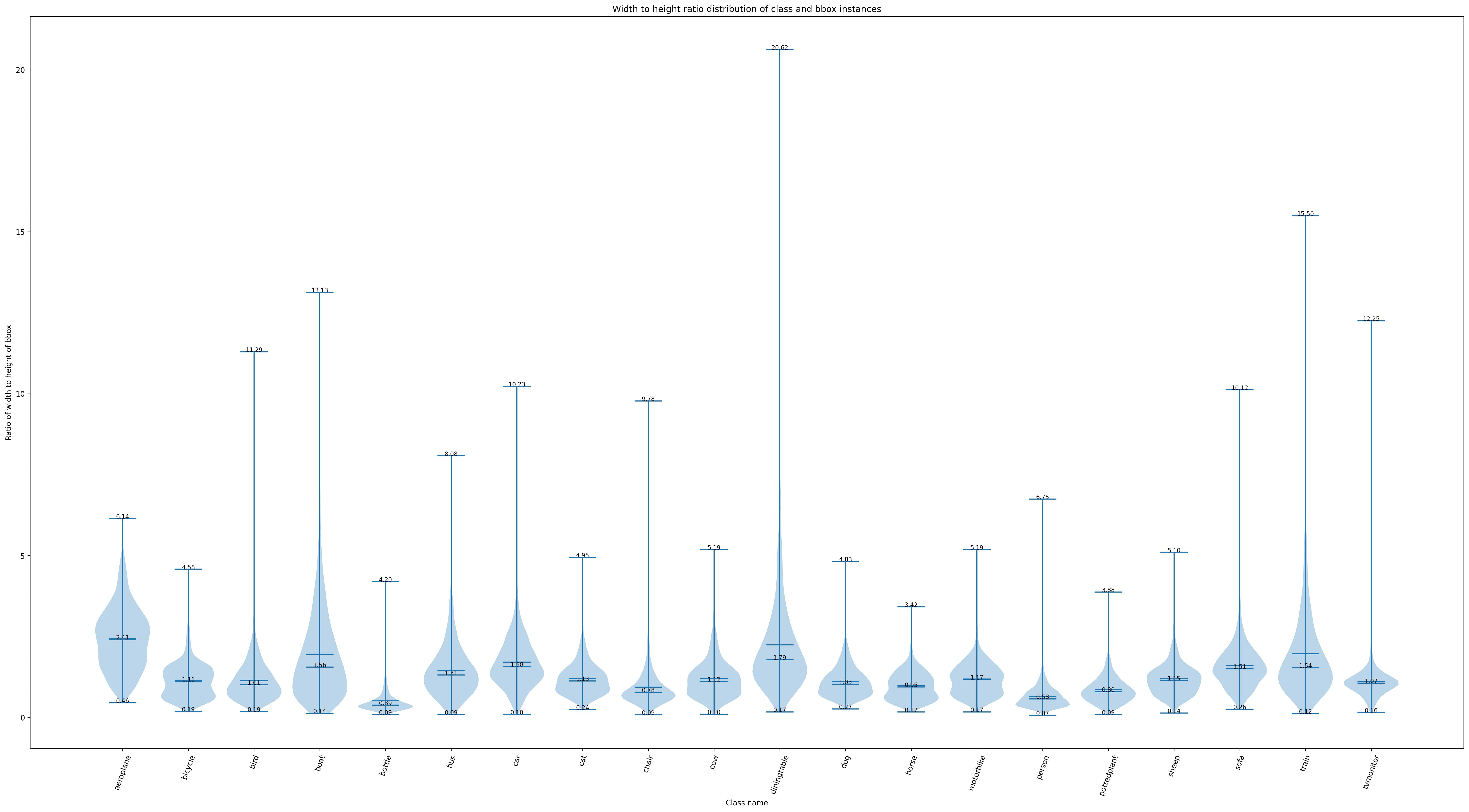
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
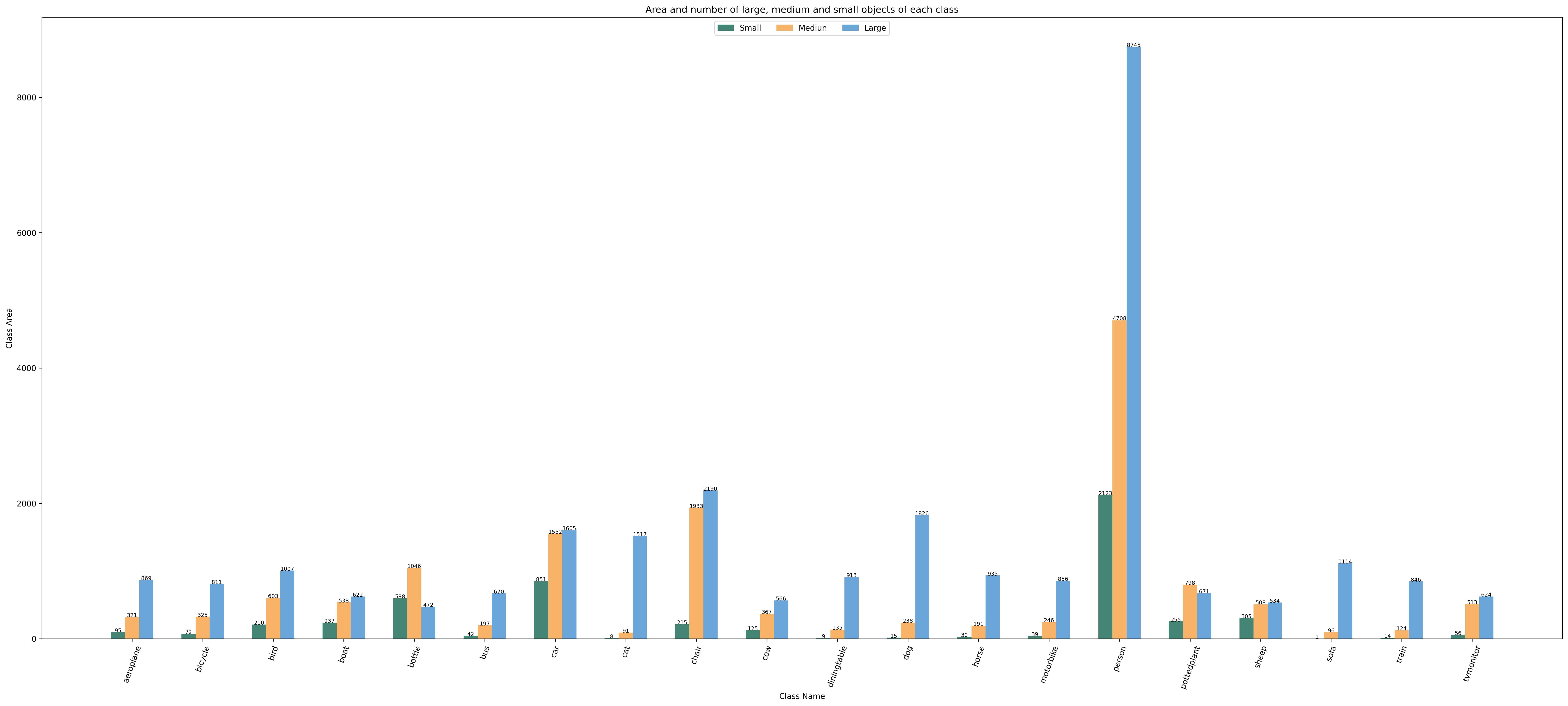
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
 Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
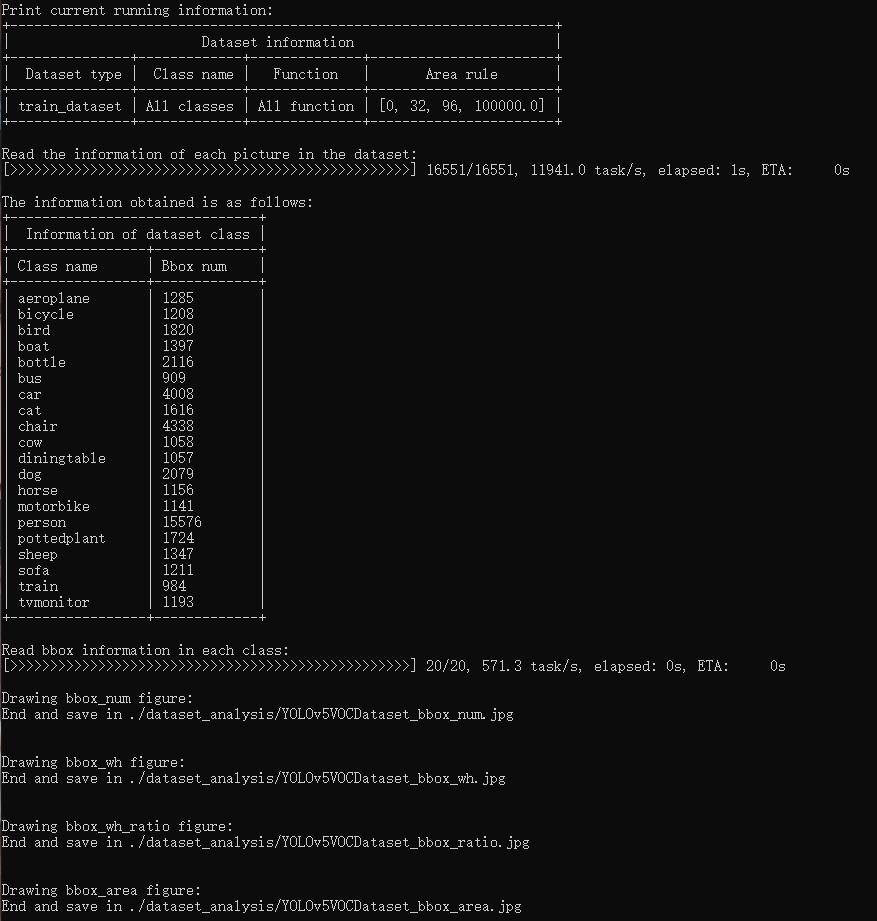 ```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loading type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_dirs/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--out-dir work_dirs/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## Optimize anchors size
Script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `Differential Evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### Differential Evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm DE \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with YOLOv5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
## Perform inference on large images
First install [`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) with:
```shell
pip install -U sahi>=0.11.4
```
Perform MMYOLO inference on large images (as satellite imagery) as:
```shell
wget -P checkpoint https://download.openmmlab.com/mmyolo/v0/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
```
Arrange slicing parameters as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--patch-size 512
--patch-overlap-ratio 0.25
```
Export debug visuals while performing inference on large images as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--debug
```
[`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) citation:
```
@article{akyon2022sahi,
title={Slicing Aided Hyper Inference and Fine-tuning for Small Object Detection},
author={Akyon, Fatih Cagatay and Altinuc, Sinan Onur and Temizel, Alptekin},
journal={2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)},
doi={10.1109/ICIP46576.2022.9897990},
pages={966-970},
year={2022}
}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number/classes/area-size of images. The user can use the `--num-img`, `--classes`, `--area-size` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified condition of images.
For example, extract images use scripts as follows:
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py \
${ROOT} \
${OUT_DIR} \
--num-img 20 \
--classes cat dog person \
--area-size small
```
It gone be extract 20 images, and only includes annotations which belongs to cat(or dog/person) and bbox area size is small, after filter by class and area size, the empty annotation images won't be chosen, guarantee the images be extracted definitely has annotation info.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```
4. Extract images by specify classes
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --classes cat dog person
```
5. Extract images by specify anchor size
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --area-size small
```
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loading type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_dirs/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--out-dir work_dirs/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## Optimize anchors size
Script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `Differential Evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### Differential Evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm DE \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with YOLOv5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
## Perform inference on large images
First install [`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) with:
```shell
pip install -U sahi>=0.11.4
```
Perform MMYOLO inference on large images (as satellite imagery) as:
```shell
wget -P checkpoint https://download.openmmlab.com/mmyolo/v0/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
```
Arrange slicing parameters as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--patch-size 512
--patch-overlap-ratio 0.25
```
Export debug visuals while performing inference on large images as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--debug
```
[`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) citation:
```
@article{akyon2022sahi,
title={Slicing Aided Hyper Inference and Fine-tuning for Small Object Detection},
author={Akyon, Fatih Cagatay and Altinuc, Sinan Onur and Temizel, Alptekin},
journal={2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)},
doi={10.1109/ICIP46576.2022.9897990},
pages={966-970},
year={2022}
}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number/classes/area-size of images. The user can use the `--num-img`, `--classes`, `--area-size` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified condition of images.
For example, extract images use scripts as follows:
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py \
${ROOT} \
${OUT_DIR} \
--num-img 20 \
--classes cat dog person \
--area-size small
```
It gone be extract 20 images, and only includes annotations which belongs to cat(or dog/person) and bbox area size is small, after filter by class and area size, the empty annotation images won't be chosen, guarantee the images be extracted definitely has annotation info.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```
4. Extract images by specify classes
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --classes cat dog person
```
5. Extract images by specify anchor size
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --area-size small
```
 Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 2: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh` to display the width and height distribution of categories and bbox instances.
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_wh_ratio` to display the width to height ratio distribution of categories and bbox instances.
 Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
Function 3: Generated by the sub function `show_bbox_area` to display the distribution map of category and bbox instance area based on area rules.
 Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
Print List: Generated by the sub function `show_class_list` and `show_data_list`.
 ```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loading type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_dirs/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--out-dir work_dirs/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## Optimize anchors size
Script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `Differential Evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### Differential Evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm DE \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with YOLOv5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
## Perform inference on large images
First install [`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) with:
```shell
pip install -U sahi>=0.11.4
```
Perform MMYOLO inference on large images (as satellite imagery) as:
```shell
wget -P checkpoint https://download.openmmlab.com/mmyolo/v0/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
```
Arrange slicing parameters as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--patch-size 512
--patch-overlap-ratio 0.25
```
Export debug visuals while performing inference on large images as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--debug
```
[`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) citation:
```
@article{akyon2022sahi,
title={Slicing Aided Hyper Inference and Fine-tuning for Small Object Detection},
author={Akyon, Fatih Cagatay and Altinuc, Sinan Onur and Temizel, Alptekin},
journal={2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)},
doi={10.1109/ICIP46576.2022.9897990},
pages={966-970},
year={2022}
}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number/classes/area-size of images. The user can use the `--num-img`, `--classes`, `--area-size` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified condition of images.
For example, extract images use scripts as follows:
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py \
${ROOT} \
${OUT_DIR} \
--num-img 20 \
--classes cat dog person \
--area-size small
```
It gone be extract 20 images, and only includes annotations which belongs to cat(or dog/person) and bbox area size is small, after filter by class and area size, the empty annotation images won't be chosen, guarantee the images be extracted definitely has annotation info.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```
4. Extract images by specify classes
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --classes cat dog person
```
5. Extract images by specify anchor size
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --area-size small
```
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py ${CONFIG} \
[--type ${TYPE}] \
[--class-name ${CLASS_NAME}] \
[--area-rule ${AREA_RULE}] \
[--func ${FUNC}] \
[--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}]
```
E,g:
1.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, By default,the data loading type is `train_dataset`, the area rule is `[0,32,96,1e5]`, generate a result graph containing all functions and save the graph to the current running directory `./dataset_analysis` folder:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py
```
2.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the data loading type from the default `train_dataset` to `val_dataset` through the `--val-dataset` setting:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--val-dataset
```
3.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of all generated classes to specific classes. Take the display of `person` classes as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--class-name person
```
4.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, redefine the area rule through `--area-rule` . Take `30 70 125` as an example, the area rule becomes `[0,30,70,125,1e5]`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--area-rule 30 70 125
```
5.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, change the display of four function renderings to only display `Function 1` as an example:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--func show_bbox_num
```
6.Use `config` file `configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py` analyze the dataset, modify the picture saving address to `work_dirs/dataset_analysis`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/dataset_analysis.py configs/yolov5/voc/yolov5_s-v61_fast_1xb64-50e_voc.py \
--out-dir work_dirs/dataset_analysis
```
## Dataset Conversion
The folder `tools/data_converters` currently contains `ballon2coco.py` and `yolo2coco.py` two dataset conversion tools.
- `ballon2coco.py` converts the `balloon` dataset (this small dataset is for starters only) to COCO format.
For a detailed description of this script, please see the `Dataset Preparation` section in [From getting started to deployment with YOLOv5](./yolov5_tutorial.md).
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/balloon2coco.py
```
- `yolo2coco.py` converts a dataset from `yolo-style` **.txt** format to COCO format, please use it as follows:
```shell
python tools/dataset_converters/yolo2coco.py /path/to/the/root/dir/of/your_dataset
```
Instructions:
1. `image_dir` is the root directory of the yolo-style dataset you need to pass to the script, which should contain `images`, `labels`, and `classes.txt`. `classes.txt` is the class declaration corresponding to the current dataset. One class a line. The structure of the root directory should be formatted as this example shows:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
2. The script will automatically check if `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` have already existed under `image_dir`. If these files are located, the script will organize the dataset accordingly. Otherwise, the script will convert the dataset into one file. The image paths in these files must be **ABSOLUTE** paths.
3. By default, the script will create a folder called `annotations` in the `image_dir` directory which stores the converted JSON file. If `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `test.txt` are not found, the output file is `result.json`. Otherwise, the corresponding JSON file will be generated, named as `train.json`, `val.json`, and `test.json`. The `annotations` folder may look similar to this:
```bash
.
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── annotations
│ ├── result.json
│ └── ...
├── classes.txt
├── labels
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── b.txt
│ └── ...
├── images
│ ├── a.jpg
│ ├── b.png
│ └── ...
└── ...
```
## Download Dataset
`tools/misc/download_dataset.py` supports downloading datasets such as `COCO`, `VOC`, `LVIS` and `Balloon`.
```shell
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name coco2017
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2007
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name voc2012
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name lvis
python tools/misc/download_dataset.py --dataset-name balloon [--save-dir ${SAVE_DIR}] [--unzip]
```
## Convert Model
The six scripts under the `tools/model_converters` directory can help users convert the keys in the official pre-trained model of YOLO to the format of MMYOLO, and use MMYOLO to fine-tune the model.
### YOLOv5
Take conversion `yolov5s.pt` as an example:
1. Clone the official YOLOv5 code to the local (currently the maximum supported version is `v6.1`):
```shell
git clone -b v6.1 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
```
2. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.1/yolov5s.pt
```
3. Copy file `tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py` to the path of YOLOv5 official code clone:
```shell
cp ${MMDET_YOLO_PATH}/tools/model_converters/yolov5_to_mmyolo.py yolov5_to_mmyolo.py
```
4. Conversion
```shell
python yolov5_to_mmyolo.py --src ${WEIGHT_FILE_PATH} --dst mmyolov5.pt
```
The converted `mmyolov5.pt` can be used by MMYOLO. The official weight conversion of YOLOv6 is also used in the same way.
### YOLOX
The conversion of YOLOX model **does not need** to download the official YOLOX code, just download the weight.
Take conversion `yolox_s.pth` as an example:
1. Download official weight file:
```shell
wget https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX/releases/download/0.1.1rc0/yolox_s.pth
```
2. Conversion
```shell
python tools/model_converters/yolox_to_mmyolo.py --src yolox_s.pth --dst mmyolox.pt
```
The converted `mmyolox.pt` can be used by MMYOLO.
## Optimize anchors size
Script `tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py` supports three methods to optimize YOLO anchors including `k-means`
anchor cluster, `Differential Evolution` and `v5-k-means`.
### k-means
In k-means method, the distance criteria is based IoU, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### Differential Evolution
In differential_evolution method, based differential evolution algorithm, use `avg_iou_cost` as minimum target function, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm DE \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
### v5-k-means
In v5-k-means method, clustering standard as same with YOLOv5 which use shape-match, python shell as follow:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/optimize_anchors.py ${CONFIG} \
--algorithm v5-k-means \
--input-shape ${INPUT_SHAPE [WIDTH HEIGHT]} \
--prior_match_thr ${PRIOR_MATCH_THR} \
--out-dir ${OUT_DIR}
```
## Perform inference on large images
First install [`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) with:
```shell
pip install -U sahi>=0.11.4
```
Perform MMYOLO inference on large images (as satellite imagery) as:
```shell
wget -P checkpoint https://download.openmmlab.com/mmyolo/v0/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
```
Arrange slicing parameters as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--patch-size 512
--patch-overlap-ratio 0.25
```
Export debug visuals while performing inference on large images as:
```shell
python demo/large_image_demo.py \
demo/large_image.jpg \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
checkpoint/yolov5_m-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220917_204944-516a710f.pth \
--debug
```
[`sahi`](https://github.com/obss/sahi) citation:
```
@article{akyon2022sahi,
title={Slicing Aided Hyper Inference and Fine-tuning for Small Object Detection},
author={Akyon, Fatih Cagatay and Altinuc, Sinan Onur and Temizel, Alptekin},
journal={2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)},
doi={10.1109/ICIP46576.2022.9897990},
pages={966-970},
year={2022}
}
```
## Extracts a subset of COCO
The training dataset of the COCO2017 dataset includes 118K images, and the validation set includes 5K images, which is a relatively large dataset. Loading JSON in debugging or quick verification scenarios will consume more resources and bring slower startup speed.
The `extract_subcoco.py` script provides the ability to extract a specified number/classes/area-size of images. The user can use the `--num-img`, `--classes`, `--area-size` parameter to get a COCO subset of the specified condition of images.
For example, extract images use scripts as follows:
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py \
${ROOT} \
${OUT_DIR} \
--num-img 20 \
--classes cat dog person \
--area-size small
```
It gone be extract 20 images, and only includes annotations which belongs to cat(or dog/person) and bbox area size is small, after filter by class and area size, the empty annotation images won't be chosen, guarantee the images be extracted definitely has annotation info.
Currently, only support COCO2017. In the future will support user-defined datasets of standard coco JSON format.
The root path folder format is as follows:
```text
├── root
│ ├── annotations
│ ├── train2017
│ ├── val2017
│ ├── test2017
```
1. Extract 10 training images and 10 validation images using only 5K validation sets.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 10
```
2. Extract 20 training images using the training set and 20 validation images using the validation set.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set
```
3. Set the global seed to 1. The default is no setting.
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --num-img 20 --use-training-set --seed 1
```
4. Extract images by specify classes
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --classes cat dog person
```
5. Extract images by specify anchor size
```shell
python tools/misc/extract_subcoco.py ${ROOT} ${OUT_DIR} --area-size small
```