12 KiB
ClearML Integration with Ultralytics YOLOv5


ℹ️ About ClearML
ClearML is an open-source MLOps platform designed to streamline your machine learning workflow and save you valuable time ⏱️. Integrating ClearML with Ultralytics YOLOv5 allows you to leverage a powerful suite of tools:
- Experiment Management: 🔨 Track every YOLOv5 training run, including parameters, metrics, and outputs. See the Ultralytics ClearML integration guide for more details.
- Data Versioning: 🔧 Version and easily access your custom training data using the integrated ClearML Data Versioning Tool, similar to concepts in DVC integration.
- Remote Execution: 🔦 Remotely train and monitor your YOLOv5 models using ClearML Agent.
- Hyperparameter Optimization: 🔬 Achieve optimal Mean Average Precision (mAP) using ClearML's Hyperparameter Optimization capabilities.
- Model Deployment: 🔭 Turn your trained YOLOv5 model into an API with just a few commands using ClearML Serving, complementing Ultralytics deployment options.
You can choose to use only the experiment manager or combine multiple tools into a comprehensive MLOps pipeline.
🦾 Setting Things Up
ClearML requires communication with a server to track experiments and data. You have two main options:
- ClearML Hosted Service: Sign up for a free account at app.clear.ml.
- Self-Hosted Server: Set up your own ClearML server. Find instructions here. The server is also open-source, ensuring data privacy.
Follow these steps to get started:
-
Install the
clearmlPython package:pip install clearmlNote: This package is included in the
requirements.txtof YOLOv5. -
Connect the ClearML SDK to your server. Create credentials (Settings -> Workspace -> Create new credentials), then run the following command and follow the prompts:
clearml-init
That's it! You're ready to integrate ClearML with your YOLOv5 projects 😎. For a general Ultralytics setup, see the Quickstart Guide.
🚀 Training YOLOv5 With ClearML
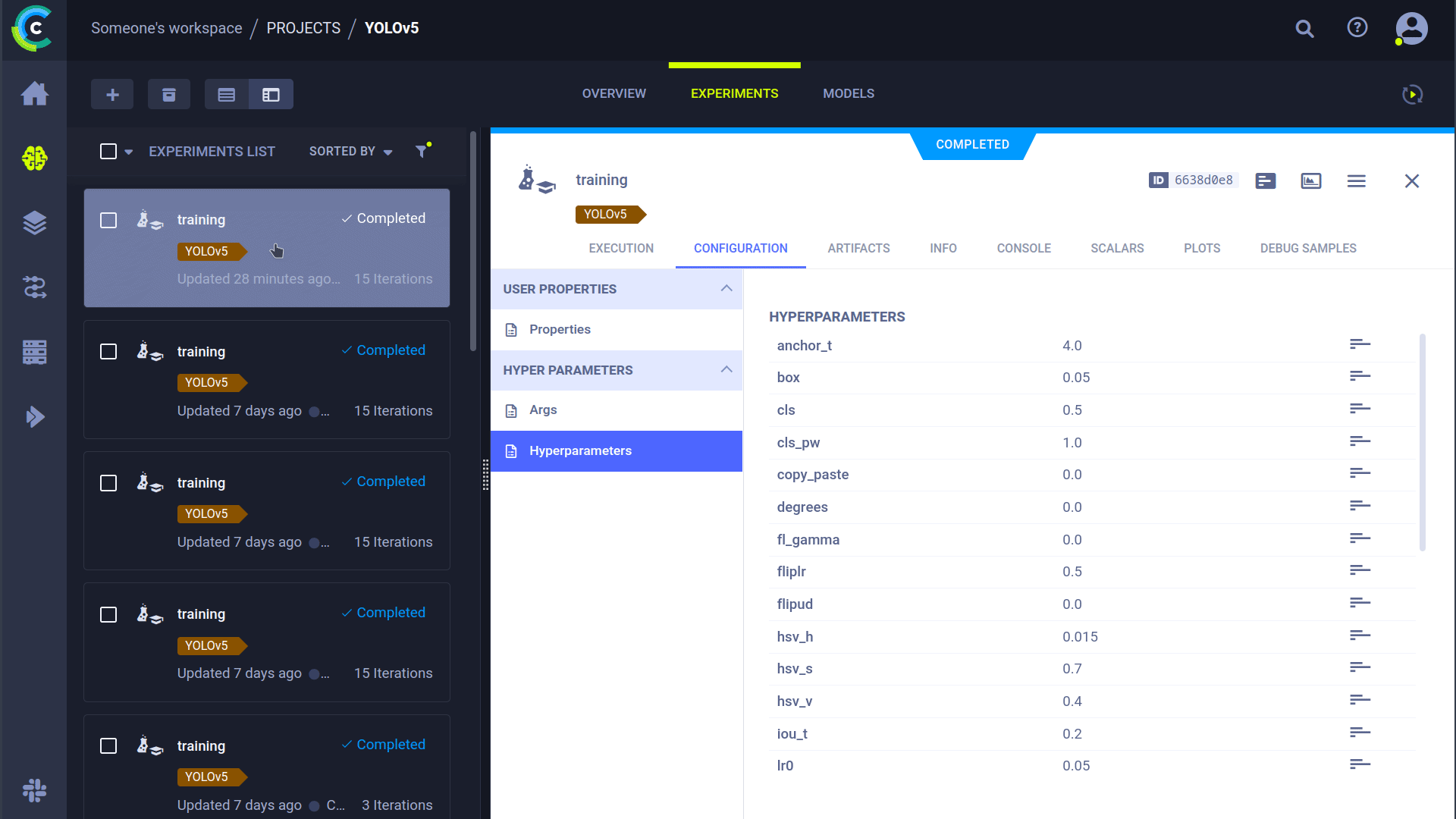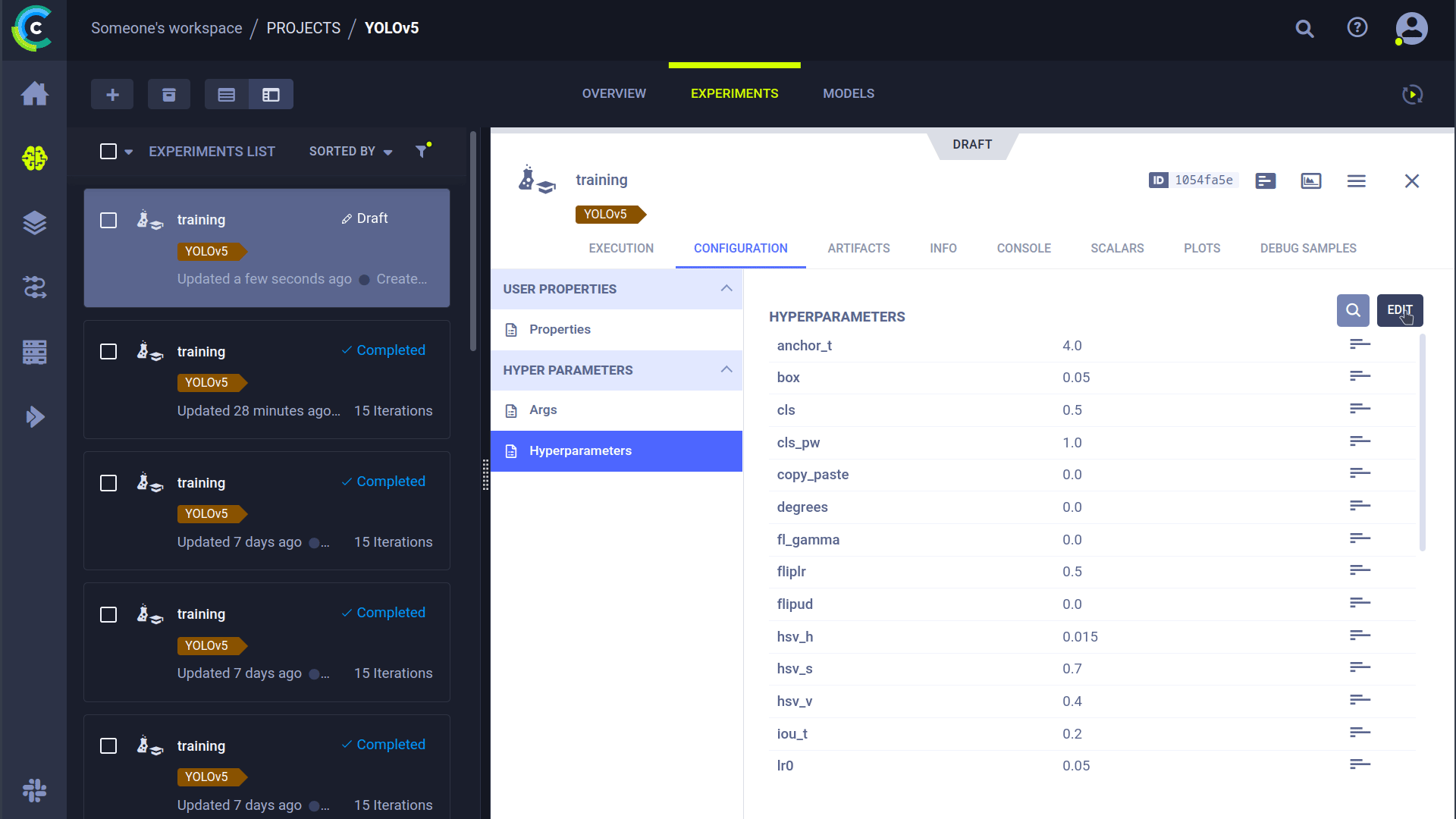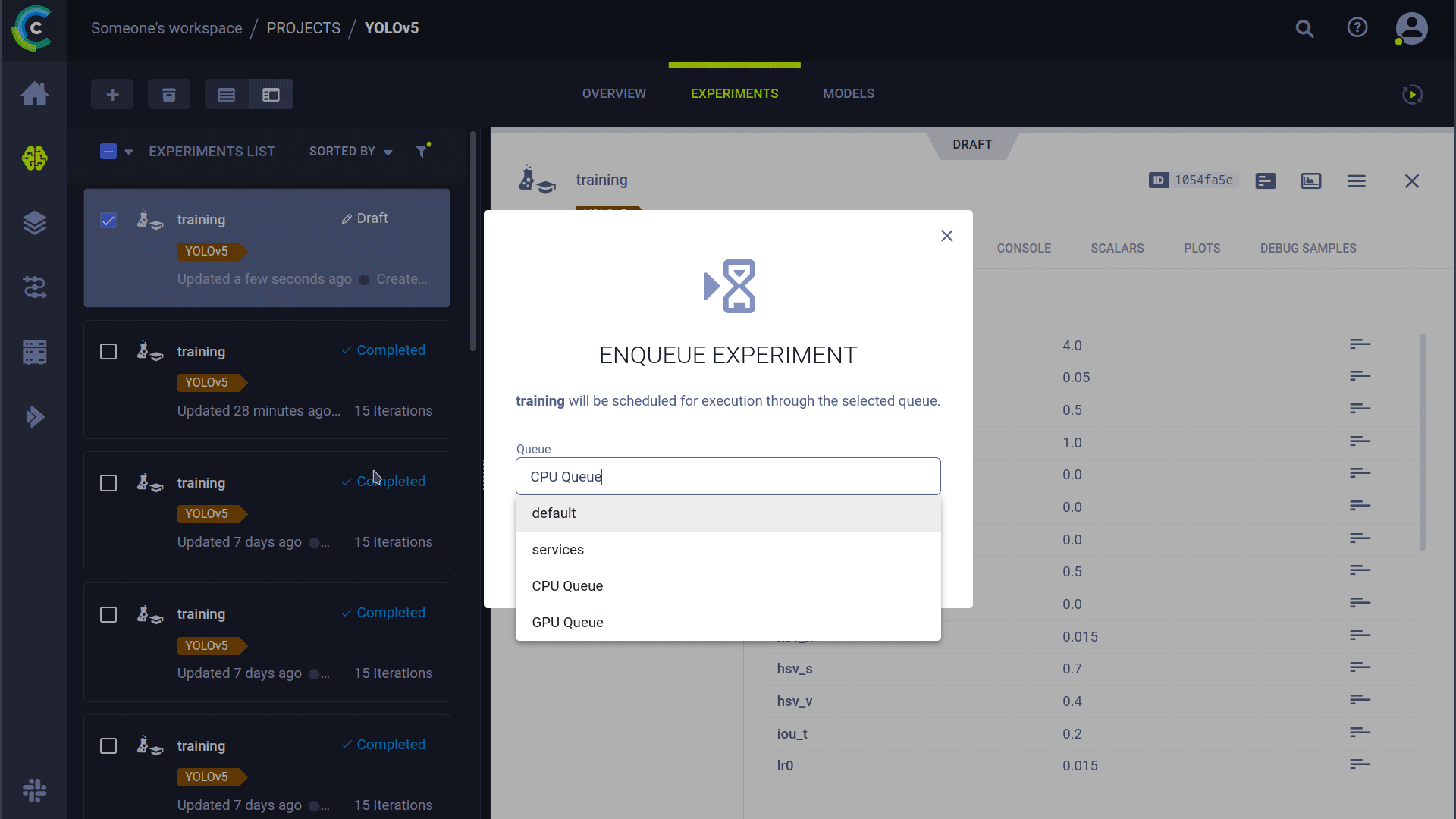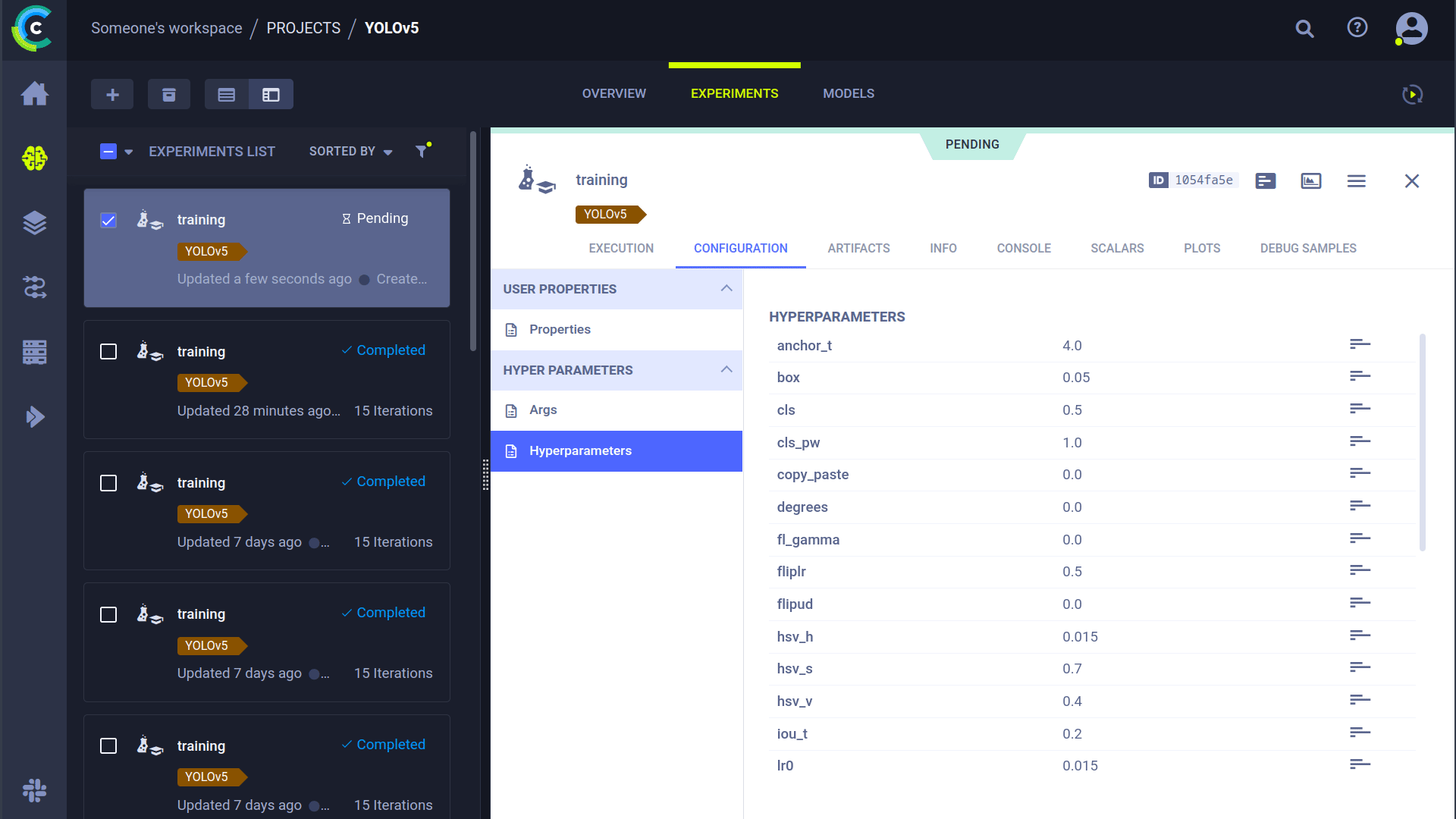
ClearML experiment tracking is automatically enabled when the clearml package is installed. Every YOLOv5 training run will be captured and stored in the ClearML experiment manager.
To customize the project or task name in ClearML, use the --project and --name arguments when running train.py. By default, the project is YOLOv5 and the task is Training. Note that ClearML uses / as a delimiter for subprojects.
Example Training Command:
# Train YOLOv5s on COCO128 dataset for 3 epochs
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache
Example with Custom Project and Task Names:
# Train with custom names
python train.py --project my_yolo_project --name experiment_001 --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache
ClearML automatically captures comprehensive information about your training run:
- Source code and uncommitted changes
- Installed Python packages
- Hyperparameters and configuration settings
- Model checkpoints (use
--save-period nto save everynepochs) - Console output logs
- Performance metrics (mAP_0.5, mAP_0.5:0.95, precision, recall, losses, learning rates, etc.)
- System details (machine specs, runtime, creation date)
- Generated plots (e.g., label correlogram, confusion matrix)
- Images with bounding boxes per epoch
- Mosaic augmentation previews per epoch
- Validation images per epoch
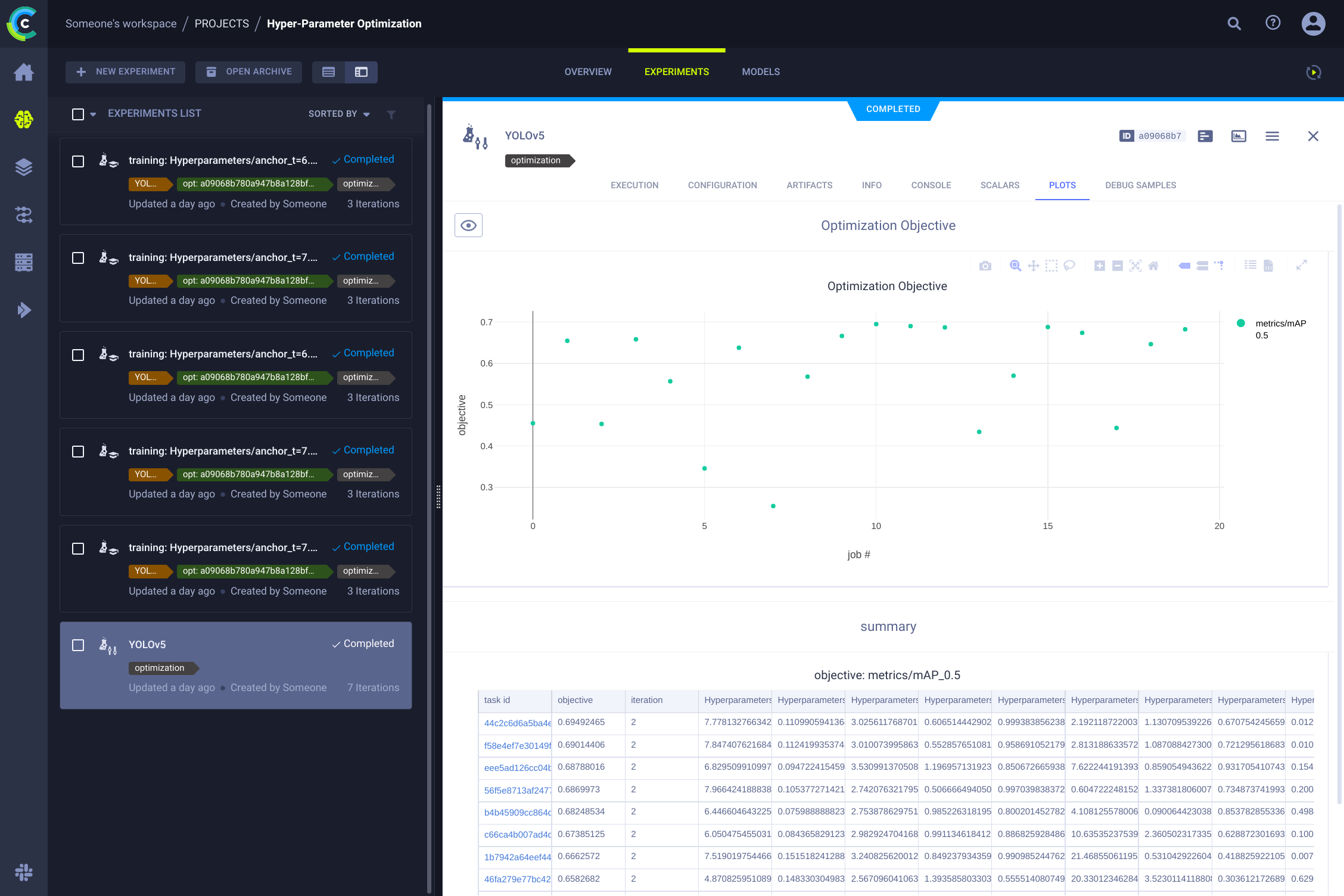
This wealth of information 🤯 can be visualized in the ClearML UI. You can customize table views, sort experiments by metrics like mAP, and directly compare multiple runs. This detailed tracking enables advanced features like hyperparameter optimization and remote execution.
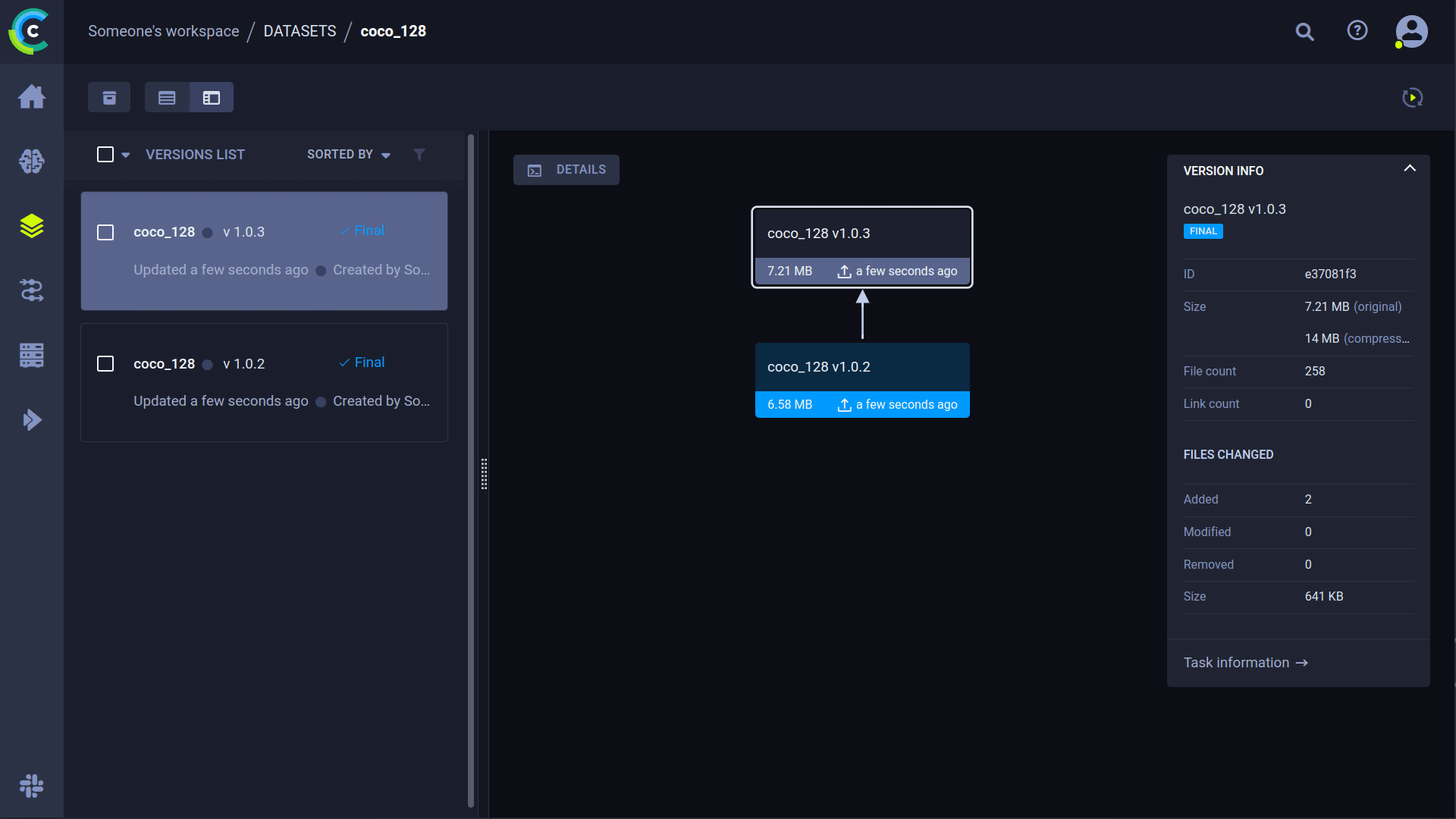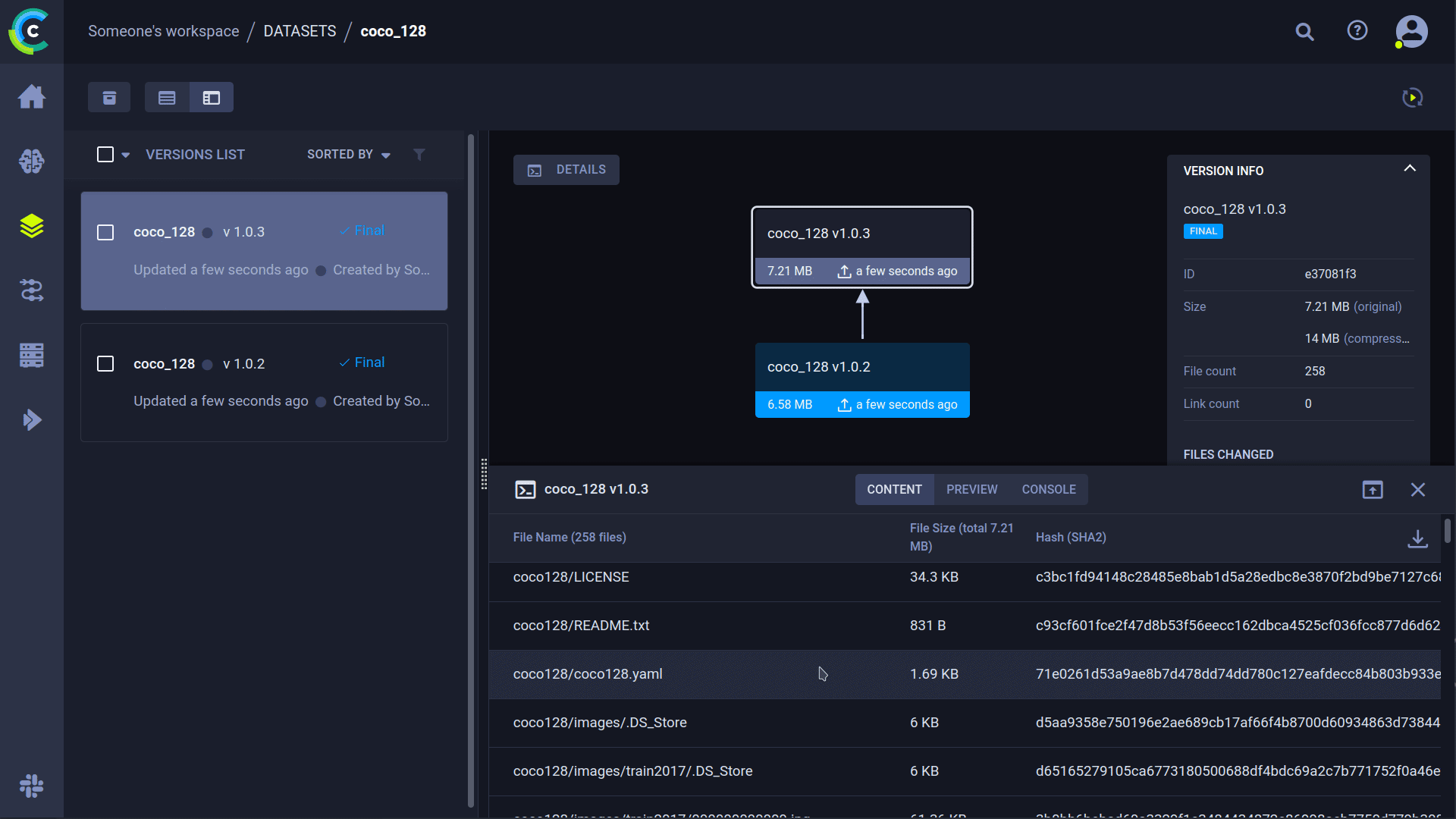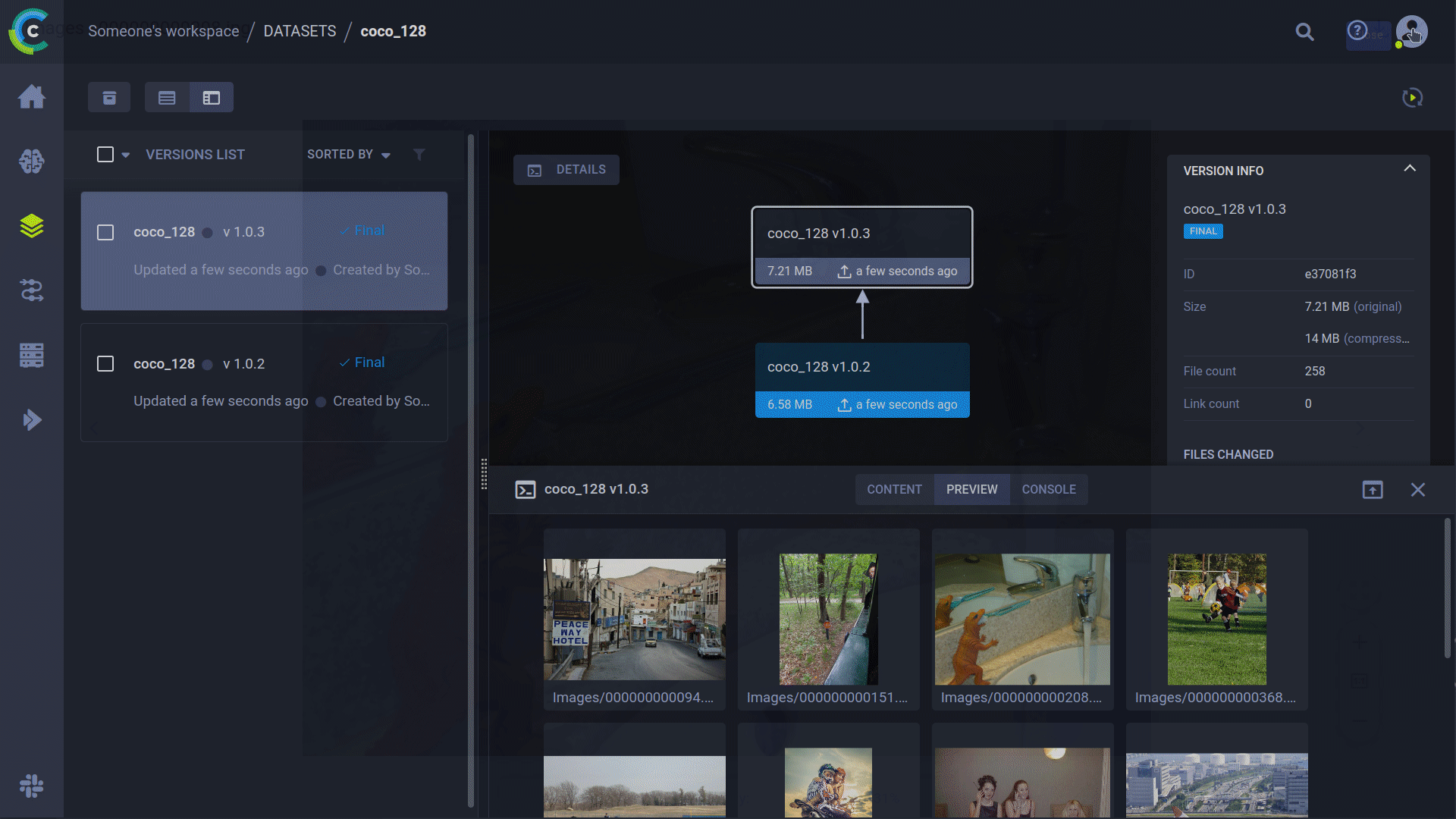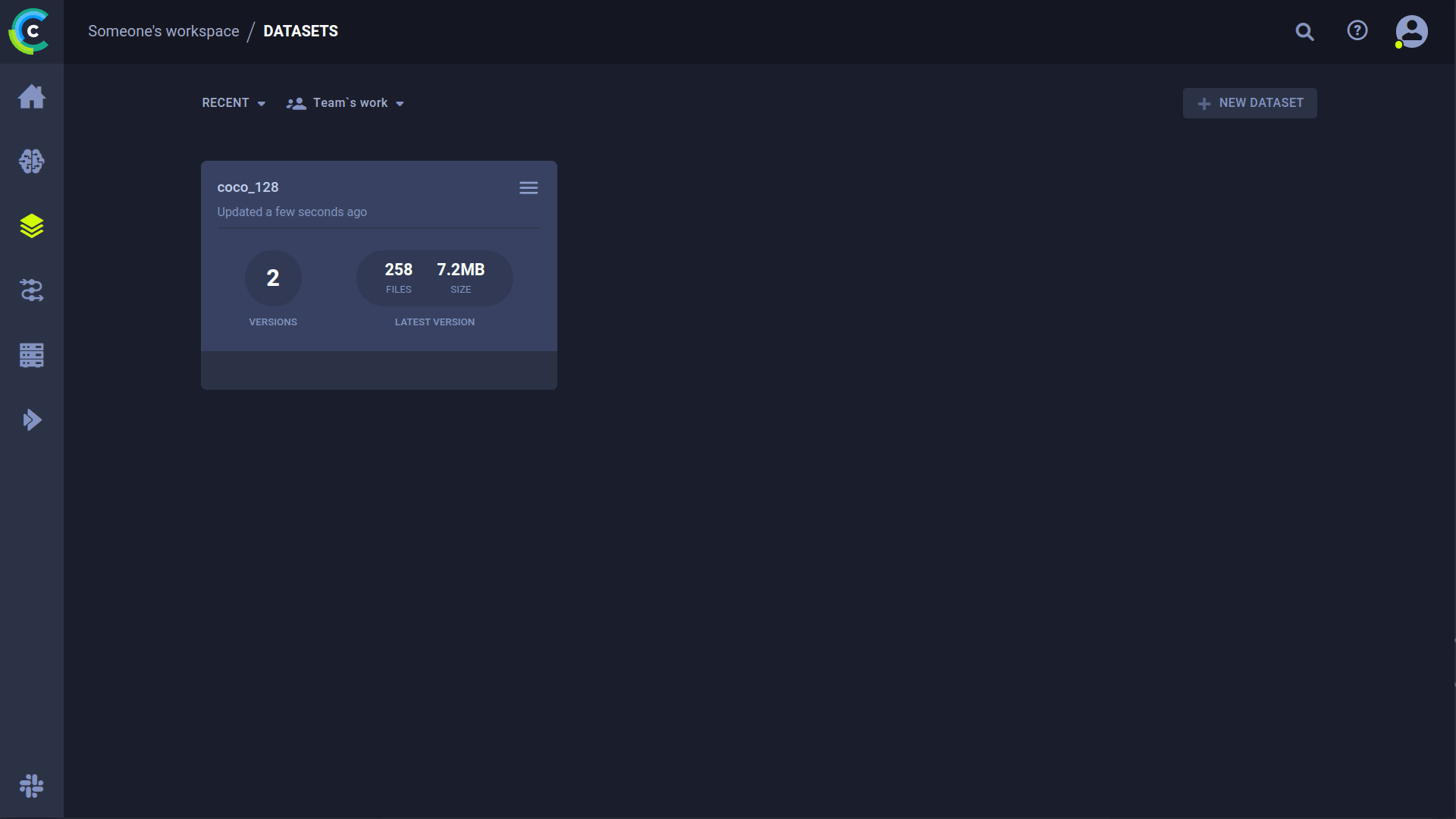
🔗 Dataset Version Management
Versioning your datasets separately from code is crucial for reproducibility and collaboration. ClearML's Data Versioning Tool helps manage this process. YOLOv5 supports using ClearML dataset version IDs, automatically downloading the data if needed. The dataset ID used is saved as a task parameter, ensuring you always know which data version was used for each experiment.
Prepare Your Dataset
YOLOv5 uses YAML files to define dataset configurations. By default, datasets are expected in the ../datasets directory relative to the repository root. For example, the COCO128 dataset structure looks like this:
../
├── yolov5/ # Your YOLOv5 repository clone
└── datasets/
└── coco128/
├── images/
├── labels/
├── LICENSE
└── README.txt
Ensure your custom dataset follows a similar structure.
Next, ⚠️copy the corresponding dataset .yaml file into the root of your dataset folder⚠️. This file contains essential information (path, train, test, val, nc, names) that ClearML needs.
../
└── datasets/
└── coco128/
├── images/
├── labels/
├── coco128.yaml # <---- Place the YAML file here!
├── LICENSE
└── README.txt
Upload Your Dataset
Navigate to your dataset's root directory in the terminal and use the clearml-data CLI tool to upload it:
cd ../datasets/coco128
clearml-data sync --project YOLOv5_Datasets --name coco128 --folder .
Alternatively, you can use the following commands:
# Create a new dataset entry in ClearML
clearml-data create --project YOLOv5_Datasets --name coco128
# Add the dataset files (use '.' for the current directory)
clearml-data add --files .
# Finalize and upload the dataset version
clearml-data close
Tip: Use --parent <parent_dataset_id> with clearml-data create to link versions and avoid re-uploading unchanged files.
Run Training Using a ClearML Dataset
Once your dataset is versioned in ClearML, you can easily use it for training by providing the dataset ID via the --data argument with the clearml:// prefix:
# Replace YOUR_DATASET_ID with the actual ID from ClearML
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data clearml://YOUR_DATASET_ID --weights yolov5s.pt --cache
👀 Hyperparameter Optimization
With experiments and data versioned, you can leverage ClearML for Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO). Since ClearML captures all necessary information (code, packages, environment), experiments are fully reproducible. ClearML's HPO tools clone an existing experiment, modify its hyperparameters, and automatically rerun it.
To run HPO locally, use the provided script utils/loggers/clearml/hpo.py. You'll need the ID of a previously run training task (the "template task") to clone. Update the script with this ID and run it.
# Install Optuna for advanced optimization strategies (optional)
# pip install optuna
# Run the HPO script
python utils/loggers/clearml/hpo.py
The script uses Optuna by default if installed; otherwise, it falls back to RandomSearch. You can modify task.execute_locally() to task.execute() in the script to enqueue the HPO tasks for a remote ClearML agent.
🤯 Remote Execution (Advanced)
ClearML Agent allows you to execute experiments on remote machines (e.g., powerful on-site servers, cloud GPUs like AWS, GCP, or Azure). The agent listens to task queues, reproduces the experiment environment, runs the task, and reports results back to the ClearML server.
Learn more about ClearML Agent:
Turn any machine into a ClearML agent by running:
# Replace QUEUES_TO_LISTEN_TO with the name(s) of your queue(s)
clearml-agent daemon --queue QUEUES_TO_LISTEN_TO [--docker] # Use --docker to run in a Docker container
Cloning, Editing, and Enqueuing Tasks
You can manage remote execution directly from the ClearML web UI:
- Clone: Right-click an existing experiment to clone it.
- Edit: Modify hyperparameters or other settings as needed in the cloned task.
- Enqueue: Right-click the modified task and select "Enqueue" to assign it to a specific queue for an agent to pick up.
Executing a Task Remotely via Code
Alternatively, you can modify your training script to automatically enqueue tasks for remote execution. Add task.execute_remotely() after the ClearML logger is initialized in train.py:
# Inside train.py, after logger initialization...
if RANK in {-1, 0}:
# Initialize loggers
loggers = Loggers(save_dir, weights, opt, hyp, LOGGER)
# Check if ClearML logger is active and enqueue the task
if loggers.clearml:
# Specify the queue name for the remote agent
loggers.clearml.task.execute_remotely(queue_name="my_remote_queue") # <------ ADD THIS LINE
# data_dict might be populated by ClearML if using a ClearML dataset
data_dict = loggers.clearml.data_dict
Running the script with this modification will package the code and its environment and send it to the specified queue, rather than executing locally.
Autoscaling Workers
ClearML also provides Autoscalers that automatically manage cloud resources (AWS, GCP, Azure). They spin up new virtual machines and configure them as ClearML agents when tasks appear in a queue, then shut them down when the queue is empty, optimizing cost.
Watch the Autoscalers getting started video:
🤝 Contributing
Contributions to enhance the ClearML integration are welcome! Please see the Ultralytics Contributing Guide for more information on how to get involved.